前面讲解了 Flutter 的几个基础组件,这节课将讲解跟布局相关的 Widget。
每个平台的应用都有其自己的布局方式,例如 Android 有线性布局、相对布局、绝对布局、帧布局、表格布局等等,HTML 前端也有自己的布局方式。Flutter 当然也不例外。那么这节课就带领大家对 Flutter 的基础布局 Widget 中的几个典型的布局Widget进行详细分析,并结合案例进行详细的用法讲解。
1.基本布局
1.1 Scaffold
Flutter 布局系列的 Widget 一般分为两种,一种是只有单个子元素的布局 Widget,也就是SingleChildRenderObjectWidget;另一个种是具有多个子元素的布局 Widget,一般都有 children 参数,继承自MultiChildRenderObjectWidget。非布局系列 Widget 也有无子元素的 Widget,如 Text、Image 组件,这些无子元素的 Widget 属于 LeafRenderObjectWidget。Flutter 中不同的布局 Widget 对子 Widget 的排列渲染方式不同。接下来我们看下其中比较常用的一个布局 Widget——Scaffold。
Scaffold 是一个页面布局脚手架,实现了基本的 Material 布局,继承自 StatefulWidget,是有状态组件。我们知道大部分的应用页面都是含有标题栏,主体内容,底部导航菜单或者侧滑抽屉菜单等等构成,那么每次都重复写这些内容会大大降低开发效率,所以 Flutter 提供了 Material 风格的 Scaffold 页面布局脚手架,可以很快地搭建出这些元素部分:
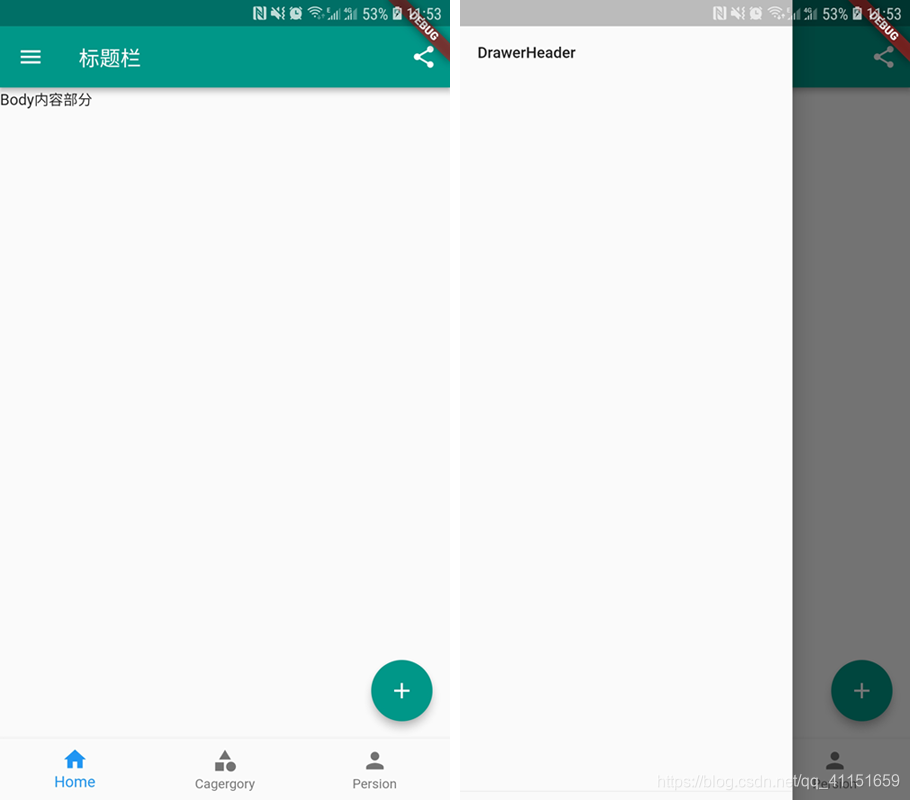
Scaffold 有下面几个主要属性。
- appBar:显示在界面上的一个标题栏 AppBar。
- body: 当前页面的主体内容 Widget。
- floatingActionButton:页面的主要功能按钮,不配置就不会显示。
- persistentFooterButtons:固定显示在下方的按钮,比如对话框下方的确定、取消按钮。
- drawer:侧滑抽屉菜单控件。
- backgroundColor:body 内容的背景颜色。
- bottomNavigationBar:显示在页面底部的导航栏。
- resizeToAvoidBottomPadding:类似于 Android 中的 android:windowSoftInputMode=‘adjustResize’,避免类似弹出键盘这种操作遮挡布局使用的。
- bottomSheet:底部拉出菜单。
具体可配置的属性参数,我们看下看下 Scaffold 构造方法:
const Scaffold({
Key key,
// 标题栏
this.appBar,
// 中间主体内容部分
this.body,
// 悬浮按钮
this.floatingActionButton,
// 悬浮按钮位置
this.floatingActionButtonLocation,
// 悬浮按钮动画
this.floatingActionButtonAnimator,
// 固定在下方显示的按钮
this.persistentFooterButtons,
// 侧滑抽屉菜单
this.drawer,
this.endDrawer,
// 底部菜单
this.bottomNavigationBar,
// 底部拉出菜单
this.bottomSheet,
// 背景色
this.backgroundColor,
this.resizeToAvoidBottomPadding,
// 重新计算body布局空间大小,避免被遮挡
this.resizeToAvoidBottomInset,
// 是否显示到底部,默认为true将显示到顶部状态栏
this.primary = true,
this.drawerDragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.down,
})
如果想显示 Snackbar 或 bottomSheet,可以这样调用:
Scaffold.of(context).showSnackBar(new SnackBar(
content: Text('Hello!'),
));
Scaffold.of(context).showBottomSheet…
接下来看个实例的代码:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/widgets.dart';
class ScaffoldSamples extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() {
return ScaffoldSamplesState();
}
}
class ScaffoldSamplesState extends State<ScaffoldSamples> {
int _selectedIndex = 0;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return scaffoldWidget(context);
}
Widget scaffoldWidget(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("标题栏"),
actions: <Widget>[
//导航栏右侧菜单
IconButton(icon: Icon(Icons.share), onPressed: () {}),
],
),
body: Text("Body内容部分"),
//抽屉
drawer: Drawer(
child: DrawerHeader(
child: Text("DrawerHeader"),
),
),
// 底部导航
bottomNavigationBar: BottomNavigationBar(
items: <BottomNavigationBarItem>[
BottomNavigationBarItem(icon: Icon(Icons.home), title: Text('Home')),
BottomNavigationBarItem(
icon: Icon(Icons.category), title: Text('Cagergory')),
BottomNavigationBarItem(
icon: Icon(Icons.person), title: Text('Persion')),
],
currentIndex: _selectedIndex,
fixedColor: Colors.blue,
onTap: _onItemTap,
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
child: Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed: () {
_onAdd();
},
),
);
}
void _onItemTap(int index) {
setState(() {
_selectedIndex = index;
});
}
void _onAdd() {}
}
这个实例实现效果如前面两张图片所示效果。
1.2 Container
Container 是一个容器类布局 Widget,Container 可以说是多个小组件的一个组合容器,如可以设置 padding、margin、Align、Decoration、Matrix4 等等,可以说用起来很方便,很高效。
我们看下 Container 构造方法相关属性和作用:
Container({
Key key,
// 容器子Widget对齐方式
this.alignment,
// 容器内部padding
this.padding,
// 背景色
Color color,
// 背景装饰
Decoration decoration,
// 前景装饰
this.foregroundDecoration,
// 容器的宽度
double width,
// 容器的高度
double height,
// 容器大小的限制条件
BoxConstraints constraints,
// 容器外部margin
this.margin,
// 变换,如旋转
this.transform,
// 容器内子Widget
this.child,
})
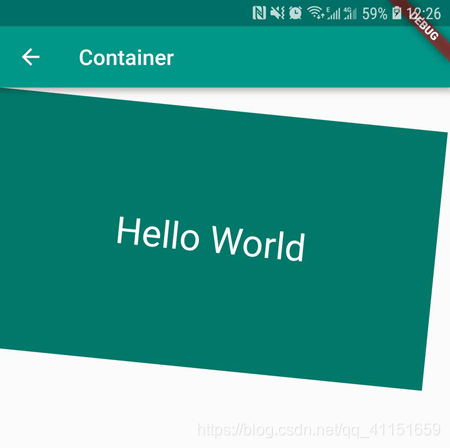
接下来看个实例的代码:
body: Container(
constraints: BoxConstraints.expand(
height: Theme.of(context).textTheme.display1.fontSize * 1.1 + 200.0,
),
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
// 背景色
color: Colors.teal.shade700,
// 子Widget居中
alignment: Alignment.center,
// 子Widget元素
child: Text('Hello World',
style: Theme.of(context)
.textTheme
.display1
.copyWith(color: Colors.white)),
// 前景装饰
foregroundDecoration: BoxDecoration(
image: DecorationImage(
image: NetworkImage('https://www.example.com/images/frame.png'),
centerSlice: Rect.fromLTRB(270.0, 180.0, 1360.0, 730.0),
),
),
// Container旋转
transform: Matrix4.rotationZ(0.1),
),
运行效果如下图所示:
1.3 Center
Center 主要用于对齐,将内部子 Widget 与自身进行居中对齐,并根据子 Widget 的大小自动调整自身大小。
Center Widget 是继承自 Align,Align 继承自 SingleChildRenderObjectWidget,也是单子元素 Widget。
看下 Center 的构造方法:
Center({
Key key,
// 宽度因子
double widthFactor,
// 高度因子
double heightFactor,
// 子元素
Widget child
})
大家可能对这个宽度和高度因子的作用不太明白,其实就是设置 Center 的宽度和高度是子元素宽度和高度的倍数的,widthFactor 和 heightFactor 可以不设置,默认 Center 容器宽度横向充满,高度包裹子元素。如将widthFactor 和 heightFactor 设置为 2.0 的话,则 Center 容器的占用宽度和高度是子元素宽度和高度的 2 倍,但是最大不超过屏幕的宽高。
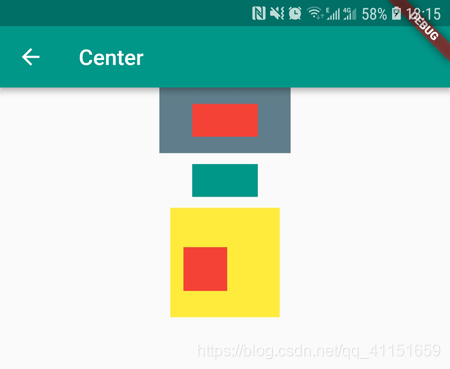
接下来看个实例演示用法:
body: Column(
children: <Widget>[
Container(
color: Colors.blueGrey,
child: Center(
widthFactor: 2,
heightFactor: 2,
child: Container(
width: 60,
height: 30,
color: Colors.red,
),
),
),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
Center(
child: Container(
width: 60,
height: 30,
color: Colors.teal,
),
),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
Center(
child: Container(
height: 100.0,
width: 100.0,
color: Colors.yellow,
child: Align(
// 设置对齐位置约束
alignment: FractionalOffset(0.2, 0.6),
child: Container(
height: 40.0,
width: 40.0,
color: Colors.red,
),
),
),
),
],
),
运行效果如下图所示:
2.线性布局
2.1 Row
Row 布局组件类似于 Android 中的 LinearLayout 线性布局,它用来做水平横向布局使用,里面的 children 子元素按照水平方向进行排列。
Row 的继承关系如下:
Row -> Flex -> MultiChildRenderObjectWidget -> RenderObjectWidget …
可以看出 Row 是 Flex 的拓展子类,也是多子元素的一个组件之一(内部可以包含多个子元素)。
我们看下 Row 布局组件的大致效果图:
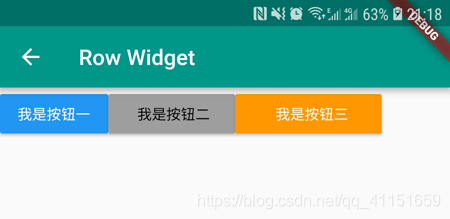
所有元素水平排成一行。
那么接下来我们看下 Row 的构造方法:
Row({
Key key,
// 主轴方向上的对齐方式(Row的主轴是横向轴)
MainAxisAlignment mainAxisAlignment = MainAxisAlignment.start,
// 在主轴方向(Row的主轴是横向轴)占有空间的值,默认是max
MainAxisSize mainAxisSize = MainAxisSize.max,
// 在交叉轴方向(Row是纵向轴)的对齐方式,Row的高度等于子元素中最高的子元素高度
CrossAxisAlignment crossAxisAlignment = CrossAxisAlignment.center,
// 水平方向子元素的排列方向:从左到右排列还是反向
TextDirection textDirection,
// 表示纵轴(垂直)的对齐排列方向,默认是VerticalDirection.down,表示从上到下。这个参数一般用于Column组件里
VerticalDirection verticalDirection = VerticalDirection.down,
// 字符对齐基线方式
TextBaseline textBaseline,
// 子元素集合
List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[],
})
接下来详细看下 Row 的主轴和交叉轴属性。
MainAxisAlignment(主轴属性:主轴方向上的对齐方式,Row 是横向轴为主轴)
enum MainAxisAlignment {
// 按照主轴起点对齐,例如:按照靠近最左侧子元素对齐
start,
// 将子元素放置在主轴的末尾,按照末尾对齐
end,
// 子元素放置在主轴中心对齐
center,
// 将主轴方向上的空白区域均分,使得子元素之间的空白区域相等,首尾子元素都靠近首尾,没有间隙。有点类似于两端对齐
spaceBetween,
// 将主轴方向上的空白区域均分,使得子元素之间的空白区域相等,但是首尾子元素的空白区域为1/2
spaceAround,
// 将主轴方向上的空白区域均分,使得子元素之间的空白区域相等,包括首尾子元素
spaceEvenly,
}
再看下 Row 的交叉属性。
CrossAxisAlignment(交叉属性:在交叉轴方向的对齐方式,Row 是纵向轴。Row 的高度等于子元素中最高的子元素高度)
enum CrossAxisAlignment {
// 子元素在交叉轴上起点处展示
start,
// 子元素在交叉轴上末尾处展示
end,
// 子元素在交叉轴上居中展示
center,
// 让子元素填满交叉轴方向
stretch,
// 在交叉轴方向,使得子元素按照baseline对齐
baseline,
}
再看下 MainAxisSize 属性。
MainAxisSize(在主轴方向子元素占有空间的方式,Row 的主轴是横向轴。默认是 max)
enum MainAxisSize {
// 根据传入的布局约束条件,最大化主轴方向占用可用空间,也就是尽可能充满可用宽度
max,
// 与max相反,是最小化占用主轴方向的可用空间
min,
}
接下来我们通过一个实例来学习下 Row 的布局特点。
Column(
children: <Widget>[
// 默认横向排列元素
Row(
verticalDirection: VerticalDirection.up,
textBaseline: TextBaseline.ideographic,
children: <Widget>[
RaisedButton(
color: Colors.blue,
child: Text(
'我是按钮一\n 按钮',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
onPressed: () {},
),
RaisedButton(
color: Colors.grey,
child: Text(
' 我是按钮二 ',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black),
),
onPressed: () {},
),
RaisedButton(
color: Colors.orange,
child: Text(
' 我是按钮三 ',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
onPressed: () {},
),
],
),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
// 默认横向排列元素
Row(
children: <Widget>[
const FlutterLogo(),
const Expanded(
child: Text(
'Flutter\'s hot reload helps you quickly and easily experiment, build UIs, add features, and fix bug faster. Experience sub-second reload times, without losing state, on emulators, simulators, and hardware for iOS and Android.'),
),
const Icon(Icons.sentiment_very_satisfied),
],
),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
// 居中排列元素
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Text(
" 我们居中显示 |",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.teal),
),
Text(" Flutter的Row布局组件 "),
],
),
],
),
运行效果如下图所示:
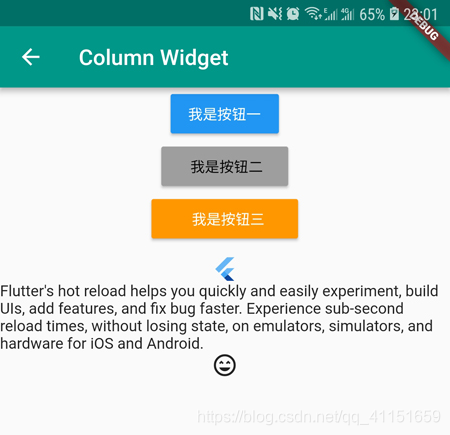
2.2 Column
在学习完了 Row 布局组件后,再学习 Column 很容易,Row 是横向排列元素,Column 是纵向排列子元素,可以对比着学习。
Column 的继承关系如下:
Column -> Flex -> MultiChildRenderObjectWidget -> RenderObjectWidget …
Column 也是 Flex 的拓展子类,也是多子元素的一个组件之一(内部可以包含多个子元素)。
我们看下 Column 布局组件的大致效果图:

所有元素纵向排成一列。
构造方法是一致的,只不过主轴和交叉轴和 Row 是相反的。这里就不再重复讲解了。
接下来看一个实例:
Column(
// 纵向排列子元素
children: <Widget>[
RaisedButton(
color: Colors.blue,
child: Text(
'我是按钮一',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
onPressed: () {},
),
RaisedButton(
color: Colors.grey,
child: Text(
' 我是按钮二 ',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black),
),
onPressed: () {},
),
RaisedButton(
color: Colors.orange,
child: Text(
' 我是按钮三 ',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
onPressed: () {},
),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
const FlutterLogo(),
Text(
'Flutter\'s hot reload helps you quickly and easily experiment, build UIs, add features, and fix bug faster. Experience sub-second reload times, without losing state, on emulators, simulators, and hardware for iOS and Android.'),
const Icon(Icons.sentiment_very_satisfied),
],
),
运行效果如下图所示:
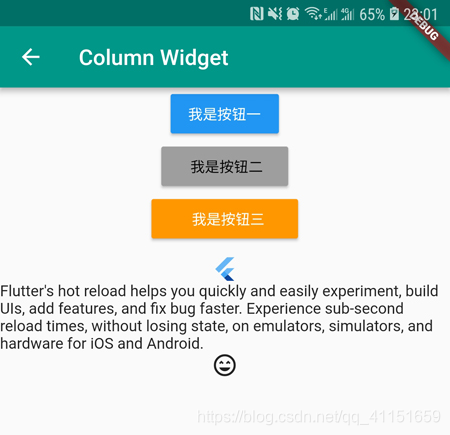
3.弹性布局
Flex 组件是 Row 和 Column 的父类,主要用于弹性布局,类似于HTML 中的 Flex 弹性盒子布局,可以按照一定比例进行分类布局空间。
Flex 继承自 MultiChildRenderObjectWidget,Flex 也是多子元素的一个组件之一(内部可以包含多个子元素)。
Flex 一般和 Expanded 搭配使用,Expanded 组件从名字就可以看出它的特点,就是让子元素扩展占用 Flex 的剩余空间。
我们看下 Flex 布局组件的大致效果图:
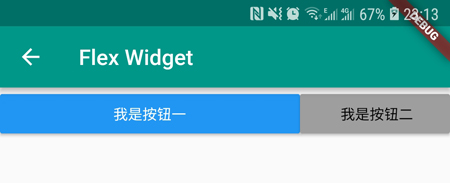
按钮一占用 2/3 的横向空间,按钮二占用剩余 1/3 空间。
我们看下 Flex 构造方法:
Flex({
Key key,
// 子元素排列方向:横向还是纵向
@required this.direction,
this.mainAxisAlignment = MainAxisAlignment.start,
this.mainAxisSize = MainAxisSize.max,
this.crossAxisAlignment = CrossAxisAlignment.center,
this.textDirection,
this.verticalDirection = VerticalDirection.down,
this.textBaseline,
List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[],
})
单独看 Flex 组件没有意义,因为一般直接用它的子类 Row 和 Column 来使用。而 Flex 主要是和 Expanded 搭配使用。我们再看下 Expanded 组件构造方法:
const Expanded({
Key key,
// 占用空间比重、权重
int flex = 1,
// 子元素
@required Widget child,
})
我们通过一个实例看下 Flex 和 Expanded 搭配用法:
body: Row(
children: <Widget>[
Expanded(
// flex设置权重,这里是占2/5空间
flex: 2,
child: RaisedButton(
color: Colors.blue,
child: Text(
'我是按钮一',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
onPressed: () {},
),
),
// flex设置权重,这里是占1/5空间
Expanded(
flex: 1,
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
Expanded(
flex: 2,
child: RaisedButton(
color: Colors.grey,
child: Text(
' 我是按钮一 ',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black),
),
onPressed: () {},
),
),
Expanded(
flex: 1,
child: RaisedButton(
color: Colors.teal,
child: Text(
' 我是按钮二 ',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
onPressed: () {},
),
)
],
),
),
// flex设置权重,这里是占2/5空间
Expanded(
flex: 2,
child: RaisedButton(
color: Colors.grey,
child: Text(
' 我是按钮二 ',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black),
),
onPressed: () {},
),
)
],
)
运行效果图如下:
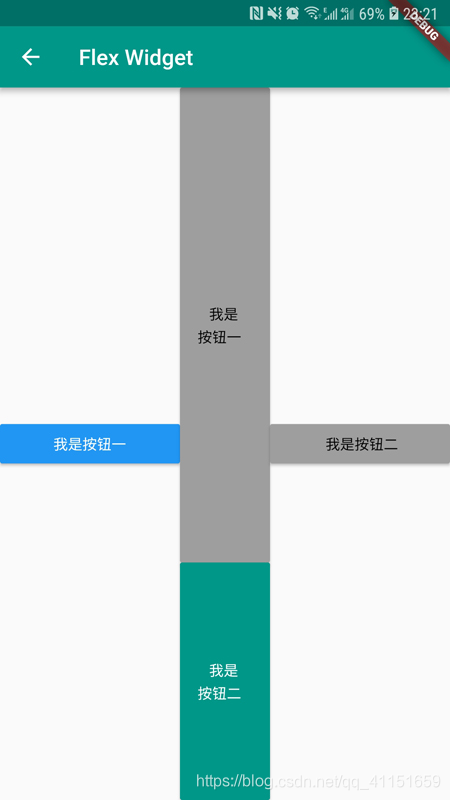
4.层叠布局
Stack 和 IndexStack 都是层叠布局方式,类似于 Android 里的 FrameLayout 帧布局,内部子元素是有层级堆起来的。
Stack 继承自 MultiChildRenderObjectWidget,Stack 也是多子元素的一个组件之一(内部可以包含多个子元素)。
而 IndexedStack 继承自 Stack,扩展了 Stack的一些特性。它的作用是显示第 index 个子元素,其他子元素都是不可见的。所以 IndexedStack 的尺寸永远是跟最大的子元素尺寸一致。
Stack 的布局行为,是根据子元素是 positioned 还是 non-positioned 来区分的:
- 对于 positioned 的子元素,它们的位置会根据所设置的 top、bottom、right 或 left 属性来确定,这几个值都是相对于 Stack 的左上角;
- 对于 non-positioned 的子元素,它们会根据 Stack 的 aligment 来设置位置。
Stack 布局的子元素层级堆叠顺序:最先布局绘制的子元素在最底层,越后绘制的越在顶层。类似于 Web 中的 z-index。
看下 Stack 布局组件的效果图:
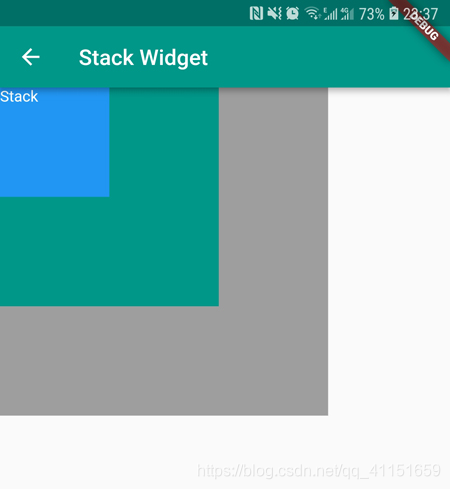
默认按照左上角,有层级的绘制排列。
看下 Stack 的构造方法:
Stack({
Key key,
// 对齐方式,默认是左上角(topStart)
this.alignment = AlignmentDirectional.topStart,
// 对齐方向
this.textDirection,
// 定义如何设置无定位子元素尺寸,默认为loose
this.fit = StackFit.loose,
// 超过的部分子元素处理方式
this.overflow = Overflow.clip,
// 子元素
List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[],
})
我们看下 alignment:
// 左上角
static const Alignment topLeft = Alignment(-1.0, -1.0);
// 主轴顶部对齐,交叉轴居中
static const Alignment topCenter = Alignment(0.0, -1.0);
// 主轴顶部对齐,交叉轴偏右
static const Alignment topRight = Alignment(1.0, -1.0);
// 主轴居中,交叉轴偏左
static const Alignment centerLeft = Alignment(-1.0, 0.0);
// 居中
static const Alignment center = Alignment(0.0, 0.0);
// 主轴居中,交叉轴偏右
static const Alignment centerRight = Alignment(1.0, 0.0);
// 主轴底部对齐,交叉轴偏左
static const Alignment bottomLeft = Alignment(-1.0, 1.0);
// 主轴底部对齐,交叉轴居中
static const Alignment bottomCenter = Alignment(0.0, 1.0);
// 主轴底部对齐,交叉轴偏右
static const Alignment bottomRight = Alignment(1.0, 1.0);
看下 fit 属性:
enum StackFit {
// 子元素宽松的取值,可以从min到max的尺寸
loose,
// 子元素尽可能的占用剩余空间,取max尺寸
expand,
// 不改变子元素的约束条件
passthrough,
}
最后看下 overflow 属性:
enum Overflow {
// 超出部分不会被裁剪,正常显示
visible,
// 超出部分会被裁剪
clip,
}
我们看下 IndexedStack 构造方法:
IndexedStack({
Key key,
AlignmentGeometry alignment = AlignmentDirectional.topStart,
TextDirection textDirection,
StackFit sizing = StackFit.loose,
// 多了一个索引,索引的这个元素显示,其他元素隐藏
this.index = 0,
// 子元素
List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[],
})
接下来通过一个实例来演示下 Stack 和 IndexedStack 的用法:
body: Column(
children: <Widget>[
// Stack层叠布局
Stack(
children: <Widget>[
Container(
width: 300,
height: 300,
color: Colors.grey,
),
Container(
width: 200,
height: 200,
color: Colors.teal,
),
Container(
width: 100,
height: 100,
color: Colors.blue,
),
Text(
"Stack",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
],
),
SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
// IndexedStack层叠布局
IndexedStack(
// 指定显示的子元素序号,其余子元素隐藏
index: 2,
children: <Widget>[
Container(
width: 300,
height: 300,
color: Colors.grey,
),
Container(
width: 200,
height: 200,
color: Colors.teal,
),
Container(
width: 100,
height: 100,
color: Colors.blue,
),
Text(
"Stack",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
],
)
],
)
运行效果图如下:

