1018 Public Bike Management(30 分)
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists from all over the world. One may rent a bike at any station and return it to any other stations in the city.
The Public Bike Management Center (PBMC) keeps monitoring the real-time capacity of all the stations. A station is said to be in perfect condition if it is exactly half-full. If a station is full or empty, PBMC will collect or send bikes to adjust the condition of that station to perfect. And more, all the stations on the way will be adjusted as well.
When a problem station is reported, PBMC will always choose the shortest path to reach that station. If there are more than one shortest path, the one that requires the least number of bikes sent from PBMC will be chosen.
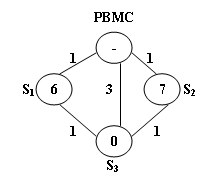
The above figure illustrates an example. The stations are represented by vertices and the roads correspond to the edges. The number on an edge is the time taken to reach one end station from another. The number written inside a vertex SSS is the current number of bikes stored at SSS. Given that the maximum capacity of each station is 10. To solve the problem at S3S_3S3, we have 2 different shortest paths:
-
PBMC -> S1S_1S1 -> S3S_3S3. In this case, 4 bikes must be sent from PBMC, because we can collect 1 bike from S1S_1S1 and then take 5 bikes to S3S_3S3, so that both stations will be in perfect conditions.
-
PBMC -> S2S_2S2 -> S3S_3S3. This path requires the same time as path 1, but only 3 bikes sent from PBMC and hence is the one that will be chosen.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 4 numbers: CmaxC_{max}Cmax (≤100\le 100≤100), always an even number, is the maximum capacity of each station; NNN (≤500\le 500≤500), the total number of stations; SpS_pSp, the index of the problem station (the stations are numbered from 1 to NNN, and PBMC is represented by the vertex 0); and MMM, the number of roads. The second line contains NNN non-negative numbers CiC_iCi (i=1,⋯,Ni=1,\cdots ,Ni=1,⋯,N) where each CiC_iCi is the current number of bikes at SiS_iSi respectively. Then MMM lines follow, each contains 3 numbers: SiS_iSi, SjS_jSj, and TijT_{ij}Tij which describe the time TijT_{ij}Tij taken to move betwen stations SiS_iSi and SjS_jSj. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print your results in one line. First output the number of bikes that PBMC must send. Then after one space, output the path in the format: 0−>S1−>⋯−>Sp0->S_1->\cdots ->S_p0−>S1−>⋯−>Sp. Finally after another space, output the number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC after the condition of SpS_pSp is adjusted to perfect.
Note that if such a path is not unique, output the one that requires minimum number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC. The judge's data guarantee that such a path is unique.
Sample Input:
10 3 3 5
6 7 0
0 1 1
0 2 1
0 3 3
1 3 1
2 3 1
Sample Output:
3 0->2->3 0Analysis:
a trap is that it's easy to mistake this problem for greedy algorithm, the number of bike sent from and to PMBC doesn't satisfy locally optimal solution,hence can't be treated as array dis[].
the best algorithm is dijkstra +dfs.
c++:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<math.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int dis[501],vertex[501],edge[501][501],vis[501];
int cmax,n,p,m,mincarry=1e9,minsurplus=1e9;
vector<int>pre[501];
vector<int>path; //temporary variable
vector<int>re;
void dijkstra()//a shorter dijkstra
{
dis[0]=0;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
int mint=1e9,v=-1;
for(int j=0;j<=n;j++){//find the shortest
if(vis[j]!=1&&dis[j]<mint){
mint=dis[j];
v=j;
}
}
if(v==-1)break;//not find
vis[v]=1;//avoid repeating
for(int j=0;j<=n;j++){
if(vis[j]!=1){
if(dis[j]>dis[v]+edge[v][j]){
dis[j]=dis[v]+edge[v][j];
pre[j].clear();//clear all the other path
pre[j].push_back(v);
}
else if(dis[j]==dis[v]+edge[v][j]){
pre[j].push_back(v);
}
}
}
}
}
void dfs(int v)
{
path.push_back(v);
if(v==0){
int carry=0,surplus=0;
for(int i=path.size()-2;i>=0;i--){
int num=vertex[path[i]];
surplus+=num-cmax/2;
if(surplus<0){
carry-=surplus;
surplus=0;
}
}
if(carry<mincarry){
mincarry=carry;
minsurplus=surplus;
re.assign(path.begin(),path.end());//copy
}
else if(carry==mincarry&&surplus<minsurplus){
minsurplus=surplus;
re.assign(path.begin(),path.end());
}
return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<pre[v].size();i++){
dfs(pre[v][i]);
path.pop_back();//backtracking
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>cmax>>n>>p>>m;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
dis[i]=1e9;
for(int j=0;j<=n;j++)
edge[i][j]=edge[i][j]=1e9;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>vertex[i];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int a,b,t;
cin>>a>>b>>t;
edge[a][b]=edge[b][a]=t;
}
dijkstra();
dfs(p);
cout<<mincarry<<" 0";
for(int i=re.size()-2;i>=0;i--)
cout<<"->"<<re[i];
cout<<" "<<minsurplus;
return 0;
}