55. Jump Game
Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Determine if you are able to reach the last index.
Simplest O(N) solution with constant space
Idea is to work backwards from the last index. Keep track of the smallest index that can “jump” to the last index. Check whether the current index can jump to this smallest index.
class Solution {
public bool canJump(int A[], int n) {
int last=n-1,i,j;
for(i=n-2;i>=0;i--){
if(i+A[i]>=last)last=i;
}
return last<=0;
}
}
406. Queue Reconstruction by Height
Suppose you have a random list of people standing in a queue. Each person is described by a pair of integers (h, k), where h is the height of the person and k is the number of people in front of this person who have a height greater than or equal to h. Write an algorithm to reconstruct the queue.
Note:
The number of people is less than 1,100.
https://leetcode.com/problems/queue-reconstruction-by-height/discuss/89345/Easy-concept-with-PythonC%2B%2BJava-Solution
621. Task Scheduler
Given a char array representing tasks CPU need to do. It contains capital letters A to Z where different letters represent different tasks. Tasks could be done without original order. Each task could be done in one interval. For each interval, CPU could finish one task or just be idle.
However, there is a non-negative cooling interval n that means between two same tasks, there must be at least n intervals that CPU are doing different tasks or just be idle.
You need to return the least number of intervals the CPU will take to finish all the given tasks.
Note:
- The number of tasks is in the range [1, 10000].
- The integer n is in the range [0, 100].
concise Java Solution O(N) time O(26) space:
// (c[25] - 1) * (n + 1) + 25 - i is frame size
// when inserting chars, the frame might be "burst", then tasks.length takes precedence
// when 25 - i > n, the frame is already full at construction, the following is still valid.
public class Solution {
public int leastInterval(char[] tasks, int n) {
int[] c = new int[26];
for(char t : tasks){
c[t - 'A']++;
}
Arrays.sort(c);
int i = 25;
while(i >= 0 && c[i] == c[25]) i--;
return Math.max(tasks.length, (c[25] - 1) * (n + 1) + 25 - i);
}
}
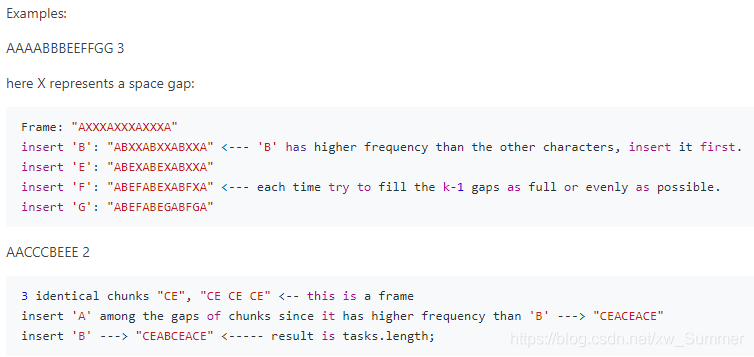
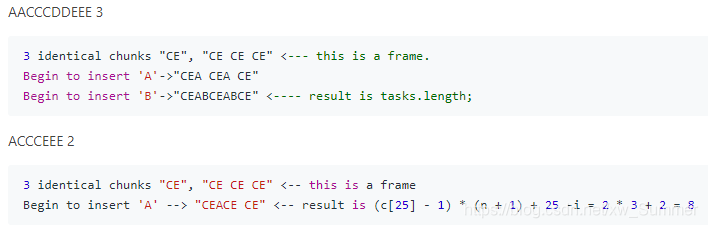
First consider the most frequent characters, we can determine their relative positions first and use them as a frame to insert the remaining less frequent characters. Here is a proof by construction:
Let F be the set of most frequent chars with frequency k.
We can create k chunks, each chunk is identical and is a string consists of chars in F in a specific fixed order.
Let the heads of these chunks to be H_i; then H_2 should be at least n chars away from H_1, and so on so forth; then we insert the less frequent chars into the gaps between these chunks sequentially one by one ordered by frequency in a decreasing order and try to fill the k-1 gaps as full or evenly as possible each time you insert a character.
In summary, append the less frequent characters to the end of each chunk of the first k-1 chunks sequentially and round and round, then join the chunks and keep their heads’ relative distance from each other to be at least n.