文章目录
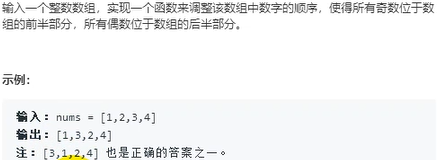
21.调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
//java版
class Solution {
public int[] exchange(int[] nums) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right)
{
//从左往右找偶数 找到偶数 停止
while(left < right && nums[left] % 2 == 1) left ++;
//从右往左找奇数 找到奇数停止
while(left < right && nums[right] % 2 == 0) right --;
if(left < right)
{
int temp = nums[left];
nums[left] = nums[right];
nums[right] = temp;
}
}
return nums;
}
}
//C++版
class Solution {
public:
void reOrderArray(vector<int> &array) {
/*
queue<int> q1, q2;
for(int i = 0; i < array.size(); i ++)
{
if(array[i] % 2 == 1)
q1.push(array[i]);
else
q2.push(array[i]);
}
array.clear();
while(q1.size())
{
array.push_back(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
while(q2.size())
{
array.push_back(q2.front());
q2.pop();
}
*/
//排序前后的稳定性
//是不是奇数
//前面偶数 后面奇数 交换
for(int i = 0; i < array.size(); i ++)
{
for(int j = array.size() - 1; j > i; j --)
{
if(array[j] % 2 == 1 && array[j - 1] % 2 == 0)
swap(array[j],array[j - 1]);
}
}
}
};
22.链表中倒数第k个节点

//java版
class Solution {
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
//单个指针 走到头 len
//从头走 len - k
//双指针
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = head;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i ++)
{
//k 大于链表长度
if(first == null) return null;
first = first.next;
}
while(first != null)
{
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
return second;
}
}
//C++版
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* head, unsigned int k) {
int n = 0;
for(ListNode* p = head; p; p = p -> next) n ++;
if(k > n) return nullptr;
ListNode* p = head;
for(int i = 0; i < n - k; i ++) p = p -> next;
return p;
}
};
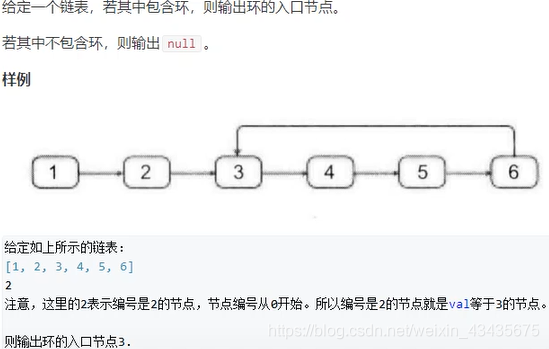
23.链表中环的入口结点
//java版
class Solution {
public ListNode entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode head) {
/*
//hash表 从头到尾遍历
Set<ListNode> hash = new HashSet<>();
while(head != null)
{
if(!hash.add(head))
return head;
head = head.next;
}
return null;
*/
//快慢指针
ListNode slow = head;//走一步
ListNode fast = head;//走两步
while(fast != null)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(fast == slow)
{
slow = head;
while(slow != fast)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}
//C++版
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* head)
{
/*
//快慢指针
auto fast = head, slow = head;
while(fast && slow)
{
fast = fast -> next;
slow = slow -> next;
if(fast) fast = fast -> next;
else break;
//相遇点
if(fast == slow)
{
slow = head;
while(fast != slow)
{
fast = fast -> next;
slow = slow -> next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return 0;
*/
//hash表
unordered_map<ListNode*,int> h;
int id = 1;
for(auto i = head; i ; i = i -> next, id ++)
{
if(h[i] != 0)
{
return i;
}
else
h[i] = id;
}
return NULL;
}
};
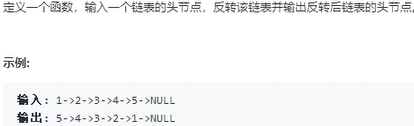
24.反转链表
//java版
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null)
{
//让cur指向 pre
//然后 pre cur 都往后走一个
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
}
//C++版
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
//找到前驱结点
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
auto cur = pHead;
while(cur)
{
auto next = cur -> next;
cur -> next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};
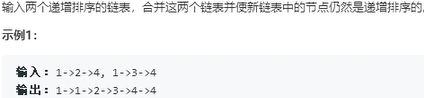
25.合并两个排序的链表
//java版
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
//归并排序思想
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null)
{
if(l1.val <= l2.val)
{
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
else
{
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(l1 != null)
{
cur.next = l1;
}
if(l2 != null)
{
cur.next = l2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
//C++版
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* p1, ListNode* p2)
{
//归并思想
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
auto cur = dummy;
while(p1 && p2)
{
if(p1 -> val <= p2 -> val)
{
cur -> next = p1;
cur = cur -> next;
p1 = p1 -> next;
}
else{
cur -> next = p2;
cur = cur -> next;
p2 = p2 -> next;
}
}
if(p1) cur -> next = p1;
else cur -> next = p2;
return dummy -> next;
}
26.树的子结构

//java版
class Solution {
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
//递归
//A根 B根
//A左子树 B
//A右子树 B
if(A == null || B == null) return false;
return (issubtree(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B)|| isSubStructure(A.right, B));
}
public boolean issubtree(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
//true
if(B == null) return true;
//false
if(A == null || A.val != B.val) return false;
return issubtree(A.left, B.left) && issubtree(A.right, B.right);
}
}
//C++版
class Solution {
public:
bool HasSubtree(TreeNode* t1, TreeNode* t2)
{
if(!t1 || !t2) return false;
if(isPart(t1, t2)) return true;
return HasSubtree(t1 -> left, t2) || HasSubtree(t1 -> right, t2);
}
//只能比较t1 t2各自为根结点的树
bool isPart(TreeNode* t1, TreeNode* t2)
{
if(!t2) return true;//t2已经遍历到了叶节点结束
if(!t1 || t1 -> val != t2 -> val) return false;
//比较左右子孩子
return isPart(t1 -> left, t2 -> left) && isPart(t1 -> right, t2 -> right);
}
};
27.二叉树的镜像

//java版
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
//左右子树交换
if(root == null) return null;
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = mirrorTree(root.right);
root.right = mirrorTree(temp);
return root;
}
}
//C++版
class Solution {
public:
void Mirror(TreeNode *root) {
if(!root) return;
Mirror(root -> left);
Mirror(root -> right);
//交换左右结点
swap(root -> left, root -> right);
}
};
28.对称的二叉树

//java版
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
return dfs(root.left, root.right);
}
public boolean dfs(TreeNode left, TreeNode right)
{
if(left == null && right == null) return true;
if(left == null || right == null || left.val != right.val) return false;
return dfs(left.left, right.right) && dfs(left.right, right.left);
}
}
//C++版
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root) return true;
return dfs(root -> left, root -> right);
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* t1, TreeNode* t2)
{
if(!t1 || !t2) return !t1 && !t2;
if(t1 -> val != t2 -> val) return false;
return dfs(t1 -> left, t2 -> right) && dfs(t1 -> right, t2 -> left);
}
};
29.顺时针打印矩阵

扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
12557801 查看本文章


//java版
class Solution {
public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
//判断边界
if(matrix.length == 0)
return new int[0];
//右下左上
int left = 0, right = matrix[0].length -1, up = 0, down = matrix.length - 1;
int num = 0;
int[] res = new int[(right + 1) * (down + 1)];
while(true)
{
//右
for(int i = left; i <= right; i ++)
res[num ++] = matrix[up][i];
if(++ up > down) break;
//下
for(int i = up; i <= down; i ++)
res[num ++] = matrix[i][right];
if(-- right < left ) break;
//左
for(int i = right; i >= left; i --)
res[num ++] = matrix[down][i];
if(-- down < up) break;
//上
for(int i = down; i >= up; i --)
res[num ++] = matrix[i][left];
if(++ left > right) break;
}
return res;
}
}
//C++版
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printMatrix(vector<vector<int> > matrix) {
vector<int> res;
//定义方向
//碰壁换方向 右下左上
if(matrix.empty()) return res;
int n = matrix.size(), m = matrix[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> state(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
int dx[4] = {
-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {
0, 1, 0, -1};
int x = 0, y = 0, d = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n * m; i ++)
{
res.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
state[x][y] = true;
int a = x + dx[d], b = y + dy[d];
if(a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= m || state[a][b] == true)
{
d = (d + 1) % 4;
a = x + dx[d], b = y + dy[d];
}
x = a, y = b;
}
return res;
}
};
30.包含min函数的栈

//java版
class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> A, B;//A正常的栈 B记录最小元素的栈
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
A = new Stack<>();
B = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
//判断当前元素 和栈内最小的元素 对比
A.add(x);
if(B.empty() || B.peek() >= x)
B.add(x);
}
public void pop() {
//栈顶元素 是不是 最小的
//if(A.pop().equals(B.peek()))
// B.pop();
if(A.peek().equals(B.peek()))//不能用 == 必须用 equals
B.pop();
A.pop();
}
public int top() {
//直接写
return A.peek();
}
public int min() {
//找到栈内最小的元素 直接写
return B.peek();
}
}
//C++版
class Solution {
public:
stack<int> stk, min_stk;
void push(int value) {
stk.push(value);
if(min_stk.empty() || min_stk.top() >= value) min_stk.push(value);
}
void pop() {
if(min_stk.top() == stk.top()) min_stk.pop();
stk.pop();
}
int top() {
return stk.top();
}
int min() {
return min_stk.top();
}
};