题目简介
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
- push(x) – 元素 x 入栈
- pop() – 移除栈顶元素
- top() – 获取栈顶元素
- empty() – 返回栈是否为空
注意:
- 你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是 push to back, peek/pop from front, size, 和 is empty 这些操作是合法的。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
- 你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。
LeetCode
C语言实现
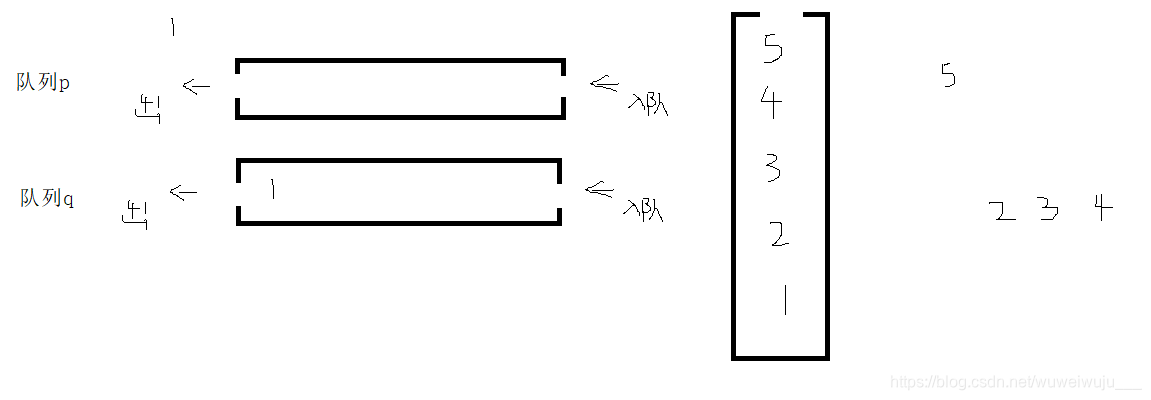
做这道题一定要清楚知道栈和队列的性质和定义,在知道这个的前提下,我们就可以完美的解决这个问题了。
在这里我是用两个队列实现出栈的性质的。具体实现可看代码。
typedef int QUDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QUDataType _data;
struct QueueNode* _next;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode* _front;//队头
QueueNode* _rear;//队尾
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
q->_front = q->_rear = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->_front;
while (cur)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->_next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->_front = pq->_rear = NULL;
}
QueueNode* BuyQueueNode(QUDataType x)
{
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc error");
exit(0);
}
newnode->_data = x;
newnode->_next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
/*void QueuePush(Queue* q, QUDataType x)
{
assert(q);
if (q->_front == NULL)
{
q->_front = q->_rear = BuyQueueNode(x);
}
else
{
q->_rear->_next = BuyQueueNode(x);
q->_rear = q->_rear->_next;
}
}*/
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QUDataType x)
{
assert(q);
if (q->_front == NULL)
{
q->_front = q->_rear = BuyQueueNode(x);
}
else
{
q->_rear->_next = BuyQueueNode(x);
q->_rear = q->_rear->_next;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{
if (q->_front)
{
QueueNode* next = q->_front->_next;
free(q->_front);
q->_front = next;
if (q->_front == NULL)
{
q->_rear = NULL;
}
}
}
int QueueSize(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
int size = 0;
QueueNode* cur = q->_front;
while (cur)
{
++size;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return size;
}
int QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->_front == NULL ? 0 : 1;
}
QUDataType QueueFront(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
if(q->_front == NULL)
return 0;
return q->_front->_data;
}
QUDataType QueueBack(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
if(q->_rear == NULL)
return 0;
return q->_rear->_data;
}
typedef struct {
Queue _p;
Queue _q
} MyStack;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* newstack = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&newstack->_p);
QueueInit(&newstack->_q);
return newstack;
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->_p) != 0)
{
QueuePush(&obj->_p, x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->_q, x);
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->_p) != 0)
{
while(QueueSize(&obj->_p)>1)
{
QueuePush(&obj->_q, QueueFront(&obj->_p));
QueuePop(&obj->_p);
}
int _obj = QueueFront(&obj->_p);
QueuePop(&obj->_p);
return _obj;
}
else
{
while(QueueSize(&obj->_q)>1)
{
QueuePush(&obj->_p, QueueFront(&obj->_q));
QueuePop(&obj->_q);
}
int _obj = QueueFront(&obj->_q);
QueuePop(&obj->_q);
return _obj;
}
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->_p) + QueueEmpty(&obj->_q) == 0 ? true : false;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->_p) != 0)
{
return QueueBack(&obj->_p);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->_q);
}
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestory(&obj->_p);
QueueDestory(&obj->_q);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyStack struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = myStackCreate();
* myStackPush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myStackPop(obj);
* int param_3 = myStackTop(obj);
* bool param_4 = myStackEmpty(obj);
* myStackFree(obj);
*/
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack* myStackCreate( ) {
MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&pst->q1);
QueueInit(&pst->q2);
return pst;
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) != 0)
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1, x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2, x);
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* pEmpty = &obj->q1, *pNonEmpty = &obj->q2;
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) != 0)
{
pEmpty = &obj->q2;
pNonEmpty = &obj->q1;
}
while(QueueSize(pNonEmpty) > 1)
{
QueuePush(pEmpty, QueueFront(pNonEmpty));
QueuePop(pNonEmpty);
}
int top = QueueFront(pNonEmpty);
QueuePop(pNonEmpty);
return top;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* pEmpty = &obj->q1, *pNonEmpty = &obj->q2;
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) != 0)
{
pEmpty = &obj->q2;
pNonEmpty = &obj->q1;
}
return QueueBack(pNonEmpty);
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) + QueueEmpty(&obj->q2) == 0 ? true:false ;
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestory(&obj->q1);
QueueDestory(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
