本文为丹麦奥尔堡大学(作者:Wei,Na)的博士论文,共187页。
为了满足UTRA长期演进(LTE)的峰值数据速率和频谱效率目标,多输入多输出(MIMO)被认为是LTE的关键技术之一。虽然MIMO是一个被广泛研究的课题,但是大多数研究都忽略了MIMO与系统中其它重要增强机制之间的交互作用,包括链路自适应(LA)、混合ARQ(HARQ)L1重传、分组调度等。因此,本博士论文的研究重点在于通过仔细设计和分析不同增益机制在不同层上的互操作,而不是仅仅评估其各自的性能潜力,将MIMO有效地集成到LTE系统中。更具体地说,本研究利用MIMO的新算法,以合理的复杂度和低信令需求联合优化LTE系统。最佳互操作/集成的一个重要考虑因素是链路和系统级的总体吞吐量性能,其中诸如可用SINR的范围、信令开销和用户公平等相关问题变得非常重要。结合这些实际因素和多重增益机制的复杂性常常需要采用蒙特卡罗仿真模拟。然而,理想假设下的理论分析也有助于确定性能上界,并支持、验证蒙特卡罗仿真工作。因此,本文从理论和蒙特卡罗仿真两个方面进行研究。
首先,为了深入分析基于OFDM系统的MIMO,首先基于线性色散码提出了概念统一的MIMO-OFDM框架。为了包括物理层中所有增益机制和实际问题对LTE单用户性能的影响,开发了一个详细的链路级模拟器,该模拟器具有LTE物理层的大部分功能和MAC层的某些功能。为了对更先进的性能和复杂性进行基准测试,根据频谱效率评估了基准MIMO方案。之后,研究了更先进的MIMO解决方案,其中,闭环发射分集(CLTD)是我们特别感兴趣的,重点介绍了如何设计有效的方法来减少CLTD所需的权值反馈。我们进一步考虑了自适应MIMO的概念,根据信道条件的实时变化选择MIMO方案,通过使用统一的SINR概念对自适应MIMO原理进行了深入分析。此外,我们还提出了衡量实际信道质量的MIMO自适应的LA算法。
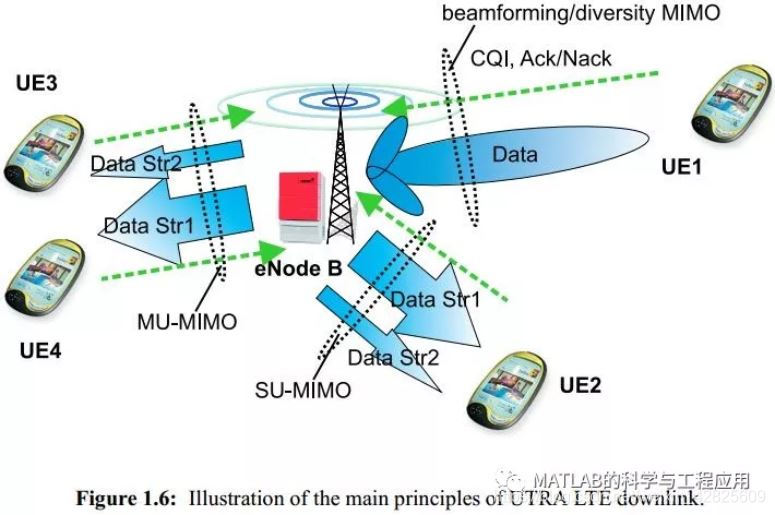
结合MIMO空分复用模式(SDM-FDPS),进一步在空域中研究探索了多用户分集增益与机会频域分组调度(FDPS)。首先,对不同的SDM-FDPS概念(即单用户(SU)和多用户(MU)MIMO),基于一些简化假设的后调度SINR分布进行了理论分析。对于MU-MIMO,可以在同一时频资源上的不同流上调度多个用户,而SU-MIMO将一个时频资源限制为单个用户。在此基础上,提出了具有中等复杂度的MIMO感知比例公平FDPS算法,然后使用准静态网络模拟器评估SDM-FDPS的性能,该模拟器提供流量建模、多用户调度以及包括HARQ的LA等。研究结果表明,在微小区场景中,假设小区中有10个在线用户,分别用SU和MU-MIMO方案获得约22%和30%的小区吞吐量增益。由于使用SDM-FDPS的信令开销与1x2 FDPS相比显著增加,因此进一步提出了多种方法来降低信令开销(上行链路为88%,下行链路为30%),而不显著影响性能(损失在7-10%以内)。
To meet the ambitious peak data rate and spectral efficiency target forthe UTRA Long Term Evolution (LTE), Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) isidentified to be one of the most essential technologies for LTE. While MIMO isa widely researched topic, most studies disregard the interaction of MIMO withother essential enhancement mechanisms in the system including Link adaptation(LA), Hybrid ARQ (HARQ) L1 retransmission, packet scheduling, etc. Therefore,this PhD study focuses on the efficient integration of MIMO in the LTE systemby making a careful design and analysis of the interoperation of different gainmechanisms at different layers, rather than an evaluation of their individualperformance potential only. More specifically, the investigation exploits newalgorithms for MIMO, which jointly optimize the LTE system with reasonablecomplexity and low signalling requirements. An important consideration for theoptimum interoperation/integration is the overall throughput performance atboth link and system level, where the associated issues like the range ofavailable SINRs, the signaling overhead, and user fairness become important.The complexity of combining those realistic factors and multiple gainmechanisms often require Monte Carlosimulations. However, theoretical analysis under ideal assumptions is alsouseful to gain insight on upper bounds and to support and verify the Monte Carlo simulation work. Thus both approaches areutilized in this Ph.D. study. First of all, in order to gain an analyticalinsight into MIMO with the OFDM based system, a conceptual unified MIMO-OFDMframework has first been formulated based on the linear dispersion code. Toinclude the impact from all gain mechanisms and practical issues in thephysical layer on the LTE single-user performance, a detailed link levelsimulator was developed which features most of the LTE Physical Layer and someMAC layer functionalities. To benchmark the performance and complexity of moreadvanced enhancements, baseline MIMO schemes are evaluated in terms of spectralefficiency. After that, more advanced MIMO solutions are investigated. Amongthem, the Closed-Loop Transmit Diversity (CLTD) is of special interest to us.The emphasis is given on designing efficient methods to reduce the requiredweights feedback for CLTD. We further considered the adaptive MIMO concept bywhich the MIMO schemes are chosen instantaneously according to the channelcondition. Useful insight into the principles of adaptive MIMO throughtheoretical analysis is provided by using a unified SINR concept. Besides, wepropose the practical channel quality metric design for LA algorithms includingMIMO adaptation. The multi-user diversity gain with opportunistic FrequencyDomain Packet Scheduling (FDPS) is further explored in spatial domain bycombining with MIMO in spatial division multiplexing mode (SDM-FDPS). Atheoretical analysis of postscheduling SINR distribution with some simplifiedassumptions is first performed to give insight into the different SDM-FDPSconcepts, namely single-user (SU-) and multi-user (MU-) MIMO. For MU-MIMO,multiple users can be scheduled on different streams on the same time-frequencyresource, while SU-MIMO restricts one time-frequency resource to a single user.After that, the MIMO aware proportional fair FDPS algorithms with moderatecomplexity are proposed. The performance of SDM-FDPS is then assessed with aquasi-static network simulator which provides traffic modelling, multi-userscheduling, and LA including HARQ, etc. Results reveal that in the micro-cellscenario a gain in cell throughput of around 22% and 30% is obtainable with SU-and MU- MIMO schemes, respectively, with precoding assuming 10 active users inthe cell. As the signalling overhead with SDM-FDPS is shown to be greatlyincreased compared to 1x2 FDPS, various methods are further proposed to bringdown the signalling overhead (88% in uplink and 30% in downlink) withoutaffecting the performance significantly (loss within 7-10%).
1 引言
2 MIMO OFDM背景
3 基本的链路级LTE评估
4 有限反馈的CLTD设计与分析
5 快速MIMO自适应的LA设计与分析
6 网络评估的系统模型
7 基于FDPS的MIMO设计与分析
8 减少信令的FDPS MIMO设计与分析
9 结论
附录A MIMO-OFDM统一框架的公式建模
附录B Turbo译码器的软信息计算
附录C 链路仿真器验证
附录D 信道中的空频编码问题
附录E 网络覆盖建模的有效性验证
下载英文原文地址:
http://page5.dfpan.com/fs/9lcdj2b21829b1620b4/
更多精彩文章请关注微信号: