LF-YOLO: A Lighter and Faster YOLO for Weld Defect Detection of X-ray Image
LF-YOLO:用于x射线图像焊缝缺陷检测的更轻、更快的YOLO
原因:不同类型缺陷的形状和规模差异很大,这给模型检测焊接缺陷带来了挑战。
改进模块:RMF(多尺度改进模块),EFE(减少计算量)
RMF 的新型多尺度融合模块。它可以通过同时使用基于参数和无参数的方法来结合 X 射线图像的局部和全局线索。
高效的特征提取EFE模块作为主干单元,它可以用很少的参数和低计算量提取有意义的特征,有效地学习表征。大大减少了特征提取的消耗。
Abstract
X-ray image plays an important role in manufacturing industry for quality assurance, because it can reflect the internal condition of weld region.However, the shape and scale of different defect types vary greatly, which makes it challenging for model to detect weld defects.
x射线图像能反映焊接区域的内部状况,在保证焊接质量方面起着重要作用。然而,不同类型缺陷的形状和规模差异很大,这给模型检测焊接缺陷带来了挑战。
a reinforced multiscale feature (RMF) module is designed to implement both parameter-based and parameter-free multi-scale information extracting operation.RMF enables the extracted feature map capable to represent more plentiful information, which is achieved by superior hierarchical fusion structure.
设计增强的多尺度特征(RMF)模块,实现了基于参数和无参数的多尺度信息提取操作。RMF使提取的特征映射能够表示更丰富的信息,这是通过更高层次的融合结构来实现的。
To improve the performance of detection network, we propose an efficient feature extraction (EFE) module.To further prove the ability of our method, we test it on public dataset MS COCO, and the results show that our LF-YOLO has a outstanding versatility detection performance.
为了提高检测网络的性能,我们提出了一种高效的特征提取(EFE)模块。为了进一步证明我们的方法的能力,我们在公共数据集MS COCO上进行了测试,结果表明我们的LF-YOLO具有出色的通用性检测性能。
I. INTRODUCTION
However, either manual or robotic welding will inevitably produce weld defects, which is a potential hazard for daily production.people utilize X-ray technology to reflect internal defect of weld into image as shown in Fig. 1, and detect them through expert or computer vision model.

但是无论是手工焊接还是机器人焊接,都会不可避免地产生焊接缺陷,这对日常生产都是一个潜在的危害。人们利用x射线技术将焊缝内部缺陷反映成如图1所示的图像,并通过专家或计算机视觉模型进行检测。

The context of weld image is complicated, and there are blurred boundaries and similar texture between defect and background. In addition, the scales and shapes of defects vary greatly among different classes, which can be seen in Fig. 2.
焊缝图像背景复杂,缺陷与背景之间边界模糊,纹理相似。此外,从图2可以看出,不同类型缺陷的尺度和形状差异较大。

All of these factors bring great challenges to the detection model [3], and it is required to capture abundant contextual information.
这些因素都给检测模型[3]带来了很大的挑战,需要获取丰富的上下文信息。
local feature is beneficial to represent the boundary, shape, and geometric texture of defect, while global feature is vital for classification and distinguishing foreground and background.
局部特征有利于表示缺陷的边界、形状和几何纹理,而全局特征对于前景和背景的分类和区分至关重要。
In this paper, we propose an reinforced multiscale feature (RMF) module, which combines both of parameter-based and parameter-free operations.
本文提出了一种基于参数和无参数操作相结合的增强多尺度特征(RMF)模块。
RMF module firstly contains a basic parameter-free hierarchical structure, which generates multiple feature maps obtained from maxpool operations of different sizes.
RMF模块首先包含一个基本的无参数层次结构,通过不同大小的maxpool操作生成多个特征映射。
Furthermore, within each branch of basic hier- archy, new features are produced through learning potential information implicitly, and the process is parameter-based.
此外,在基本层次结构的每个分支中,新特征是通过隐式学习潜在信息产生的,这个过程是基于参数的。
Finally, the output data of each hierarchy would be fused for finer estimation. Besides the contribution of multi-scale feature utilization, original feature extraction also determines the performance of the network.
最后,对各层次的输出数据进行融合,进行更精细的估计。除了多尺度特征利用的贡献外,原始特征提取也决定了网络的性能。
To effectively extract feature of weld defect, we design an efficient feature extraction (EFE) module elaborately, and build a superior backbone by stacking EFE repeatedly.
为了有效地提取焊缝缺陷特征,我们精心设计了一个高效的特征提取(EFE)模块,并通过反复叠加EFE构建了一个优质的主干。
In summary, this work makes the following contributions.
总而言之,这项工作有以下贡献。
A novel multi-scale fusion module named RMF is pro- posed. It can combine local and global cues of X- ray image by using parameter-based and parameter-free methods simultaneously.
提出了一种新的多尺度融合模块RMF。它可以同时使用基于参数和无参数的方法来结合X射线图像的局部线索和全局线索。
To efficiently learn representation, we design a novel EFE module as the unit of backbone, and it can extract mean- ingful feature with few parameters and low computation.
为了高效地学习表示,我们设计了一种新颖的EFE模块作为骨干单元,它能以较少的参数和较低的计算量提取出均值特征。
deal with multiple defect classes, and the proposed network is memory and computation friendly.
该网络可以处理多个缺陷类,具有良好的内存和计算友好性。
III. METHOD
efficient feature extraction (EFE) module and reinforced multi- scale feature (RMF) module
高效特征提取(EFE)模块和增强多尺度特征(RMF)模块
A. EFE module
Feature extraction module is the basic block of deep learning network.
特征提取模块是深度学习网络的基本模块。
to better accomplish corresponding tasks. In addition, feature extraction operation is the main source of parameters and computation. Therefore, the weight of feature extraction module determines the weight of whole network.
更好地完成相应的任务。此外,特征提取操作是参数和计算的主要来源。因此,特征提取模块的权重决定了整个网络的权重。
Inspired by the inverted residual block in MobileNetV2 [22], EFE module maps the input data into a higher dimension space in the middle stage, because the expansion of feature space is beneficial to obtain more meaningful representation.
EFE模块受MobileNetV2[22]中反向残差块的启发,在中间阶段将输入数据映射到一个更高维的空间,因为特征空间的扩展有利于获得更有意义的表示。
MobileNetV2 [21] solves this problem by using depthwise separable convolutions. In this paper, we employ a more wise strategy.
MobileNetV2[21]通过使用深度可分离卷积解决了这个问题。在本文中,我们采用了一个更明智的策略。
Following the idea of [34], we design the middle expansion structure based on “split-transform-merge” theory. After the first 1×1 Conv, feature maps are split into two branches, and split ratio ra is set as 0.25 in this paper.
我们遵循[34]的思想,基于“分裂-转换-合并”理论设计了中间扩展结构。在进行了第一次1×1 Conv之后,特征映射被拆分为两个分支,本文设置拆分比ra为0.25。
One of them is an identity branch, which does not utilize any operation on the data. Another branch is a dense block in [35], which is used to further extract features.
其中之一是身份分支,它不利用对数据的任何操作。另一个分支是[35]中的密集块,用于进一步提取特征。
To optimize the complexity, EFE module introduces Ghost Conv [24].
为了优化复杂度,EFE模块引入了Ghost Conv[24]。
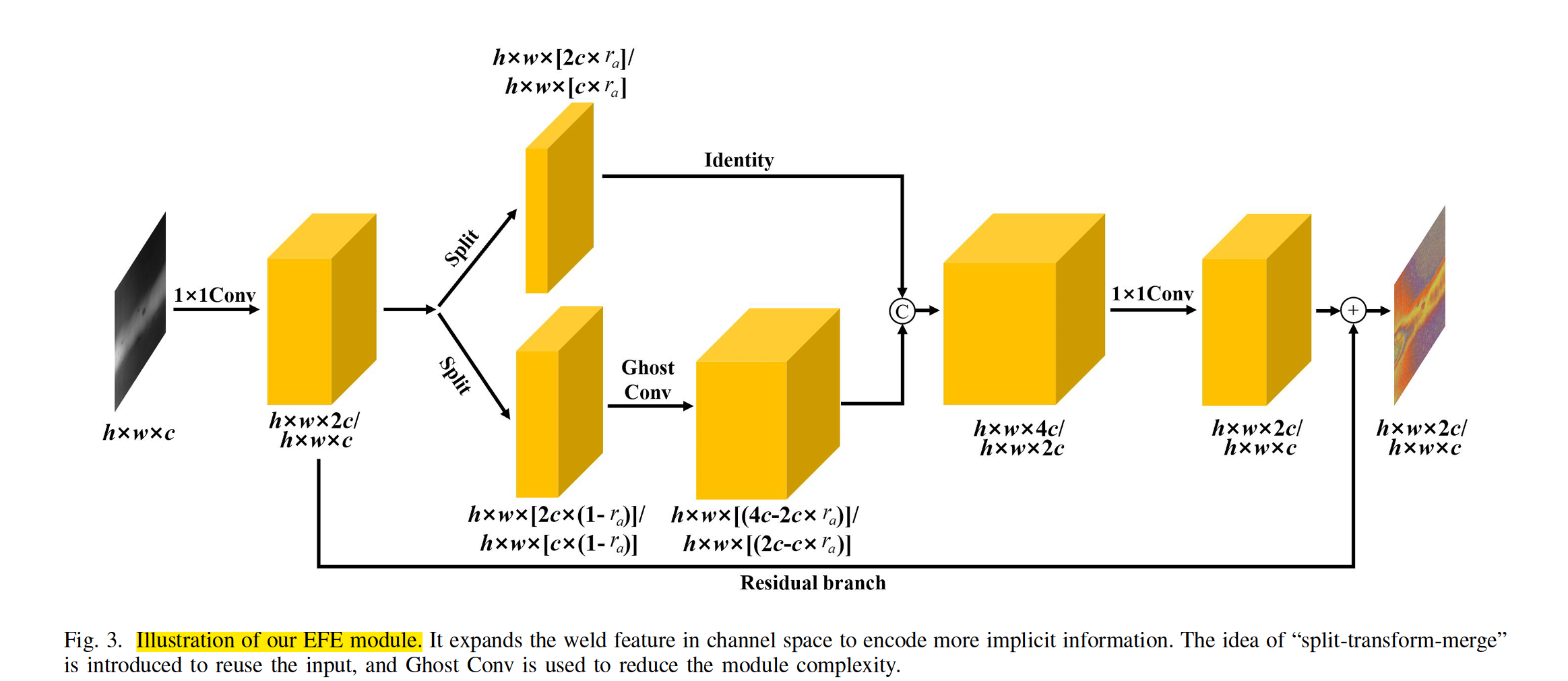
At the tail of EFE module, the second 1×1 Conv is used to compress the number of channels back to 2c/c. Finally, the input of expansion operation and the output of second 1×1 Conv are added element-wise by a residual branch.
在EFE模块的尾部,第二个1×1 Conv用于将通道数压缩回2c/c。最后,将展开运算的输入和第二个1×1 Conv的输出通过一个剩余分支逐项相加。
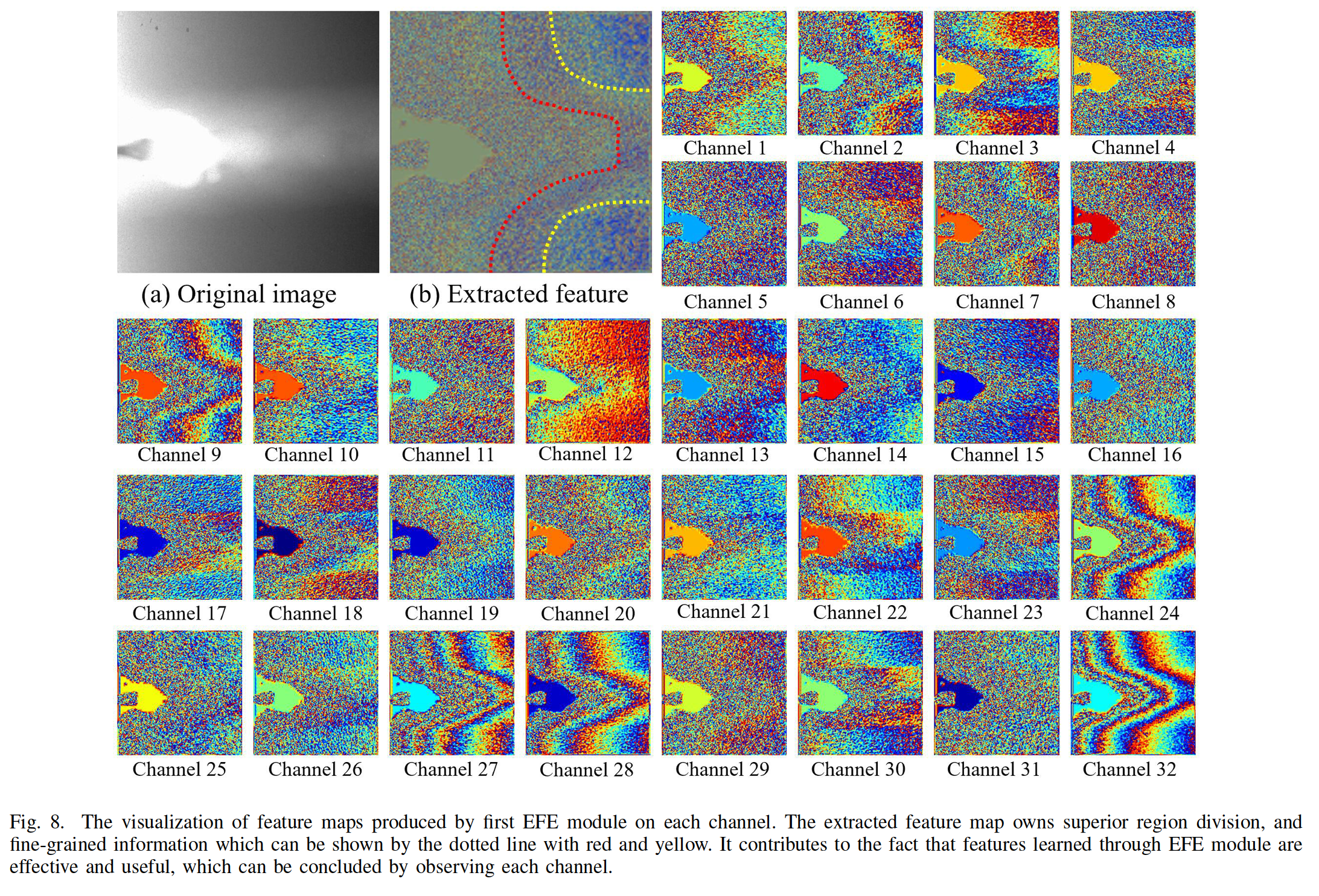
Compared with the conventional residual block, our EFE module greatly decreases the consumption of feature extraction.
与传统的残差块相比,该EFE模块大大减少了特征提取的消耗。
B. RMF module
Scale problem is a classical research topic for CNN, because it is not robust enough for the sizes of objects.Especially when the sizes of objects vary greatly, the plain topology model will encounter an awful performance.
尺度问题是CNN的一个经典研究课题,因为它对物体的大小不够鲁棒。特别是当对象的大小变化较大时,纯拓扑模型的性能会很差。

through multi-scale strategy, we design a RMF module combining the parameter-based and parameter-free methods.
通过多尺度策略,设计了基于参数和无参数相结合的RMF模块。
RMF module is a hierarchical structure for obtaining multi- scale contextual information.
RMF模块是一种用于获取多尺度上下文信息的分层结构。
which utilizes multiple maxpool operations with different sizes on input feature map. There are not any parameters introduced in this stage, hence we regard it as parameter-free.
在输入特征映射上利用多个不同大小的maxpool操作。由于此阶段未引入任何参数,因此我们认为它是无参数的。
Parameter-free method makes the most of existing data, but not generating new information in a sense.
无参数方法充分利用了现有数据,但在某种意义上不会产生新的信息
Dilated convolution can enhance the ability to extract un- derlying information through changing the receptive field [5].
扩张卷积可以通过改变接收野[5]来增强提取底层信息的能力。
If we use dilated convolution directly at the tail of backbone, it would be expensive on storage and computation.
如果直接在主干尾部使用扩张卷积,将会增加存储和计算的成本。
To address this problem, GDConv achieves dilation process based on a lighter form. Specifically, we retain the structure of original Ghost Conv but operate depthwise Conv with dilation version, and its inner detail is shown in Fig. 5.
为了解决这一问题,GDConv基于更轻的形式实现了膨胀过程。具体来说,我们保留了原来的Ghost Conv的结构,但对扩张版进行了深度Conv,其内部细节如图5所示。

GDConv is the core ingredient for RMF module to learn implicit information through parameters of convolution kernels. Three GDConvs form the elements of a hierarchy group, and their dilation rates are set as 1, 5, 9 respectively.
GDConv是RMF模块通过卷积核参数学习隐式信息的核心组成部分。三个GDConvs组成一个层次组的元素,它们的膨胀率分别设为1、5、9。
Note that when dilation rate is 1, it is equivalent to normal Ghost Conv, and the new features from different dilation branches would be concatenated.
需要注意的是,当膨胀率为1时,它相当于正常的Ghost Conv,将不同膨胀分支的新特征串联起来。
the parameter-free method provides a multi-scale base through optimizing existing feature maps, and parameter- based method exploits new multi-scale data based on the former. Hence, the base and expansion pyramid of hierarchy have a superposition effect and enhance the ability to better develop effective representation.
无参数方法通过优化已有的特征图来提供多尺度的基础,而基于参数的方法则在前者的基础上利用新的多尺度数据。因此,层次的基础和扩展金字塔具有叠加效应,增强了更好地发展有效表征的能力。
C. The architecture of LF-YOLO
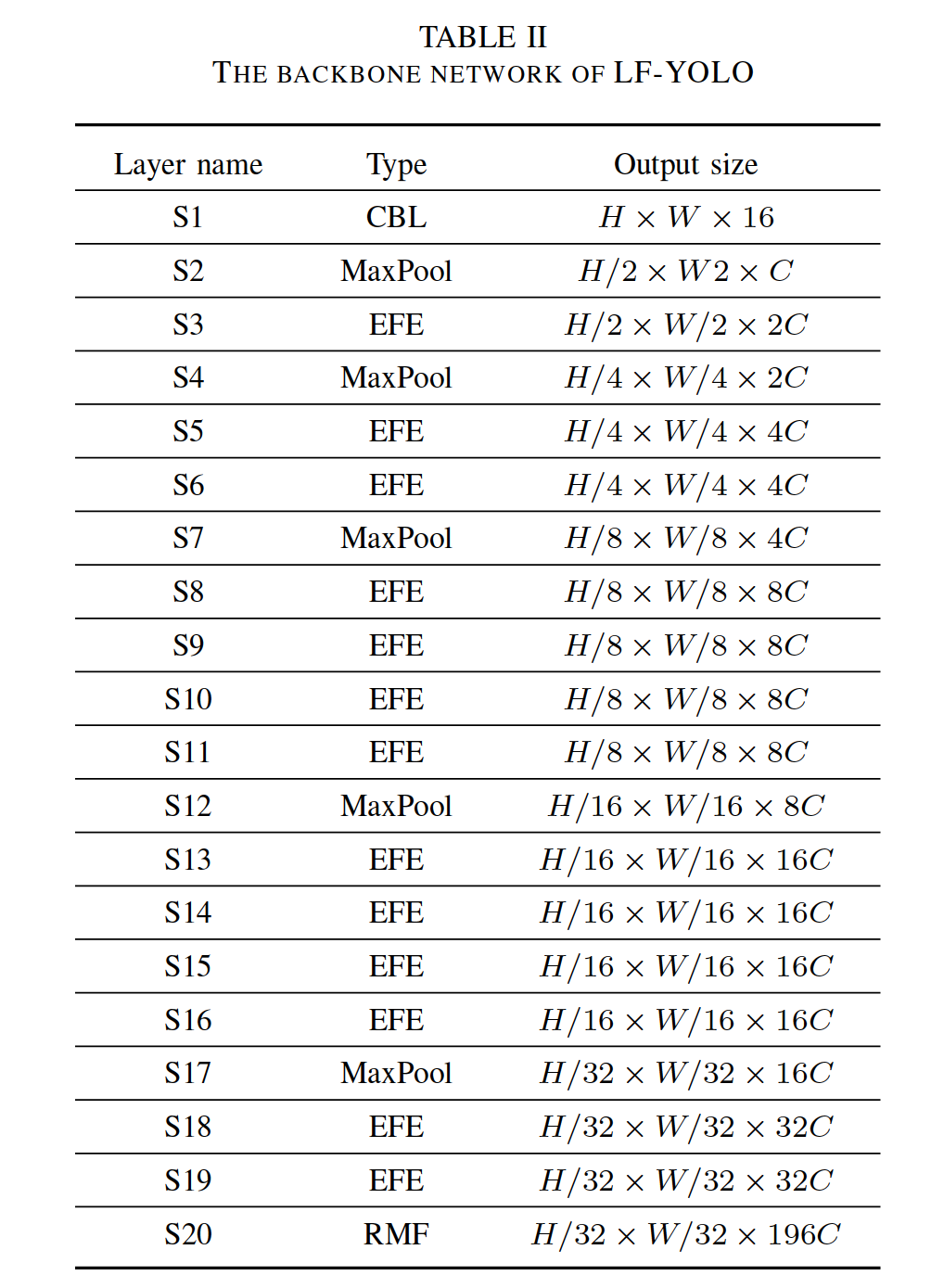
V. CONCLUSION
In this paper, we propose a highly effective EFE module as the basic feature extraction block, and it can encode sufficient information of X-ray weld image with low consumption.
本文提出了一种高效的EFE模块作为基本特征提取块,该模块能够以较低的消耗对x射线焊缝图像进行足够的信息编码。
The parameter-free stage contributes to a basis containing existing multi-scale information, and parameter-based stage further learn implicit feature among different receptive fields.
无参数阶段形成包含已有多尺度信息的基础,基于参数阶段进一步学习不同接受域之间的隐式特征。
