文章目录
前言
需要开通vip的题目暂时跳过
笔记导航
点击链接可跳转到所有刷题笔记的导航链接
641. 设计循环双端队列
设计实现双端队列。
你的实现需要支持以下操作:
- MyCircularDeque(k):构造函数,双端队列的大小为k。
- insertFront():将一个元素添加到双端队列头部。 如果操作成功返回 true。
- insertLast():将一个元素添加到双端队列尾部。如果操作成功返回 true。
- deleteFront():从双端队列头部删除一个元素。 如果操作成功返回 true。
- deleteLast():从双端队列尾部删除一个元素。如果操作成功返回 true。
- getFront():从双端队列头部获得一个元素。如果双端队列为空,返回 -1。
- getRear():获得双端队列的最后一个元素。 如果双端队列为空,返回 -1。
- isEmpty():检查双端队列是否为空。
- isFull():检查双端队列是否满了。

-
解答
class MyCircularDeque { Node head; Node tail; int capacity; int size; /** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the deque to be k. */ public MyCircularDeque(int k) { this.capacity = k; } /** Adds an item at the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */ public boolean insertFront(int value) { if(size == capacity)return false; Node node = new Node(value); if(head == null){ head = node; tail = node; size = 1; }else{ head.pre = node; node.next = head; head = node; size++; } return true; } /** Adds an item at the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */ public boolean insertLast(int value) { if(size == capacity)return false; Node node = new Node(value); if(tail == null){ tail = node; head = node; size = 1; }else{ tail.next = node; node.pre = tail; tail = node; size++; } return true; } /** Deletes an item from the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */ public boolean deleteFront() { if(size == 0)return false; if(size == 1){ head = null; tail = null; size = 0; }else{ Node p = head.next; head.next = null; head = p; head.pre = null; size--; } return true; } /** Deletes an item from the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */ public boolean deleteLast() { if(size == 0)return false; if(size == 1){ head = null; tail = null; size = 0; }else{ Node p = tail.pre; tail.pre = null; tail = p; tail.next = null; size--; } return true; } /** Get the front item from the deque. */ public int getFront() { if(size == 0)return -1; return head.val; } /** Get the last item from the deque. */ public int getRear() { if(size == 0)return -1; return tail.val; } /** Checks whether the circular deque is empty or not. */ public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } /** Checks whether the circular deque is full or not. */ public boolean isFull() { return size == capacity; } class Node{ int val; Node pre; Node next; public Node(int val){ this.val = val; } } } -
分析
- 模仿LinkedList 实现的双端队列,队中的结点定义为Node
- Node结点属性包括 前驱 后继,本身的值。
- 容量k 赋值给capacity 标记双端队列的最大值。
- size为双端队列的实际容量。
-
提交结果

643. 子数组最大平均数 I
给定 n 个整数,找出平均数最大且长度为 k 的连续子数组,并输出该最大平均数。

-
解答
public double findMaxAverage(int[] nums, int k) { double res = -(30000 * 10000 + 1); double sum = 0; for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++){ if(i < k){ sum += nums[i]; continue; } res = Math.max(res,sum); sum -= nums[i-k]; sum += nums[i]; } res = Math.max(res,sum); return res/k; } -
分析
- 滑动窗口
- 求窗口内的最大值平均值
-
提交结果

645. 错误的集合
集合 S 包含从1到 n 的整数。不幸的是,因为数据错误,导致集合里面某一个元素复制了成了集合里面的另外一个元素的值,导致集合丢失了一个整数并且有一个元素重复。
给定一个数组 nums 代表了集合 S 发生错误后的结果。你的任务是首先寻找到重复出现的整数,再找到丢失的整数,将它们以数组的形式返回。

-
解答
public int[] findErrorNums(int[] nums) { Arrays.sort(nums); int[] res = new int[2]; int last = nums[0]; for(int i = 1;i < nums.length;i++){ if(nums[i] == last){ res[0] = nums[i]; break; } last = nums[i]; } int r = 0; for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++){ r ^= i+1; if(nums[i] == res[0])continue; r ^= nums[i]; } r ^= res[0]; res[1] = r; return res; } -
分析
- 数组排序,相同的数字必定出现在相邻的位置。第一个for找到重复的数字
- 第二个for循环 利用异或 来找到只出现一次的数字 也就是丢失的那个数字
-
提交结果

646. 最长数对链
给出 n 个数对。 在每一个数对中,第一个数字总是比第二个数字小。
现在,我们定义一种跟随关系,当且仅当 b < c 时,数对(c, d) 才可以跟在 (a, b) 后面。我们用这种形式来构造一个数对链。
给定一个数对集合,找出能够形成的最长数对链的长度。你不需要用到所有的数对,你可以以任何顺序选择其中的一些数对来构造。

-
解答
public int findLongestChain(int[][] pairs) { Arrays.sort(pairs,new Comparator<int[]>(){ public int compare(int[] o1,int[] o2){ return o1[0] - o2[0]; } }); int res = 1,lastEnd = pairs[0][1]; for(int i = 1; i < pairs.length;i++){ int[] cur = pairs[i]; if(cur[1] < lastEnd){ lastEnd = cur[1]; }else if(cur[0] > lastEnd){ res++; lastEnd = cur[1]; } } return res; } -
分析
- 这是一道最长上升子序列的问题
- 数组按照第一位升序排序
- 寻找第二位能组成的最长上升子序列。
- 一次遍历,结合贪心的思想,每次结尾的数字尽可能的小,这样才有可能构成最长的上升子序列。
-
提交结果

647. 回文子串
给定一个字符串,你的任务是计算这个字符串中有多少个回文子串。
具有不同开始位置或结束位置的子串,即使是由相同的字符组成,也会被视作不同的子串。

-
解答
//方法1 public int countSubstrings(String s) { int len = s.length(); int[][] nums = new int[len][len]; int res = len; for(int i = 0;i < len-1;i++){ nums[i][i] = 1; if(s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(i+1)){ nums[i][i+1] = 1; res++; } } for(int l = 3;l <= len;l++){ for(int start = 0;start < len - l + 1;start++){ int end = start + l - 1; if(s.charAt(start) == s.charAt(end) && nums[start+1][start+1] == 1 && nums[start + 1][end - 1]== 1){ nums[start][end] = 1; res++; } } } return res; } //方法2 -
分析
-
方法1
-
滑动窗口+记忆集,记录所有的回文子串。
-
方法2
-
Manacher 算法
-
在所有的相邻字符中间插入 #,比如 abaa 会被处理成 #a#b#a#a#,这样可以保证所有找到的回文串都是奇数长度的,以任意一个字符为回文中心,既可以包含原来的奇数长度的情况,也可以包含原来偶数长度的情况。假设原字符串为 S,经过这个处理之后的字符串为 s。
我们用 f(i) 来表示以 s 的第 i 位为回文中心,可以拓展出的最大回文半径,那么 f(i) - 1 就是以 i 为中心的最大回文串长度
-
rMax用来记录当前遍历到的回文中心的最右侧的最大值,iMax是对应的回文中心
-
开始遍历新的字符串
-
初始化f[i],若i<rMax
-
那么f[i]就取 rMax - i + 1和 f[2 * iMax - i]中的较小者。f[2 * iMax - i]是i关于iMax对称的点。
-
若i >= rMax
-
那么初始化为1,然后进行中心拓展,寻找该中心可构成的最长回文字符串。
-
之后再是更新最右侧值和回文中心
-
结果是f[i]的一半的累加,因为这个半径内 有一半是”#“
-
-
提交结果
方法1

方法2

648. 单词替换
在英语中,我们有一个叫做 词根(root)的概念,它可以跟着其他一些词组成另一个较长的单词——我们称这个词为 继承词(successor)。例如,词根an,跟随着单词 other(其他),可以形成新的单词 another(另一个)。
现在,给定一个由许多词根组成的词典和一个句子。你需要将句子中的所有继承词用词根替换掉。如果继承词有许多可以形成它的词根,则用最短的词根替换它。
你需要输出替换之后的句子。

-
解答
//方法1 暴力 public String replaceWords(List<String> dictionary, String sentence) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); Collections.sort(dictionary, Comparator.comparingInt(String::length)); String[] words = sentence.split(" "); for (String word : words) { if(sb.length() > 0)sb.append(" "); boolean flag = false; for (String s : dictionary) { if(word.startsWith(s)){ sb.append(s); flag = true; break; } } if(!flag){ sb.append(word); } } return sb.toString(); } //方法2 前缀树 class Solution { public String replaceWords(List<String> roots, String sentence) { TrieNode trie = new TrieNode(); for (String root: roots) { TrieNode cur = trie; for (char letter: root.toCharArray()) { if (cur.children[letter - 'a'] == null) cur.children[letter - 'a'] = new TrieNode(); cur = cur.children[letter - 'a']; } cur.word = root; } StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder(); for (String word: sentence.split("\\s+")) { if (ans.length() > 0) ans.append(" "); TrieNode cur = trie; for (char letter: word.toCharArray()) { if (cur.children[letter - 'a'] == null || cur.word != null) break; cur = cur.children[letter - 'a']; } ans.append(cur.word != null ? cur.word : word); } return ans.toString(); } } class TrieNode { TrieNode[] children; String word; TrieNode() { children = new TrieNode[26]; } } -
分析
- 方法1 暴力
- 先将词根按照长度 从小到大排序。
- 将句子 根据空格拆成一个个word
- 然后遍历word ,从词根词典中寻找可以替换的单词,若找到,则将其替换,若没有则使用原来的
- 方法2 前缀树
- 将词根放入到前缀树当中。
- 将句子拆成一个个单词
- 然后遍历这些单词,在前缀树当中去匹配。
-
提交结果
方法1

方法2

649. Dota2 参议院
Dota2 的世界里有两个阵营:Radiant(天辉)和 Dire(夜魇)
Dota2 参议院由来自两派的参议员组成。现在参议院希望对一个 Dota2 游戏里的改变作出决定。他们以一个基于轮为过程的投票进行。在每一轮中,每一位参议员都可以行使两项权利中的一项:
禁止一名参议员的权利:
参议员可以让另一位参议员在这一轮和随后的几轮中丧失所有的权利。
宣布胜利:
如果参议员发现有权利投票的参议员都是同一个阵营的,他可以宣布胜利并决定在游戏中的有关变化。
给定一个字符串代表每个参议员的阵营。字母 “R” 和 “D” 分别代表了 Radiant(天辉)和 Dire(夜魇)。然后,如果有 n 个参议员,给定字符串的大小将是 n。
以轮为基础的过程从给定顺序的第一个参议员开始到最后一个参议员结束。这一过程将持续到投票结束。所有失去权利的参议员将在过程中被跳过。
假设每一位参议员都足够聪明,会为自己的政党做出最好的策略,你需要预测哪一方最终会宣布胜利并在 Dota2 游戏中决定改变。输出应该是 Radiant 或 Dire。

-
解答
public String predictPartyVictory(String senate) { int Rnumber = 0; int Dnumber = 0; int curBanR = 0;//当前被ban int curBanD = 0;//当前被ban int totalBanR = 0;//被ban总数 int totalBanD = 0;//被ban总数 char[] chars = senate.toCharArray(); boolean flag = true; while(true){ for(int i = 0;i < chars.length;i++){ char cur = chars[i]; if(cur == 'R'){ if(flag) Rnumber++; if(curBanR == 0){ curBanD++; totalBanD++; if(totalBanD == Dnumber && !flag)return "Radiant"; }else{ curBanR--; chars[i] = 'r'; } }else if(cur == 'D'){ if(flag) Dnumber++; if(curBanD == 0){ curBanR++; totalBanR++; if(totalBanR == Rnumber && !flag)return "Dire"; }else{ curBanD--; chars[i] = 'd'; } } } flag = false; if(totalBanD >= Dnumber)return "Radiant"; if(totalBanR >= Rnumber)return "Dire"; } } -
分析
- 6个变量,分别是记录字符串中R出现的总次数,D出现的总次数,当前被ban的R的次数,当前被ban的D的次数,被banR的总次数,被banD的总次数。
- 遍历字符串
- 若当前的字符是R,那么判断当前的curBanR是否等于0.若等于0的话,说明当前R没有被ban,此时可以行使权利banD,使当前被banD的次数+1,被banD的总次数+1
- curBanR不为0,说明当前R被ban了,不能行使权利,则跳过它,那么curBanR减1,并修改字符R为r
- 若当前字符是D,和上面同理。
- 遍历结束后,若满足D被ban的总次数大于D的总数,或者D的总数为0,那么Radiant胜利
- 若满足R被ban的总次数大于R的总数,或者R的总数为0,那么Dire胜利。
- 否则进入下一次的遍历,直到返回结果。
-
提交结果

650. 只有两个键的键盘
最初在一个记事本上只有一个字符 ‘A’。你每次可以对这个记事本进行两种操作:
- Copy All (复制全部) : 你可以复制这个记事本中的所有字符(部分的复制是不允许的)。
- Paste (粘贴) : 你可以粘贴你上一次复制的字符。
给定一个数字 n 。你需要使用最少的操作次数,在记事本中打印出恰好 n 个 ‘A’。输出能够打印出 n 个 ‘A’ 的最少操作次数。

-
解答
//方法1 public int minSteps(int n) { int[] dp = new int[n+1]; Arrays.fill(dp,Integer.MAX_VALUE); if(n == 1)return 0; dp[1] = 0; dp[2] = 2; for(int i = 3;i <=n;i++){ for(int j = i-1;j >0;j--){ int remain = i - j; if(remain % j == 0){ dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i],dp[j] + remain / j + 1); } } } return dp[n]; } //方法2 public int minSteps(int n) { int ans = 0, d = 2; while (n > 1) { while (n % d == 0) { ans += d; n /= d; } d++; } return ans; } -
分析
-
方法1 动态规划实现
-
当前数字i 可以从比他小的数字j 复制得到。若当前数字和比他小的数字的差remain 可以整除比他小的数字,那么就可以通过这个比他小的数字copy得到。
-
copy的次数 就等于remain/j 因为copy算一次操作。所以需要加1
-
所以动态转移方程就有了 得到j数字的次数 + 1次copy All操作 + remain/j 次 Paste操作
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i],dp[j] + remain / j + 1);
-
方法2 素数分解
操作次数等于 构成n的素数之和 例如
14 = 2 * 7 那么结果就是2 + 7
18 = 2 * 3 * 3 结果就是 2 + 3 + 3 = 8
20 = 2 * 2 * 5 结果就是 2 + 2 + 5 = 9
-
-
提交结果
方法1

方法2

652. 寻找重复的子树
给定一棵二叉树,返回所有重复的子树。对于同一类的重复子树,你只需要返回其中任意一棵的根结点即可。
两棵树重复是指它们具有相同的结构以及相同的结点值。

-
解答
public List<TreeNode> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode root) { dfs(root); return res; } Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); List<TreeNode> res = new ArrayList<>(); public String dfs(TreeNode root){ if(root == null)return "#"; String s = root.val + "," + dfs(root.left) + "," + dfs(root.right); map.put(s,map.getOrDefault(s,0) + 1); if(map.get(s) == 2){ res.add(root); } return s; } -
分析
- 递归实现
- map用来记录 子树序列话结果作为key,数量作为value
- 当数量为2的时候,说明出现了重复,添加到res当中。
- 超过2 不再重复添加
-
提交结果

653. 两数之和 IV - 输入 BST
给定一个二叉搜索树和一个目标结果,如果 BST 中存在两个元素且它们的和等于给定的目标结果,则返回 true。
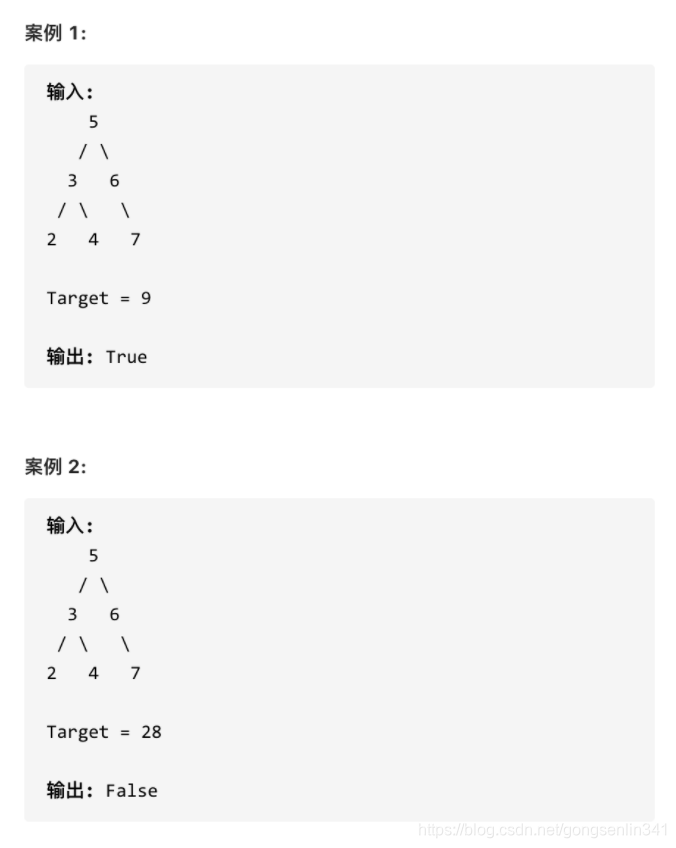
-
解答
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) { if(root == null)return false; if(set.contains(root.val))return true; set.add(k - root.val); boolean left = findTarget(root.left,k); boolean right = findTarget(root.right,k); return left || right; } -
分析
- set保留k-node.val
- 这样在遍历树的过程中,若出现了结点的值和set中的某个值相同,那么就返回true
-
提交结果

654. 最大二叉树
给定一个不含重复元素的整数数组 nums 。一个以此数组直接递归构建的 最大二叉树 定义如下:
- 二叉树的根是数组 nums 中的最大元素。
- 左子树是通过数组中 最大值左边部分 递归构造出的最大二叉树。
- 右子树是通过数组中 最大值右边部分 递归构造出的最大二叉树。
返回有给定数组 nums 构建的 最大二叉树 。
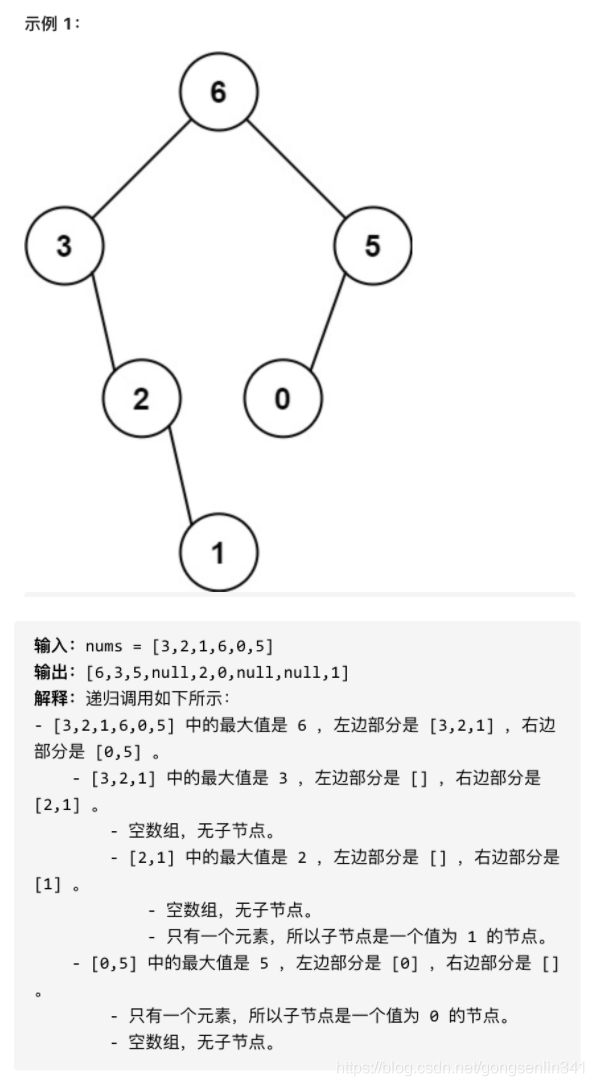
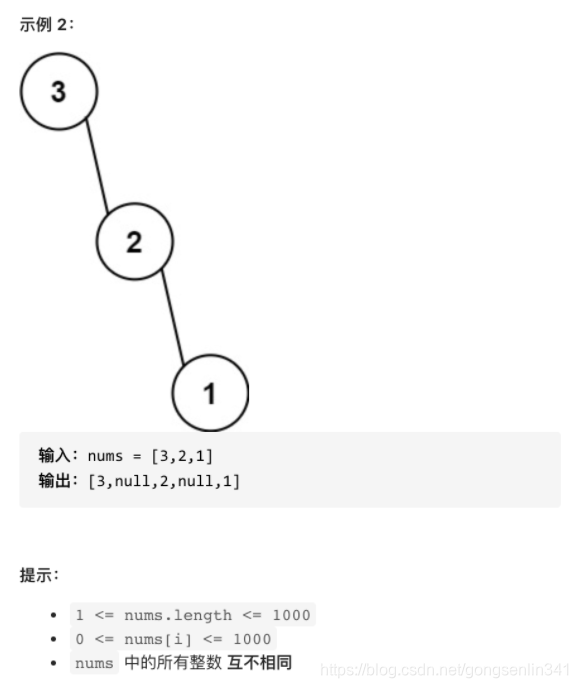
-
解答
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) { return constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums,0,nums.length-1); } public int findMaxIndex(int[] nums,int start,int end){ int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int maxIndex = -1; for(int i = start;i <= end;i++){ if(nums[i] > max){ max = nums[i]; maxIndex = i; } } return maxIndex; } public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums,int start,int end) { if(start > end)return null; int maxIndex = findMaxIndex(nums,start,end); TreeNode node = new TreeNode(nums[maxIndex]); node.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums,start,maxIndex - 1); node.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums,maxIndex + 1,end); return node; } -
分析
- 递归 分而治之
- 找到区间start-end中的最大值对应的索引
- 这个最大值作为当前最大二叉树的根,最大值索引左边的部分,递归的构造左子树,左边的最大二叉树,同理 最大值索引右边的部分,递归的构造右子树
-
提交结果
655. 输出二叉树
在一个 m*n 的二维字符串数组中输出二叉树,并遵守以下规则:
- 行数 m 应当等于给定二叉树的高度。
- 列数 n 应当总是奇数。
- 根节点的值(以字符串格式给出)应当放在可放置的第一行正中间。根节点所在的行与列会将剩余空间划分为两部分(左下部分和右下部分)。你应该将左子树输出在左下部分,右子树输出在右下部分。左下和右下部分应当有相同的大小。即使一个子树为空而另一个非空,你不需要为空的子树输出任何东西,但仍需要为另一个子树留出足够的空间。然而,如果两个子树都为空则不需要为它们留出任何空间。
- 每个未使用的空间应包含一个空的字符串""。
- 使用相同的规则输出子树。

-
解答
int maxHeight = 0; public List<List<String>> printTree(TreeNode root) { calHeight (root,1); List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(root); int curHeight = 1; List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>(); while(!list.isEmpty()){ int blankNumber = (int)Math.pow(2,maxHeight-curHeight) - 1; List<String> r = new ArrayList<>(); List<TreeNode> temp = new ArrayList<>(); boolean flag = false; for(int i = 0;i < list.size();i++){ addBlank(r,blankNumber); TreeNode curNode = list.get(i); if(curNode != null) r.add(""+curNode.val); else r.add(""); if(curNode != null && curNode.left != null){ flag = true; temp.add(curNode.left); }else{ temp.add(null); } if(curNode != null && curNode.right != null){ flag = true; temp.add(curNode.right); }else{ temp.add(null); } addBlank(r,blankNumber); if(i < list.size() - 1) r.add(""); } if(flag){ list = temp; }else{ list = new ArrayList<>(); } curHeight++; res.add(r); } return res; } public void calHeight(TreeNode root,int height){ if (root == null) return 0; return 1 + Math.max(getHeight(root.left), } public void addBlank(List<String> list,int number){ for(int i = 0;i < number;i++){ list.add(""); } } -
分析
- 先计算树高,根据树高 可以计算出矩阵的宽度 ,所以高度和宽度都有了。
- 利用层次遍历,完成输出二叉树
-
提交结果
657. 机器人能否返回原点
在二维平面上,有一个机器人从原点 (0, 0) 开始。给出它的移动顺序,判断这个机器人在完成移动后是否在 (0, 0) 处结束。
移动顺序由字符串表示。字符 move[i] 表示其第 i 次移动。机器人的有效动作有 R(右),L(左),U(上)和 D(下)。如果机器人在完成所有动作后返回原点,则返回 true。否则,返回 false。
注意:机器人“面朝”的方向无关紧要。 “R” 将始终使机器人向右移动一次,“L” 将始终向左移动等。此外,假设每次移动机器人的移动幅度相同。

-
解答
public boolean judgeCircle(String moves) { int len = moves.length(); if(len % 2 != 0)return false; int upDown = 0; int leftRight = 0; for(int i = 0;i < len;i++){ char ch = moves.charAt(i); if(ch == 'U') upDown++; if(ch == 'D') upDown--; if(ch == 'L') leftRight++; if(ch == 'R') leftRight--; } return upDown == 0 && leftRight == 0; } -
分析
- upDown记录上下移动的距离,leftRIght记录左右移动的距离
- 若upDown == 0 并且 leftRight == 0 说明返回原点。
-
提交结果
658. 找到 K 个最接近的元素
给定一个排序好的数组 arr ,两个整数 k 和 x ,从数组中找到最靠近 x(两数之差最小)的 k 个数。返回的结果必须要是按升序排好的。
整数 a 比整数 b 更接近 x 需要满足:
- |a - x| < |b - x| 或者
- |a - x| == |b - x| 且 a < b

-
解答
//方法1 public List<Integer> findClosestElements(int[] arr, int k, int x) { PriorityQueue<A> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<A>(){ public int compare(A a1,A a2){ if(a1.cha != a2.cha) return a1.cha - a2.cha; return a1.number - a2.number; } }); for(int a:arr){ queue.add(new A(a,Math.abs(a-x))); } List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); while(k > 0){ res.add(queue.poll().number); k--; } Collections.sort(res); return res; } class A{ int number; int cha; public A(int number,int cha){ this.number = number; this.cha = cha; } } //方法2 public List<Integer> findClosestElements(int[] arr, int k, int x) { int size = arr.length; int left = 0; int right = size - 1; int removeNums = size - k; while (removeNums > 0) { if (x - arr[left] <= arr[right] - x) { right--; } else { left++; } removeNums--; } List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = left; i < left + k; i++) { res.add(arr[i]); } return res; } -
分析
- 方法1堆实现,前k个的题目都可以用堆来实现
- 根据数值和目标的差排序,若差相同则 小的数字在前面
- 方法2双指针
- 选择k个等于 删除 (数组长度-k) 个
- 双指针 一个数组开头,一个数组的结尾,两个指向的数字和目标值进行比较,删除掉差值大的。也就是移动指针
-
提交结果
方法1

方法2
659. 分割数组为连续子序列
给你一个按升序排序的整数数组 num(可能包含重复数字),请你将它们分割成一个或多个子序列,其中每个子序列都由连续整数组成且长度至少为 3 。
如果可以完成上述分割,则返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。

-
解答
public boolean isPossible(int[] nums) { Map<Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>> map = new HashMap<Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>>(); for (int x : nums) { if (!map.containsKey(x)) { map.put(x, new PriorityQueue<Integer>()); } if (map.containsKey(x - 1)) { int prevLength = map.get(x - 1).poll(); if (map.get(x - 1).isEmpty()) { map.remove(x - 1); } map.get(x).offer(prevLength + 1); } else { map.get(x).offer(1); } } Set<Map.Entry<Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>> entry : entrySet) { PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = entry.getValue(); if (queue.peek() < 3) { return false; } } return true; } -
分析
- hashMap 结合小顶堆
- Map中的key表示以key结尾的连续子序列。
- value表示以key结尾的连续子序列的长度。以小顶堆来存储,这样相同key结尾的时候,取出来的就是最短的子序列。
- 遍历数组
- 若当前map中不存在x结尾的子序列,则将其加入构建新的子序列
- 若当前map中存在x-1结尾的子序列,则取出以x-1结尾的子序列中长度最短的长度。若取出后,x-1结尾的子序列没有了,则从map当中删除。然后将得到的最短长度加1,作为x结尾的子序列的长度,加入到x结尾的子序列长度集合当中。
- 若当前map中不存在x-1结尾的子序列,说明x是序列的头,那么就将长度1 加入到x结尾的子序列集合当中。
-
提交结果
