版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/Phone_1070333541/article/details/78976204
最近想写一个斗地主的游戏,就在创作的途中遇到了一个界面上的小问题,怎么让纸牌重叠起来,于是就研究了一下绝对定位和相对定位。
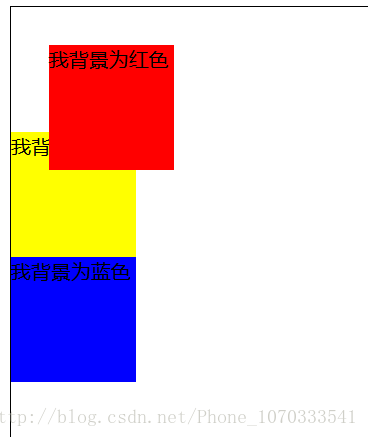
首先,这是 没有加定位 时的代码及效果:
<style>
.div-relative {
color: #000;
border: 1px solid #000;
width: 500px;
height: 400px
}
/* css注释说明: 背景为红色 */
.div-a {
/*position: relative;*/
/*left: 30px;*/
/*top: 30px;*/
background: #F00;
width: 100px;
height: 100px
}
/* 背景为黄色 */
.div-b {
background: #FF0;
width: 100px;
height: 100px
}
/* DIV背景颜色为蓝色 */
.div-c {
background: #00F;
width: 100px;
height: 100px
}
</style>
<div class="div-relative">
<div class="div-a"></div>
<div class="div-b"></div>
<div class="div-c"></div>
</div>效果图如下:
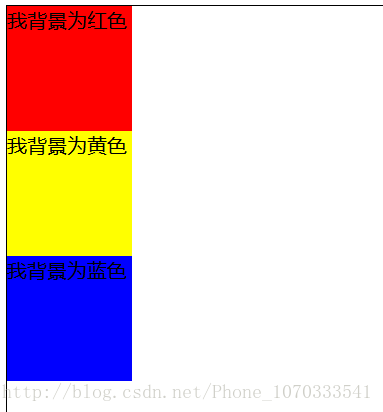
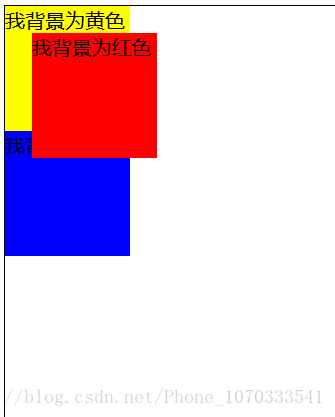
当我把注释放开也就是相对定位时,效果如下:
也就是说在我设置相对定位时,元素的位置是 相对于它自己本来的位置 来进行移动,移动的大小是通过 top:30px ; left:30px ;来设置。
而当我设置红色背景是绝对定位时,代码如下:
/* css注释说明: 背景为红色 */
.div-a {
position: absolute;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
background: #F00;
width: 100px;
height: 100px
}效果如下:
也就是说我在设置了绝对定位后,这个元素就会脱离这个页面变得独立,其他的元素就会认为它不存在,所以其他没有设置元素就顶替了它原来的位置。它相对偏移的元素是它的最近的已经定位的容器,如果没有就会相对与它的父容器,它还有一个好处就是可以指定谁在上谁在下通过 z-index 属性指定一个值,浏览器就通过这个值的大小来确定谁来遮盖谁,(大值的在上面)
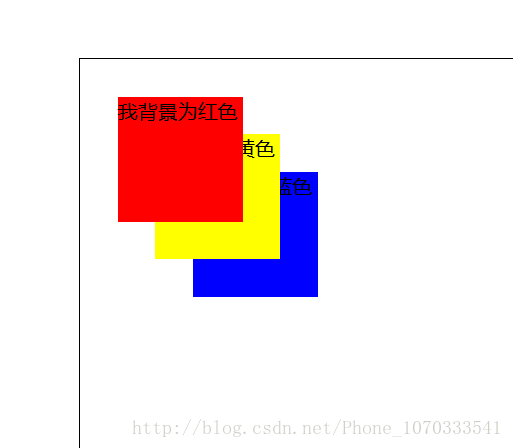
这个时候来个demo测试:
<style>
.div-relative {
position: relative;
left: 300px;
top:100px;
color: #000;
border: 1px solid #000;
width: 500px;
height: 400px
}
/* css注释说明: 背景为红色 */
.div-a {
position: absolute;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
z-index: 90;
background: #F00;
width: 100px;
height: 100px
}
/* 背景为黄色 */
.div-b {
position: absolute;
left: 60px;
top: 60px;
z-index: 80;
background: #FF0;
width: 100px;
height: 100px
}
/* DIV背景颜色为蓝色 */
.div-c {
position: absolute;
left: 90px;
top: 90px;
z-index: 70;
background: #00F;
width: 100px;
height: 100px
}
</style>效果如下:
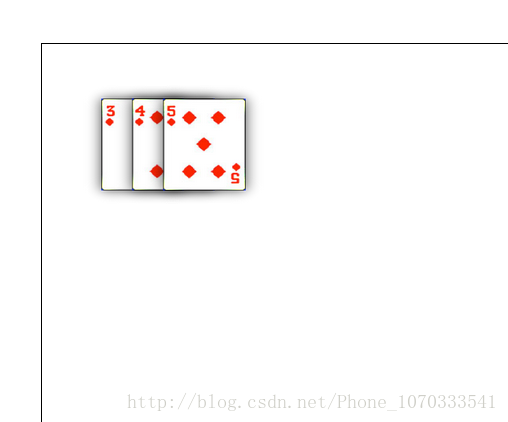
哇塞,很酷炫对不对,肯定用它来设置我的纸牌啦,emmmm:
<style>
.div-relative {
position: relative;
left: 300px;
top:100px;
color: #000;
border: 1px solid #000;
width: 500px;
height: 400px;
}
.div-a {
position: absolute;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
z-index: 1;
background-image: url(img/1.png);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-repeat: round;
}
.div-b {
position: absolute;
left: 55px;
top: 30px;
z-index: 2;
background-image: url(img/2.png);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-repeat: round;
}
.div-c {
position: absolute;
left: 80px;
top: 30px;
z-index: 3;
background-image: url(img/3.png);
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-repeat: round;
}
</style>