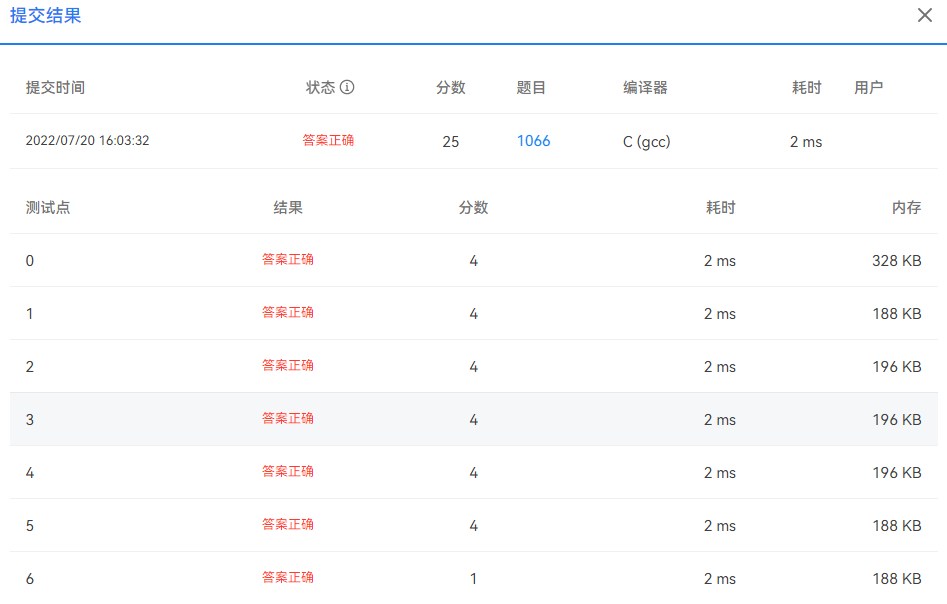
Root of AVL Tree 2013年浙江大学计算机学院免试研究生上机考试真题,是关于AVL树的基本训练。
原题链接:PTA | 程序设计类实验辅助教学平台
题目描述
AVL 树是一种自平衡的二叉搜索树。 在 AVL 树中,任何节点的两个子树的高度最多相差 1; 如果它们的差异超过 1,则会进行重新平衡以恢复此属性。 图 1-4 说明了轮换规则。
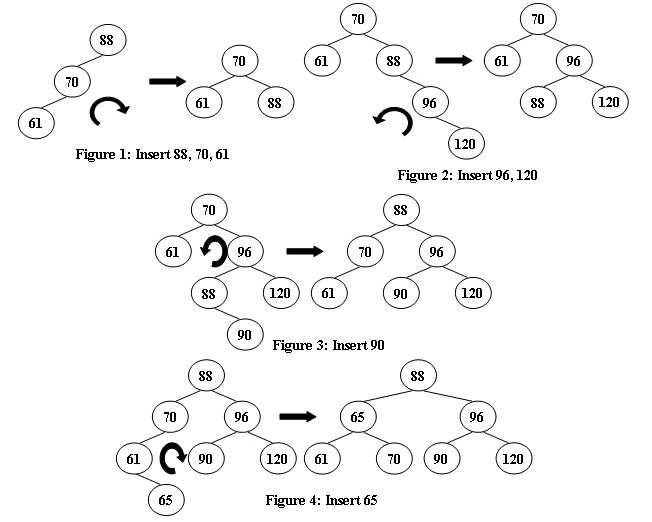
现在给定一个插入序列,求 AVL 树的根。
输入格式
每个输入文件包含一个测试用例。 对于每种情况,第一行包含一个正整数 N (≤20),它是要插入的树的总数。 然后在下一行给出 N 个不同的整数值。 一行中的所有数字都用空格分隔。
输出格式
对于每个测试用例,在一行中打印生成的 AVL 树的根。
示例输入 1
5
88 70 61 96 120示例输出 1
70
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复: 14788939 查看本文章
示例输入 2
7
88 70 61 96 120 90 65示例输出 2
88
题目分析
浙大讲解视频:数据结构_浙江大学_中国大学MOOC(慕课)
代码
参考浙大MOOC讲解视频,补充课程提供的不完整代码,使用C语言实现,通过平台测试。
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct AVLNode* AVLTree;
struct AVLNode
{
int Data;
AVLTree Left, Right;
int Height;
};
int GetHeight(AVLTree T);
AVLTree Insert(AVLTree T, int X);
AVLTree SingleLeftRotation(AVLTree A); // LL
AVLTree DoubleLeftRightRotation(AVLTree A); // LR
AVLTree SingleRightRotation(AVLTree A); // RR
AVLTree DoubleRightLeftRotation(AVLTree A); // RL
int Max(int a, int b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
int main() {
int N;
scanf("%d", &N);
AVLTree root = NULL;
int X;
while (N--) {
scanf("%d", &X);
root = Insert(root, X);
}
printf("%d", root->Data);
return 0;
}
int GetHeight(AVLTree T) {
int h = 0;
if (T) {
h = Max(GetHeight(T->Left), GetHeight(T->Right)) + 1;
T->Height = h;
}
return h;
}
// 将X插入AVL树,并返回调整后的AVL树
AVLTree Insert(AVLTree T, int X) {
if (!T) { // 若插入的树为空树,则新建包含一个结点的树
T = (AVLTree)malloc(sizeof(struct AVLNode));
T->Data = X;
T->Height = 0;
T->Left = T->Right = NULL;
}
else if (X < T->Data) { // 插入到T的左子树
T->Left = Insert(T->Left, X);
// 如果需要左旋
if (GetHeight(T->Left) - GetHeight(T->Right) == 2)
if (X < T->Left->Data)
T = SingleLeftRotation(T); // 需要LL
else
T = DoubleLeftRightRotation(T); // 需要LR
}
else if (X > T->Data) {
T->Right = Insert(T->Right, X);
// 如果需要右旋
if (GetHeight(T->Left) - GetHeight(T->Right) == -2)
if (X > T->Right->Data)
T = SingleRightRotation(T); // 需要RR
else
T = DoubleRightLeftRotation(T); // 需要RL
}
T->Height = Max(GetHeight(T->Left), GetHeight(T->Right)) + 1;
return T;
}
// LL: A必须有一个左子节点B
// 将A与B做左单旋,更新A与B的高度,返回新的根节点B
AVLTree SingleLeftRotation(AVLTree A) {
AVLTree B = A->Left;
A->Left = B->Right;
B->Right = A;
A->Height = Max(GetHeight(A->Left), GetHeight(A->Right)) + 1;
B->Height = Max(GetHeight(B->Left), A->Height) + 1;
return B;
}
// LR: A必须有一个左子节点B,且B必须有一个右子节点C
// 将A、B与C做两次单旋,返回新的根节点C
AVLTree DoubleLeftRightRotation(AVLTree A) {
A->Left = SingleRightRotation(A->Left); // B与C做右单旋,C被返回
return SingleLeftRotation(A); // A与C做左单旋,C被返回
}
// RR——与LL对称
AVLTree SingleRightRotation(AVLTree A) {
AVLTree B = A->Right;
A->Right = B->Left;
B->Left = A;
A->Height = Max(GetHeight(A->Left), GetHeight(A->Right)) + 1;
B->Height = Max(A->Height, GetHeight(B->Right)) + 1;
return B;
}
// RL——与LR对称
AVLTree DoubleRightLeftRotation(AVLTree A) {
A->Right = SingleLeftRotation(A->Right);
return SingleRightRotation(A);
}测试结果