文件加载
path = r'./data/ren_pd.csv'
df_pifu = pd.read_csv(path,low_memory=False,dtype={'MBR_NO':np.str})
一些参数的解释
官网:
http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/
索引的那些坑
# pandas groupby 之后都需要进行索引的重新设置
df_pifu["CNT"] = df_pifu["CODE_DESC"].apply(lambda x : 1)
df_pifu_疾病 = df_pifu.groupby(["CODE_DESC"])["CNT"].count().reset_index()
df_pifu_疾病 = df_pifu_疾病.sort_values(by=['CNT'],ascending = False).head(10)
杂项
jupyter notebook 显示所有行和列
pd.set_option('max_columns',1000)
pd.set_option('max_row',300)
pd.set_option('display.float_format', lambda x: '%.5f' % x)
数据清洗
在下面的代码片段中,数据清洗代码被封装在了一些函数中,代码的目的十分直观。你可以直接使用这些代码,无需将它们嵌入到需要进行少量参数修改的函数中。
- 删除多列数据
def drop_multiple_col(col_names_list, df):
'''
AIM -> Drop multiple columns based on their column names
INPUT -> List of column names, df
OUTPUT -> updated df with dropped columns
------
'''
df.drop(col_names_list, axis=1, inplace=True)
return df
有时,并不是所有列的数据都对我们的数据分析工作有用。因此,「df.drop」可以方便地删掉你选定的列。
- 转换 Dtypes
def change_dtypes(col_int, col_float, df):
'''
AIM -> Changing dtypes to save memory
INPUT -> List of column names (int, float), df
OUTPUT -> updated df with smaller memory
------
'''
df[col_int] = df[col_int].astype('int32')
df[col_float] = df[col_float].astype('float32')
当我们面对更大的数据集时,我们需要对「dtypes」进行转换,从而节省内存。如果你有兴趣学习如何使用「Pandas」来处理大数据,我强烈推荐你阅读「Why and How to Use Pandas with Large Data」这篇文章(https://towardsdatascience.com/why-and-how-to-use-pandas-with-large-data-9594dda2ea4c)。
- 将分类变量转换为数值变量
def convert_cat2num(df):
# Convert categorical variable to numerical variable
num_encode = {'col_1' : {'YES':1, 'NO':0},
'col_2' : {'WON':1, 'LOSE':0, 'DRAW':0}}
df.replace(num_encode, inplace=True)
有一些机器学习模型要求变量是以数值形式存在的。这时,我们就需要将分类变量转换成数值变量然后再将它们作为模型的输入。对于数据可视化任务来说,我建议大家保留分类变量,从而让可视化结果有更明确的解释,便于理解。
- 检查缺失的数据
def check_missing_data(df):
# check for any missing data in the df (display in descending order)
return df.isnull().sum().sort_values(ascending=False)
如果你想要检查每一列中有多少缺失的数据,这可能是最快的方法。这种方法可以让你更清楚地知道哪些列有更多的缺失数据,帮助你决定接下来在数据清洗和数据分析工作中应该采取怎样的行动。
- 删除列中的字符串
def remove_col_str(df):
# remove a portion of string in a dataframe column - col_1
df['col_1'].replace('\n', '', regex=True, inplace=True)
# remove all the characters after &# (including &#) for column - col_1
df['col_1'].replace(' &#.*', '', regex=True, inplace=True)
有时你可能会看到一行新的字符,或在字符串列中看到一些奇怪的符号。你可以很容易地使用 df[‘col_1’].replace 来处理该问题,其中「col_1」是数据帧 df 中的一列。
- 删除列中的空格
def remove_col_white_space(df):
# remove white space at the beginning of string
df[col] = df[col].str.lstrip()
当数据十分混乱时,很多意想不到的情况都会发生。在字符串的开头有一些空格是很常见的。因此,当你想要删除列中字符串开头的空格时,这种方法很实用。
- 将两列字符串数据(在一定条件下)拼接起来
def concat_col_str_condition(df):
# concat 2 columns with strings if the last 3 letters of the first column are 'pil'
mask = df['col_1'].str.endswith('pil', na=False)
col_new = df[mask]['col_1'] + df[mask]['col_2']
col_new.replace('pil', ' ', regex=True, inplace=True) # replace the 'pil' with emtpy space
当你希望在一定条件下将两列字符串数据组合在一起时,这种方法很有用。例如,你希望当第一列以某些特定的字母结尾时,将第一列和第二列数据拼接在一起。根据你的需要,还可以在拼接工作完成后将结尾的字母删除掉。
- 转换时间戳(从字符串类型转换为日期「DateTime」格式)
def convert_str_datetime(df):
'''
AIM -> Convert datetime(String) to datetime(format we want)
INPUT -> df
OUTPUT -> updated df with new datetime format
------
'''
df.insert(loc=2, column='timestamp', value=pd.to_datetime(df.transdate, format='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f'))
在处理时间序列数据时,你可能会遇到字符串格式的时间戳列。这意味着我们可能不得不将字符串格式的数据转换为根据我们的需求指定的日期「datetime」格式,以便使用这些数据进行有意义的分析和展示
最近看到的python 杰出的自学资料这个项目里面的例子基本都是开源领域的大咖写的,让你用不到500行的Python代码实现一个非常牛逼实用的功能。
比如说做一个Python解释器,在比如说做一个光学文字识别系统。听起来就非常高大上。然后500行以内就能搞定,但是这个项目肯定需要大家有了一定水平之后才能去研究了。
链接:
http://aosabook.org/en/index.html
探索性数据分析
https://www.jianshu.com/p/8982ad63eb85
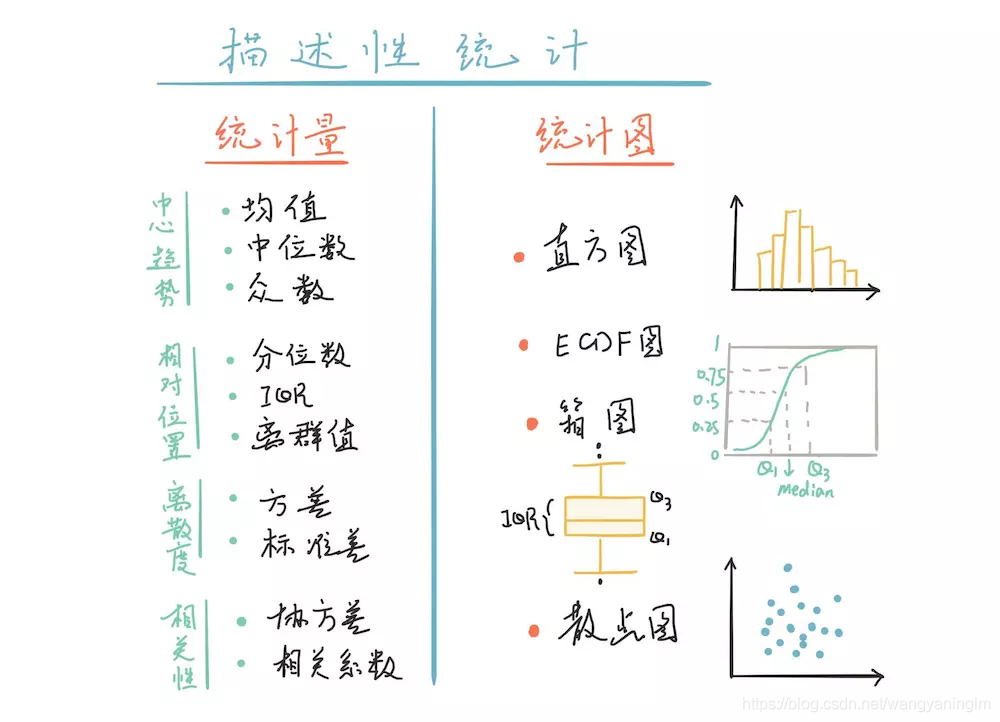
数据可视化
中文显示
pandas 处理完成数据后,大家经常使用的可视化库有matplotlib ,seaborn,pyecharts 等
前两个中文字体显示成问题,最后一个因为是国产库中文支持比较好但是在jupyter notebook中生成的结果是网页,图片不知道怎么显示出来。 以下参考链接为 我博客另一个系列中针对matplotlib ,seaborn中文显示问题的探讨
https://blog.csdn.net/wangyaninglm/article/details/84901376#matplotlib_seaborn__221
参考教程
https://tianchi.aliyun.com/course/courseDetail?courseId=261