众所周知 HashMap 是一个无序的 Map,因为每次根据 key 的 hashcode映射到Entry数组上,所以遍历出来的顺序并不是写入的顺序。
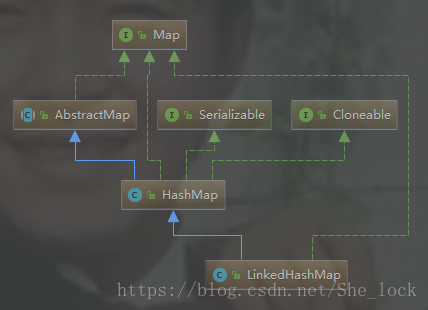
因此 JDK 推出一个基于 HashMap 但具有顺序的 LinkedHashMap 来解决有排序需求的场景。
它的底层是继承于 HashMap实现的,由一个双向链表所构成。
类图
源码
数据结构
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
{
//继承了HashMap 的静态内部类HashMap.Node
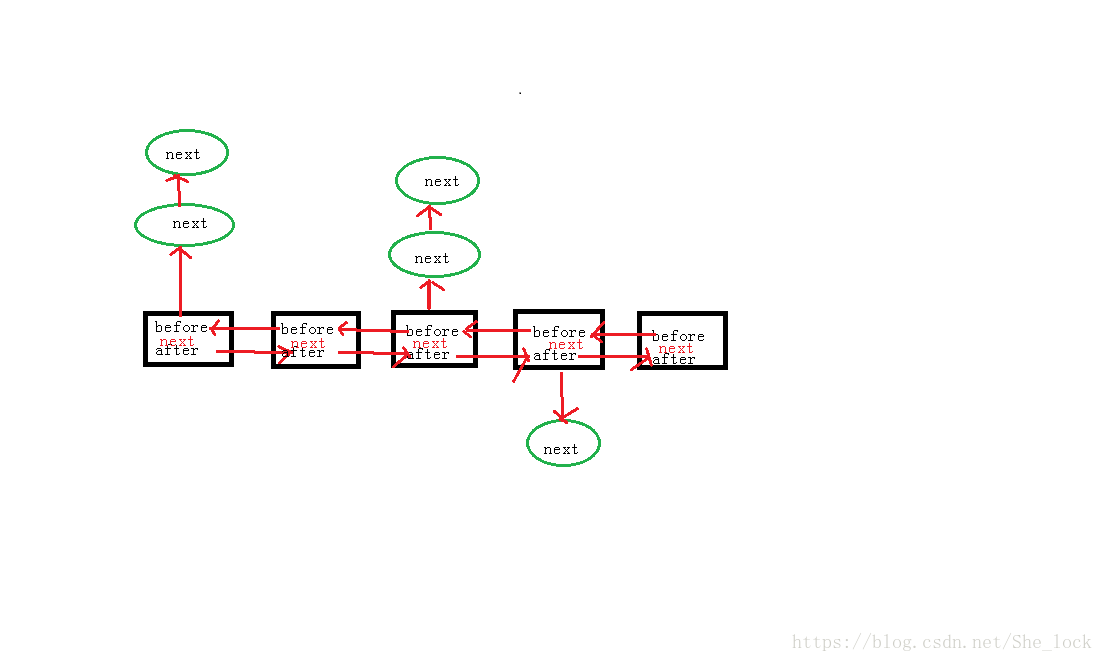
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {//双向链表
Entry<K,V> before, after; //父节点和子节点
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
//头结点
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
//尾节点
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
//排序, 默认是 false,默认按照插入顺序排序,为 true 时按照访问顺序排序
final boolean accessOrder;
}其中HashMap.Node源码如下:
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { //单向链表
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next; //下一个节点
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
//...
}由源码可知,LinkedHashMap原本是一个双向链表,但是,由于链表中装有单向链表的节点HashMap.Node,所以就变成了双向链中存放着单向链。
由此可得如下数据模型:
构造方法
public LinkedHashMap() {
super(); //这里的super实际上就是HashMap的构造方法
accessOrder = false; //排序字段默认为false
}
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
}
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
}
put方法
put方法依然继承至HashMap。
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e); //排序,这个由子类实现
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}子类LinkedHashMap重写afterNodeAccess方法,从而实现了排序功能:
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}总的来说 LinkedHashMap 其实就是对 HashMap 进行了拓展,使用了双向链表来保证了顺序性。
因为是继承与 HashMap 的,所以一些 HashMap 存在的问题 LinkedHashMap 也会存在,比如不支持并发等。
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
2834171 查看本文章