注意:文中彩色代码均在Visual Studio 2022编译器中编写,本文为C语言数据结构手抄版,文中有部分改动,非原创。
目录
6.3.图的遍历
与树的遍历类似,图的遍历也是从某个顶点出发,沿着某条搜索路径对图中每个顶点做且仅做一次访问。遍历图的算法是求解图的连通性、图的拓扑排序等算法的基础。然而,图的遍历要比树的遍历复杂得多,因为图的任一顶点都可能和其余的顶点相邻接,所以在访问了某个顶点之后,可能顺着某条路径搜索又回到了该顶点。为了避免顶点的重复访问,可设一个布尔数组visited[0..n-1],用来标记某个顶点是否已被访问过,初始值均为假,若该顶点已被访问,则以顶点序号作为下标,将其所对应的数组元素置为真。
图的遍历方法很多,但最常用的是深度优先搜索遍历和广度优先搜索遍历两种方法。下面分别介绍这两种遍历方法,它们对无向图和有向图都适用。
6.3.1.深度优先搜索遍历
深度优先搜索(Depth First Search, DFS)遍历类似于树的前序(先根)遍历。假设初始状态是图中所有顶点都未曾访问过,则可从图G中任选一顶点v为初始出发点,首先访问出发点v,并将其标记为已访问过;然后依次从v出发搜索v的每个邻接点w,若w未曾访问过,则以w作为新的出发点出发,继续进行深度优先遍历,直到图中所有和v有路径相通的顶点都被访问到;若此时图中仍有顶点未被访问,则另选一个未曾访问的顶点作为起点,重复上述过程,直到图中所有顶点都被访问到为止。
下面以图6.11中的无向图G8为例,分析深度优先搜索遍历图的过程。假设以v0为出发点(起点)进行搜索,在访问了顶点v0之后,将visited[0]置为真,接着选择v0的邻接点v1。因为v1未曾访问过,访问v1,再从顶点v1出发进行搜索,接着访问v2,访问v5:这时,顶点v5、v2的邻接点都已被访问过,因此回溯到顶点v1,由于v1的邻接点v0和v2已访问过,只有其邻接点v4未被访问。所以访问v4。在访问了v4之后,由于v4的邻接点v0和v1已访问过,则搜索到v6,访问v6,再从v6搜索访问v3和v7,然后回溯到v4, 由于v4的另一个邻接点v8未曾访问,访问v8。至此,所有顶点都已被访问,搜索结束。整个搜索过程及访问顶点的顺序如图6.11 (b)所示。由此,可得到深度优先搜索遍历图G8的顶点访问序列: v0,v1,v2,v5,v4,v6,v3,v6,v8。
对图进行深度优先遍历时,按访问顶点的先后次序得到的顶点序列称为图的深度优先遍历序列,或简称为DFS序列。
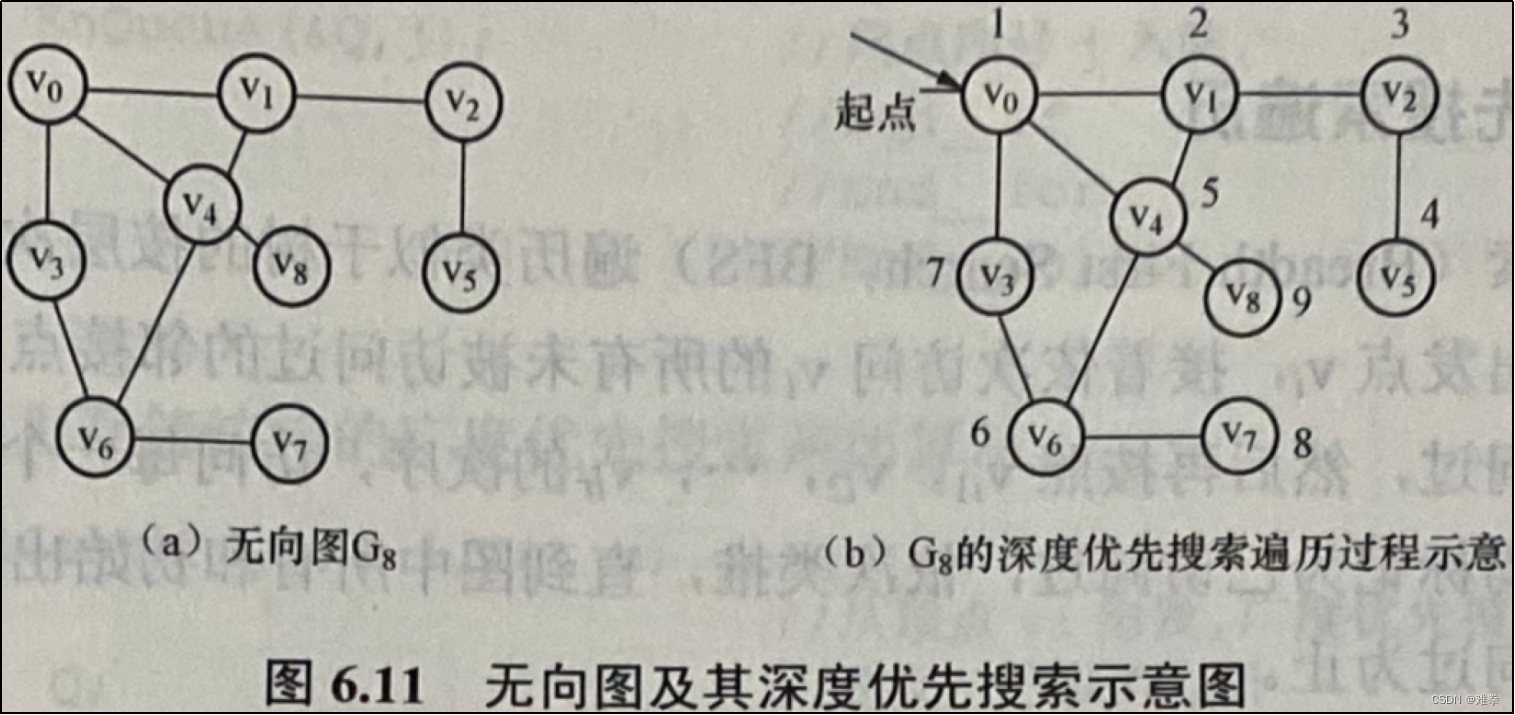
显然,图的深度优先搜索遍历的过程是递归的,假设visited[Max VertexNum]为一全局量数组,用以标记某个顶点是否被访问过,其初值均为假值(FALSE)。下面分别以邻接矩阵和邻接表作为图的存储结构,给出相应的深度优先搜索遍历的递归算法。
下图中的数字显示了深度优先搜索顶点被访问的顺序。
(1)以邻接矩阵为存储结构的深度优先搜索遍历递归算法。
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #define FLAG 0 #define MaxVertex 50 struct Graph { char vertex[MaxVertex][8]; int edge[MaxVertex][MaxVertex]; int vertexNum; int edgeNum; }; int findVertex(struct Graph* graph, char* vertex) { for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (strcmp(vertex, graph->vertex[i]) == 0) { return i; } } return INT_MAX; } void printfGraph(struct Graph* graph) { printf("\t"); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { printf("%s\t", graph->vertex[i]); } printf("\n"); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { printf("%s\t", graph->vertex[i]); for (int j = 0; j < graph->vertexNum; j++) { if (graph->edge[i][j] == INT_MAX) { printf("∞\t"); } else { printf("%d\t", graph->edge[i][j]); } } printf("\n"); } } struct Graph* createGraph() { struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)); #if FLAG printf("请输入无向图的顶点数和边数:\n顶点 边。\n"); #else printf("请输入有向图的顶点数和边数:\n顶点 边。\n"); #endif scanf("%d", &graph->vertexNum); scanf("%d", &graph->edgeNum); printf("请输入%d个顶点的值。\n", graph->vertexNum); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { scanf("%s", graph->vertex[i]); } for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < graph->vertexNum; j++) { #if FLAG graph->edge[i][j] = 0; #else graph->edge[i][j] = INT_MAX; #endif } } #if FLAG printf("请输入%d条边:\n顶点1 顶点2\n", graph->edgeNum); #else printf("请输入%d条边:\n弧尾 弧头 权重\n", graph->edgeNum); int weight; #endif char tail[8] = { 0 }, head[8] = { 0 }; for (int i = 1; i <= graph->edgeNum; i++) { printf("请输入第%d条边:\n", i); scanf("%s", tail); scanf("%s", head); #if !FLAG scanf("%d", &weight); #endif int tailIndex = findVertex(graph, tail); int headIndex = findVertex(graph, head); if (tailIndex == INT_MAX || headIndex == INT_MAX) { #if FLAG printf("输入的顶点不存在,请重新输入:\n"); #else printf("输入的狐尾和狐头不存在,请重新输入:\n"); #endif i--; continue; } #if FLAG graph->edge[tailIndex][headIndex] = 1; graph->edge[headIndex][tailIndex] = 1; #else graph->edge[tailIndex][headIndex] = weight; #endif } printfGraph(graph); return graph; } void recursion(struct Graph* graph, int* visited, int index) { printf("%s ", graph->vertex[index]); visited[index] = 1; for (int i = 0; i < (int)graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (!visited[i] && graph->edge[index][i] > 0 && graph->edge[index][i] != INT_MAX) { recursion(graph, visited, i); } } } void depthFirstSearch(struct Graph* graph) { #if FLAG printf("深度优先遍历邻接矩阵--无向图:\n"); #else printf("深度优先遍历邻接矩阵--有向图:\n"); #endif int* visited = malloc(sizeof(int) * (unsigned int)graph->vertexNum); if (visited == NULL) return; memset(visited, 0, sizeof(int) * (int)graph->vertexNum); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { recursion(graph, visited, i); } } free(visited); visited == NULL; } int main() { // struct Graph* graph = createGraph(); // FILE* file = fopen("D:/Graph.data", "wb+"); // if (file == NULL) // { // printf("Open file can not be null!"); // } // fwrite(graph, sizeof(struct Graph), 1, file); // fclose(file); FILE* file = fopen("D:/Graph.data", "rb+"); if (file == NULL) { printf("Open file can not be null!"); return; } struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)); if (graph == NULL) { printf("There not enough memory to be create object of graph!"); return; } fread(graph, sizeof(struct Graph), 1, file); fclose(file); printfGraph(graph); depthFirstSearch(graph); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| A B C D E F G H I A 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 B 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 C 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 D 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 E 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 F 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 G 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 H 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 I 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 深度优先遍历邻接矩阵--无向图: A B F H C D G I E |
(2)以邻接表为存储结构的深度优先搜索遍历算法
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #define FLAG 0 #define MaxVertex 50 struct EdgeNode { int adjvex; struct EdgeNode* next; int weight; }; struct EdgeHeader { char data[sizeof(int)]; struct EdgeNode* firstEdge; }; struct Graph { struct EdgeHeader* vertex[MaxVertex]; int vertexNum; int edgeNum; }; void printfGraph(struct Graph* graph) { #if FLAG printf("无向图邻接表:\n"); #else printf("有向图邻接表:\n"); #endif for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { printf("%d %s", i, graph->vertex[i]->data); if (graph->vertex[i]->firstEdge == NULL) { printf("\n"); continue; } struct EdgeNode* currentNode = graph->vertex[i]; do { currentNode = currentNode->next; printf("---->%d", currentNode->adjvex); } while (currentNode->next != NULL); printf("\n"); } } int findVertex(struct Graph* graph, char* vertex) { for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (strcmp(vertex, graph->vertex[i]->data) == 0) { return i; } } return INT_MAX; } void insertEdge(struct Graph* graph, int tailIndex, int headIndex) { struct EdgeNode* edgeNode = malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeNode)); if (edgeNode == NULL) { return; } edgeNode->adjvex = headIndex; edgeNode->next = NULL; if (graph->vertex[tailIndex]->firstEdge == NULL) { graph->vertex[tailIndex]->firstEdge = edgeNode; return; } struct EdgeNode* currentNode = graph->vertex[tailIndex]->firstEdge; struct EdgeNode* priorNode = graph->vertex[tailIndex]; // move the pointer while (currentNode->next != NULL && currentNode->adjvex < headIndex) { priorNode = currentNode; currentNode = currentNode->next; } // insert top if (headIndex < currentNode->adjvex) { priorNode->next = edgeNode; edgeNode->next = currentNode; } else if (headIndex > currentNode->adjvex) { // insert tail if (currentNode->next == NULL) { currentNode->next = edgeNode; } else { struct EdgeNode* nextNode = currentNode->next; currentNode->next = edgeNode; edgeNode->next = nextNode; } } else { return; } } struct Graph* createGraph() { struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)); if (graph == NULL) { return; } printf("请输入图的顶点数和边数:\n顶点 边。\n"); scanf("%d", &graph->vertexNum); scanf("%d", &graph->edgeNum); printf("请输入%d个顶点的值。\n", graph->vertexNum); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { struct EdgeHeader* vertex = malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeHeader)); if (vertex == NULL) { return; } graph->vertex[i] = vertex; scanf("%s", graph->vertex[i]->data); graph->vertex[i]->firstEdge = NULL; } printf("请输入%d条边:\n顶点1 顶点2\n", graph->edgeNum); char tail[8] = { 0 }, head[8] = { 0 }; for (int i = 1; i <= graph->edgeNum; i++) { printf("请输入第%d条边:\n", i); scanf("%s", tail); scanf("%s", head); int tailIndex = findVertex(graph, tail); int headIndex = findVertex(graph, head); if (tailIndex == INT_MAX || headIndex == INT_MAX) { printf("输入的顶点不存在,请重新输入:\n"); i--; continue; } insertEdge(graph, tailIndex, headIndex); #if FLAG insertEdge(graph, headIndex, tailIndex); #endif } return graph; } void recursion(struct Graph* graph, int* visited, int index) { printf("%s ", graph->vertex[index]->data); visited[index] = 1; struct EdgeHeader* edgeHeader = graph->vertex[index]; if (edgeHeader->firstEdge == NULL) { return; } struct EdgeNode* edgeNode = edgeHeader->firstEdge; while (edgeNode != NULL) { int next = edgeNode->adjvex; if (!visited[next]) { recursion(graph, visited, next); } edgeNode = edgeNode->next; } } void depthFirstSearch(struct Graph* graph) { #if FLAG printf("深度优先遍历邻接表--无向图:\n"); #else printf("深度优先遍历邻接表--有向图:\n"); #endif int* visited = malloc(sizeof(int) * (unsigned int)graph->vertexNum); if (visited == NULL) return; memset(visited, 0, sizeof(int) * (int)graph->vertexNum); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { recursion(graph, visited, i); } } } int main() { struct Graph* graph = createGraph(); printfGraph(graph); depthFirstSearch(graph); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| 请输入图的顶点数和边数: 顶点 边。 9 8 请输入9个顶点的值。 A B C D E F G H I 请输入8条边: 顶点1 顶点2 请输入第1条边: A B 请输入第2条边: A C 请输入第3条边: A D 请输入第4条边: A E 请输入第5条边: B F 请输入第6条边: F H 请输入第7条边: D G 请输入第8条边: G I 有向图邻接表: 0 A---->1---->2---->3---->4 1 B---->5 2 C 3 D---->6 4 E 5 F---->7 6 G---->8 7 H 8 I 深度优先遍历邻接表--有向图: A B F H C D G I E |
分析上述算法,在遍历图时,对图中每个顶点至多调用一次DFS函数,因为一旦某个顶点被标记为已访问过,就不再从该顶点开始搜索。因此,遍历图的过程实际上是对每个顶点查找其邻接点的过程。当用邻接矩阵表示图时,需要对n个顶点进行访问,所以共需搜索n2个矩阵元素,而在邻接表上则需要将边表中所有O(e)个结点搜索一遍。因此,深度优先搜索遍历算法的时间复杂度为O(n2)或O(n+e)。
【例6.1】 试编写一个实现连通图G的深度优先遍历(从顶点v出发)的非递归算法。
分析:本题的算法思想是,首先访问图G的指定起始顶点v;从v出发,访问一个与v邻接的顶点p↑(代表p(~)指向的结点)后,再从p↑出发,访问与p↑邻接而未被访问过的顶点q↑,然后从q↑出发,重复上述过程,直到找不到未被访问过的邻接顶点为止;回退到访问过的但尚有未被访问过邻接点的顶点,从该顶点出发重复前面的步骤,直到所有被访问过的顶点的邻接点都已被访问为止。为此,用一个栈S来保存被访问过的结点,以便回溯查找被访问过结点的未被访问过的邻接点。
深度优先搜索通过栈来实现的算法,首先选择一个起始顶点并需要遵守三个规则:
1.如果可能,访问一个邻接的未访问顶点,标记它,并把它放入栈中。
2.当不能执行规则1时,如果栈不空,就从栈中弹出一个顶点。
3.如果不能执行规则1和规则2,就完成了整个搜索过程。
深度优先搜索采用前面的邻接矩阵存储结构(邻接矩阵--无向图),栈采用前面的顺序结构栈(第三章3.1小节)来实现遍历逻辑,这里只介绍邻接矩阵代码,邻接表读者可以自己实现。
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "serialStack.h" #define MaxVertex 50 struct Graph { char vertex[MaxVertex][8]; int edge[MaxVertex][MaxVertex]; int vertexNum; int edgeNum; }; int findVertex(struct Graph* graph, char* vertex) { for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (strcmp(vertex, graph->vertex[i]) == 0) { return i; } } return INT_MAX; } void printfGraph(struct Graph* graph) { printf("\t"); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { printf("%s\t", graph->vertex[i]); } printf("\n"); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { printf("%s\t", graph->vertex[i]); for (int j = 0; j < graph->vertexNum; j++) { if (graph->edge[i][j] == INT_MAX) { printf("∞\t"); } else { printf("%d\t", graph->edge[i][j]); } } printf("\n"); } } struct Graph* createGraph() { struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)); printf("请输入图的顶点数和边数:\n顶点 边。\n"); scanf("%d", &graph->vertexNum); scanf("%d", &graph->edgeNum); printf("请输入%d个顶点的值。\n", graph->vertexNum); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { // graph->vertex[i] = malloc(sizeof(char) * 8);; scanf("%s", graph->vertex[i]); } for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < graph->vertexNum; j++) { graph->edge[i][j] = 0; } } printf("请输入%d条边:\n顶点1 顶点2\n", graph->edgeNum); char tail[8] = { 0 }, head[8] = { 0 }; for (int i = 1; i <= graph->edgeNum; i++) { printf("请输入第%d条边:\n", i); scanf("%s", tail); scanf("%s", head); int tailIndex = findVertex(graph, tail); int headIndex = findVertex(graph, head); if (tailIndex == INT_MAX || headIndex == INT_MAX) { printf("输入的顶点不存在,请重新输入:\n"); i--; continue; } graph->edge[tailIndex][headIndex] = 1; graph->edge[headIndex][tailIndex] = 1; } printfGraph(graph); return graph; } void depthSearch(struct Graph* graph, struct SequenceStack* stack, int* visited, int index) { visited[index] = 1; int* num = malloc(sizeof(int)); if (num == NULL) return; *num = index; stack->push(num, stack); printf("%s ", graph->vertex[index]); while (stack->isNotEmpty(stack)) { for (int i = 0; i < (int)graph->vertexNum; i++) { int* top = stack->top(stack); if (!visited[i] && graph->edge[*top][i] > 0) { printf("%s ", graph->vertex[i]); visited[i] = 1; int* index = malloc(sizeof(int)); if (index == NULL) return; *index = i; stack->push(index, stack); i = 0; } } int* top = stack->top(stack); stack->pop(stack); free(top); top = NULL; } } void depthFirstSearch(struct Graph* graph) { printf("深度优先遍历邻接矩阵--无向图:\n"); int* visited = malloc(sizeof(int) * (unsigned int)graph->vertexNum); if (visited == NULL) return; memset(visited, 0, sizeof(int) * (int)graph->vertexNum); struct SequenceStack* stack = initSequenceStack(); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { depthSearch(graph, stack, visited, i); } } free(visited); visited = NULL; free(stack); stack = NULL; } int main() { // struct Graph* graph = createGraph(); // FILE* file = fopen("D:/Graph.data", "wb+"); // if (file == NULL) // { // printf("Open file can not be null!"); // } // fwrite(graph, sizeof(struct Graph), 1, file); // fclose(file); FILE* file = fopen("D:/Graph.data", "rb+"); if (file == NULL) { printf("Open file can not be null!"); return; } struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)); if (graph == NULL) { printf("There not enough memory to be create object of graph!"); return; } fread(graph, sizeof(struct Graph), 1, file); fclose(file); printfGraph(graph); depthFirstSearch(graph); return 0; } |
运用I/O流将建立好的邻接矩阵图结构存储到磁盘上方便重复测试,运行结果:
| A B C D E F G H I A 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 B 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 C 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 D 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 E 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 F 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 G 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 H 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 I 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 深度优先遍历邻接矩阵--无向图: A B F H C D G I E |
6.3.2.广度优先搜索遍历
广度优先搜索(Breadth First Search, BFS)遍历类似于树的按层次遍历。其基本思想是:首先访问出发点vi,接着依次访问vi的所有未被访问过的邻接点vi1, vi2, ···,vit并均标记为已访问过,然后再按照vi1, vi2, ···,vit的次序,访问每一个顶点的所有未曾访问过的顶点并均标记为已访问过,依次类推,直到图中所有和初始出发点vi有路径相通的顶点都被访问过为止。
例如,对于图6.11中的图G8,按图6.12给出的按层遍历搜索的示意图,很容易给出以v0为出发点的广义优先搜索遍历序列: v0,v1,v2,v4,v2,v6,v8,v5,v7。

在广度优先搜索遍历中,先被访问的顶点,其邻接点也先被访问,即符合队列的性质:先进先出。所以在算法的实现中可使用一个队列,用来依次记住被访问过的顶点。算法开始时,将初始点vi访问后入队列,以后每从队列中删除一个元素,就依次访问它的每一个未曾访问过邻接点,并将其入队列。这样,当队列为空时,表明所有与初始点有路径相通的顶点都已访问完毕,算法结束。
同深度优先搜索遍历一样,假设visited[Max VertexNum]为一全局量数组,其初值均为假值(FALSE),用以标记某个顶点是否被访问过。下面分别以邻接矩阵和邻接表作为图的存储结构,给出相应的广度优先搜索遍历的算法。
(1)邻接矩阵为存储结构的广度优先搜索遍历算法,队列分别采用前面的链式队列(第三章3.3.1小节)与)顺序队列(第三章3.3.2小节来实现遍历逻辑。
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "linkQueue.h" #include "sequenceQueue.h" #define FLAG 1 #define MaxVertex 50 struct Graph { char vertex[MaxVertex][8]; int edge[MaxVertex][MaxVertex]; int vertexNum; int edgeNum; }; int findVertex(struct Graph* graph, char* vertex) { for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (strcmp(vertex, graph->vertex[i]) == 0) { return i; } } return INT_MAX; } void printfGraph(struct Graph* graph) { printf("\t"); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { printf("%s\t", graph->vertex[i]); } printf("\n"); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { printf("%s\t", graph->vertex[i]); for (int j = 0; j < graph->vertexNum; j++) { if (graph->edge[i][j] == INT_MAX) { printf("∞\t"); } else { printf("%d\t", graph->edge[i][j]); } } printf("\n"); } } struct Graph* createGraph() { struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)); #if FLAG printf("请输入无向图的顶点数和边数:\n顶点 边。\n"); #else printf("请输入有向图的顶点数和边数:\n顶点 边。\n"); #endif scanf("%d", &graph->vertexNum); scanf("%d", &graph->edgeNum); printf("请输入%d个顶点的值。\n", graph->vertexNum); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { scanf("%s", graph->vertex[i]); } for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < graph->vertexNum; j++) { #if FLAG graph->edge[i][j] = 0; #else graph->edge[i][j] = INT_MAX; #endif } } #if FLAG printf("请输入%d条边:\n顶点1 顶点2\n", graph->edgeNum); #else printf("请输入%d条边:\n弧尾 弧头 权重\n", graph->edgeNum); int weight; #endif char tail[8] = { 0 }, head[8] = { 0 }; for (int i = 1; i <= graph->edgeNum; i++) { printf("请输入第%d条边:\n", i); scanf("%s", tail); scanf("%s", head); #if !FLAG scanf("%d", &weight); #endif int tailIndex = findVertex(graph, tail); int headIndex = findVertex(graph, head); if (tailIndex == INT_MAX || headIndex == INT_MAX) { #if FLAG printf("输入的顶点不存在,请重新输入:\n"); #else printf("输入的狐尾和狐头不存在,请重新输入:\n"); #endif i--; continue; } #if FLAG graph->edge[tailIndex][headIndex] = 1; graph->edge[headIndex][tailIndex] = 1; #else graph->edge[tailIndex][headIndex] = weight; #endif } printfGraph(graph); return graph; } void breadthSearchSequence(struct Graph* graph, struct SequenceQueue* queue, int* visited, int index) { visited[index] = 1; int* num = malloc(sizeof(int)); if (num == NULL) return; *num = index; queue->push(num, queue); printf("%s ", graph->vertex[index]); while (queue->isNotEmpty(queue)) { int* front = queue->front(queue); for (int i = 0; i < (int)graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (!visited[i] && graph->edge[*front][i] > 0) { printf("%s ", graph->vertex[i]); visited[i] = 1; int* index = malloc(sizeof(int)); if (index == NULL) return; *index = i; queue->push(index, queue); } } int* index = queue->pop(queue); free(index); index = NULL; } } void breadthFirstSearchSequence(struct Graph* graph) { #if FLAG printf("广度优先遍历邻接矩阵--无向图:\n"); #else printf("广度优先遍历邻接矩阵--有向图:\n"); #endif int* visited = malloc(sizeof(int) * (int)graph->vertexNum); if (visited == NULL) return; memset(visited, 0, sizeof(int) * (int)graph->vertexNum); struct SequenceQueue* queue = initSequenceQueue(); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { breadthSearchSequence(graph, queue, visited, i); } } free(visited); visited = NULL; free(queue); queue = NULL; } struct Num { void* next; int index; }; void breadthSearchLink(struct Graph* graph, struct LinkQueue* queue, int* visited, int index) { visited[index] = 1; struct Num* num = malloc(sizeof(struct Num)); if (num == NULL) return; num->index = index; queue->push(num, queue); printf("%s ", graph->vertex[index]); while (queue->isNotEmpty(queue)) { struct Num* front = queue->front(queue); for (int i = 0; i < (int)graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (!visited[i] && graph->edge[front->index][i] > 0) { printf("%s ", graph->vertex[i]); visited[i] = 1; struct Num* index = malloc(sizeof(struct Num)); if (index == NULL) return; index->index = i; queue->push(index, queue); } } int* index = queue->pop(queue); free(index); index = NULL; } } void breadthFirstSearchLink(struct Graph* graph) { #if FLAG printf("广度优先遍历邻接矩阵--无向图:\n"); #else printf("广度优先遍历邻接矩阵--有向图:\n"); #endif int* visited = malloc(sizeof(int) * (int)graph->vertexNum); if (visited == NULL) return; memset(visited, 0, sizeof(int) * (int)graph->vertexNum); struct LinkQueue* queue = initLinkQueue(); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { breadthSearchLink(graph, queue, visited, i); } } free(visited); visited = NULL; free(queue); queue = NULL; } int main() { // struct Graph* graph = createGraph(); // FILE* file = fopen("D:/Graph.data", "wb+"); // if (file == NULL) // { // printf("Open file can not be null!"); // } // fwrite(graph, sizeof(struct Graph), 1, file); // fclose(file); FILE* file = fopen("D:/Graph.data", "rb+"); if (file == NULL) { printf("Open file can not be null!"); return; } struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)); if (graph == NULL) { printf("There not enough memory to be create object of graph!"); return; } fread(graph, sizeof(struct Graph), 1, file); fclose(file); printfGraph(graph); breadthFirstSearchSequence(graph); printf("\n"); breadthFirstSearchLink(graph); return 0; } |
(2)以邻接表为存储结构的广度优先搜索遍历算法,队列分别采用前面的链式队列(第三章3.3.1小节)与)顺序队列(第三章3.3.2小节来实现遍历逻辑。
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "linkQueue.h" #include "sequenceQueue.h" #define FLAG 0 #define MaxVertex 50 struct EdgeNode { int adjvex; struct EdgeNode* next; int weight; }; struct EdgeHeader { char data[sizeof(int)]; struct EdgeNode* firstEdge; int nodeSize; }; struct Graph { struct EdgeHeader* vertex[MaxVertex]; int vertexNum; int edgeNum; }; int findVertex(struct Graph* graph, char* vertex) { for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (strcmp(vertex, graph->vertex[i]->data) == 0) { return i; } } return INT_MAX; } void printfGraph(struct Graph* graph) { #if FLAG printf("无向图邻接表:\n"); #else printf("有向图邻接表:\n"); #endif for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { printf("%d %s", i, graph->vertex[i]->data); if (graph->vertex[i]->firstEdge == NULL) { printf("\n"); continue; } struct EdgeNode* currentNode = graph->vertex[i]; do { currentNode = currentNode->next; printf("---->%d", currentNode->adjvex); } while (currentNode->next != NULL); printf("\n"); } } int insertEdge(struct Graph* graph, int tailIndex, int headIndex) { struct EdgeNode* edgeNode = malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeNode)); if (edgeNode == NULL) { return 0; } edgeNode->adjvex = headIndex; edgeNode->next = NULL; if (graph->vertex[tailIndex]->firstEdge == NULL) { graph->vertex[tailIndex]->firstEdge = edgeNode; return 1; } struct EdgeNode* currentNode = graph->vertex[tailIndex]->firstEdge; struct EdgeNode* priorNode = graph->vertex[tailIndex]; // move the pointer while (currentNode->next != NULL && currentNode->adjvex < headIndex) { priorNode = currentNode; currentNode = currentNode->next; } // insert top if (headIndex < currentNode->adjvex) { priorNode->next = edgeNode; edgeNode->next = currentNode; } else if (headIndex > currentNode->adjvex) { // insert tail if (currentNode->next == NULL) { currentNode->next = edgeNode; } else { struct EdgeNode* nextNode = currentNode->next; currentNode->next = edgeNode; edgeNode->next = nextNode; } } else { return 0; } return 1; } struct Graph* createGraph() { struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)); if (graph == NULL) { return; } printf("请输入图的顶点数和边数:\n顶点 边。\n"); scanf("%d", &graph->vertexNum); scanf("%d", &graph->edgeNum); printf("请输入%d个顶点的值。\n", graph->vertexNum); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { struct EdgeHeader* vertex = malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeHeader)); if (vertex == NULL) { return; } graph->vertex[i] = vertex; scanf("%s", graph->vertex[i]->data); graph->vertex[i]->firstEdge = NULL; graph->vertex[i]->nodeSize = 0; } printf("请输入%d条边:\n顶点1 顶点2\n", graph->edgeNum); char tail[8] = { 0 }, head[8] = { 0 }; for (int i = 1; i <= graph->edgeNum; i++) { printf("请输入第%d条边:\n", i); scanf("%s", tail); scanf("%s", head); int tailIndex = findVertex(graph, tail); int headIndex = findVertex(graph, head); if (tailIndex == INT_MAX || headIndex == INT_MAX) { printf("输入的顶点不存在,请重新输入:\n"); i--; continue; } if (insertEdge(graph, tailIndex, headIndex)) { graph->vertex[tailIndex]->nodeSize++; } #if FLAG if (insertEdge(graph, headIndex, tailIndex)) { graph->vertex[headIndex]->nodeSize++; } #endif } printfGraph(graph); return graph; } void writeGraph(struct Graph* graph, char* path) { if (graph == NULL) { printf("邻接表--%s图不存在!\n", !FLAG ? "有向" : "无向"); return; } printf("邻接表--%s图写入磁盘%s!\n", !FLAG ? "有向" : "无向", path); FILE* file = fopen(path, "wb+"); if (file == NULL) { printf("邻接表--%s图,Open file can not be null!\n", !FLAG ? "有向" : "无向"); return; } fwrite(&graph->vertexNum, sizeof(int), 1, file); fwrite(&graph->edgeNum, sizeof(int), 1, file); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { struct EdgeHeader* header = graph->vertex[i]; fwrite(header, sizeof(struct EdgeHeader), 1, file); if (header->firstEdge != NULL) { struct EdgeNode* edgeNode = header->firstEdge; while (edgeNode != NULL) { fwrite(edgeNode, sizeof(struct EdgeNode), 1, file); edgeNode = edgeNode->next; } } } fclose(file); } struct Graph* readGraph(char* path) { if (path == NULL) { printf("邻接表--%s图,Input path can not be null.\n", !FLAG ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } printf("邻接表--%s图读出磁盘%s保存的数据!\n", !FLAG ? "有向" : "无向", path); FILE* file = fopen(path, "rb+"); if (file == NULL) { printf("邻接表--%s图,Open file can not be null!\n", !FLAG ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)); if (graph == NULL) { printf("读取邻接表--%s图,分配内存空间失败!\n", !FLAG ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } fread(&graph->vertexNum, sizeof(int), 1, file); fread(&graph->edgeNum, sizeof(int), 1, file); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { struct EdgeHeader* header = malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeHeader)); if (header == NULL) return NULL; graph->vertex[i] = header; fread(header, sizeof(struct EdgeHeader), 1, file); if (header->nodeSize > 0) { struct EdgeNode* edgeNode = malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeNode)); if (edgeNode == NULL) return NULL; header->firstEdge = edgeNode; fread(edgeNode, sizeof(struct EdgeNode), 1, file); } if (header->nodeSize > 1) { struct EdgeNode* edgeNode = header->firstEdge; for (int i = 1; i < header->nodeSize; i++) { struct EdgeNode* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeNode)); if (newNode == NULL) return NULL; edgeNode->next = newNode; fread(newNode, sizeof(struct EdgeNode), 1, file); edgeNode = newNode; } } } fclose(file); return graph; } void breadthSearchSequence(struct Graph* graph, struct SequenceQueue* queue, int* visited, int index) { visited[index] = 1; int* num = malloc(sizeof(int)); if (num == NULL) return; *num = index; queue->push(num, queue); struct EdgeHeader* edgeHeader = graph->vertex[index]; printf("%s ", edgeHeader->data); while (queue->isNotEmpty(queue)) { int* front = queue->front(queue); struct EdgeHeader* edgeHeader = graph->vertex[*front]; if (edgeHeader->firstEdge == NULL) { queue->pop(queue); free(front); front = NULL; continue; } struct EdgeNode* edgeNode = edgeHeader->firstEdge; while (edgeNode != NULL) { if (!visited[edgeNode->adjvex]) { visited[edgeNode->adjvex] = 1; printf("%s ", graph->vertex[edgeNode->adjvex]->data); int* index = malloc(sizeof(int)); if (index == NULL) return; *index = edgeNode->adjvex; queue->push(index, queue); } edgeNode = edgeNode->next; } queue->pop(queue); free(front); front = NULL; } } void breadthFirstSearchSequence(struct Graph* graph) { #if FLAG printf("广度优先遍历邻接表--无向图:\n"); #else printf("广度优先遍历邻接表--有向图:\n"); #endif int* visited = malloc(sizeof(int) * (int)graph->vertexNum); if (visited == NULL) return; memset(visited, 0, sizeof(int) * (int)graph->vertexNum); struct SequenceQueue* queue = initSequenceQueue(); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { breadthSearchSequence(graph, queue, visited, i); } } free(visited); visited = NULL; free(queue); queue = NULL; } struct Num { void* next; int index; }; void breadthSearchLink(struct Graph* graph, struct LinkQueue* queue, int* visited, int index) { visited[index] = 1; struct Num* num = malloc(sizeof(struct Num)); if (num == NULL) return; num->index = index; queue->push(num, queue); printf("%s ", graph->vertex[index]->data); while (queue->isNotEmpty(queue)) { struct Num* front = queue->front(queue); struct EdgeHeader* edgeHeader = graph->vertex[front->index]; if (edgeHeader->firstEdge == NULL) { queue->pop(queue); free(front); front = NULL; continue; } struct EdgeNode* edgeNode = edgeHeader->firstEdge; while (edgeNode != NULL) { if (!visited[edgeNode->adjvex]) { visited[edgeNode->adjvex] = 1; printf("%s ", graph->vertex[edgeNode->adjvex]->data); struct Num* index = malloc(sizeof(struct Num)); if (index == NULL) return; index->index = edgeNode->adjvex; queue->push(index, queue); } edgeNode = edgeNode->next; } queue->pop(queue); free(front); front = NULL; } } void breadthFirstSearchLink(struct Graph* graph) { #if FLAG printf("广度优先遍历邻接表--无向图:\n"); #else printf("广度优先遍历邻接表--有向图:\n"); #endif int* visited = malloc(sizeof(int) * (int)graph->vertexNum); if (visited == NULL) return; memset(visited, 0, sizeof(int) * (int)graph->vertexNum); struct LinkQueue* queue = initLinkQueue(); for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { breadthSearchLink(graph, queue, visited, i); } } free(visited); visited = NULL; free(queue); queue = NULL; } int main() { //struct Graph* graph = createGraph(); //writeGraph(graph, "D:/LinkGraph.data"); struct Graph* graph = readGraph("D:/LinkGraph.data"); printfGraph(graph); breadthFirstSearchSequence(graph); printf("\n"); breadthFirstSearchLink(graph); return 0; } |
与图的深度优先搜索遍历一样,对于图的广度优先搜索遍历,若采用邻接矩阵表示,其算法时间复杂度为O(n2),若采用邻接表表示,其时间复杂度为O(n+e),两者的空间复杂度均为O(n)。
从图的某个顶点出发进行广度优先搜索遍历时,访问各顶点的次序可能由于邻接表的不同,其遍历序列也不同,这一点也与图的深度优先搜索遍历时的情形一样。
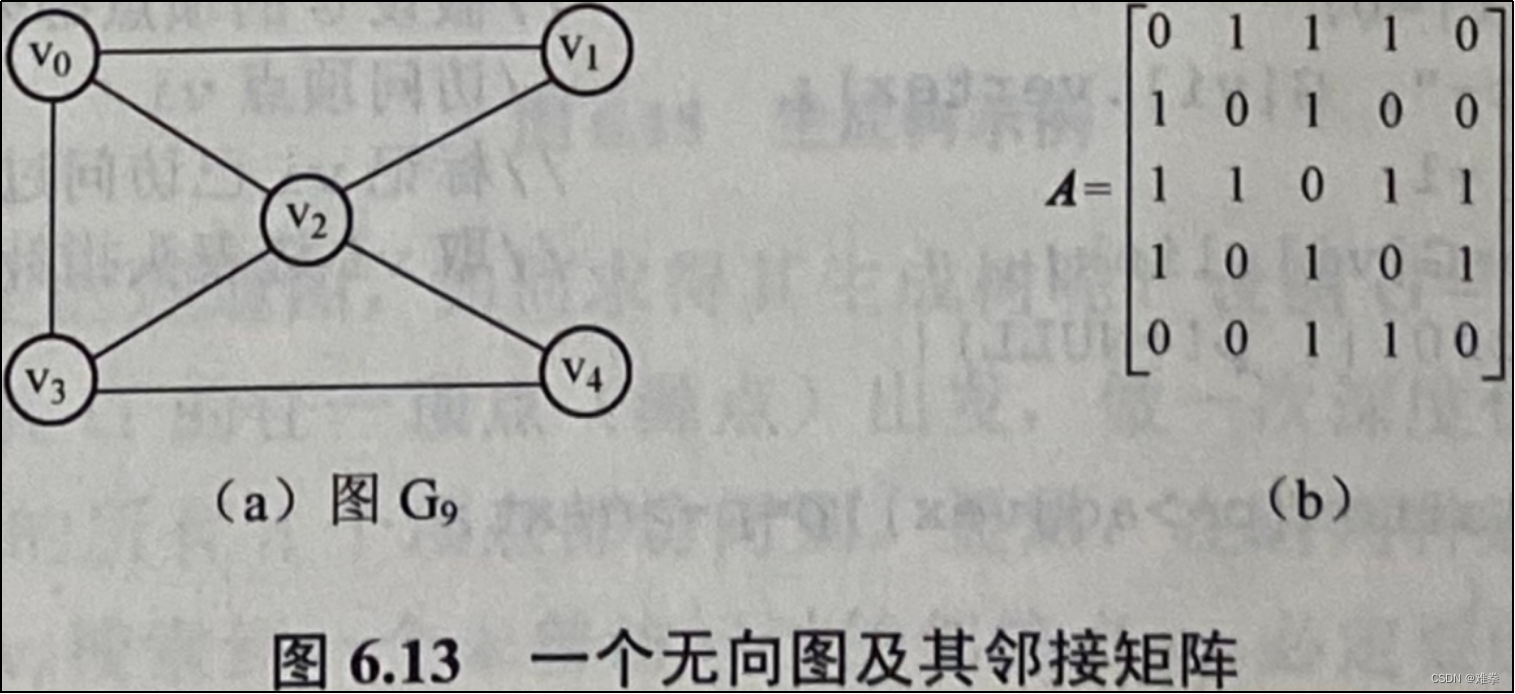
【例6.2】假设有如图6.13所示的无向图G9试写出该图的邻接矩阵和邻接表以及该图在邻接矩阵存储表示下从顶点v3开始搜索所得的深度优先(DFS)和广度优先(BFS)遍历序列。
求解如下:
1.根据邻接矩阵定义,可得如图6.13(b)所示的矩阵。
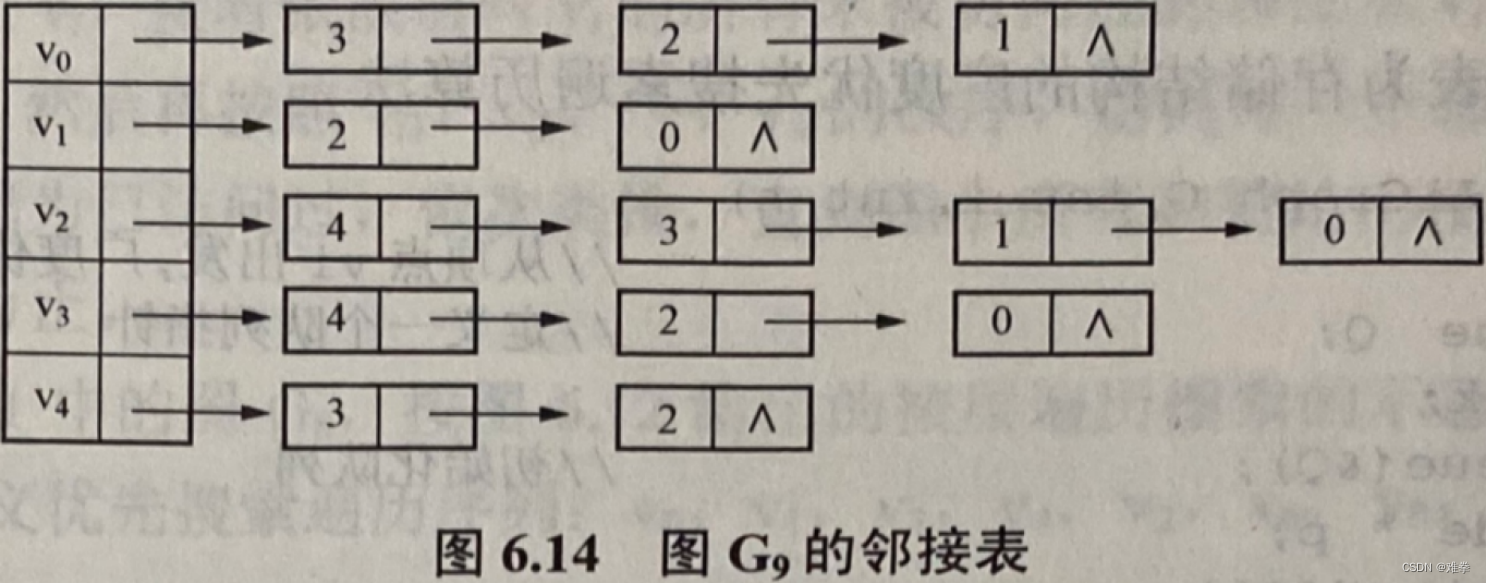
2.根据邻接表的定义建立的邻接表如图6.14所示。
- 图的深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索遍历序列分两种情况讨论。
一种是在邻接矩阵表示的顺序存储结构上,图G9的两种遍历序列如下:
DFS序列为: v3,v0,v1,v2,v4
BFS序列为: v3,v0,v2,v4,v1
另一种是在以邻接表表示的链式存储结构上,如图6.14所示的邻接表,从顶点v3出发的DFS和BFS遍历序列如下:
DFS序列为: v3,v4,v2,v1,v0
BFS序列为: v3,v4,v2,v0,v1
6.4.图的生成树和最小生成树
6.4.1.图的生成树
图G1是图G的连通子图,从子图G1中删除任何一条边,子图G1不再连通,则称子图G1为图G的极小连通子图。
在图论中,常常将树定义为一个无回路的连通图。一个连通图G的一个子图如果是一棵包含G的所有顶点的树,则该子图称为G的生成树。生成树是连通的包含图中所有顶点的一个极小连通子图(边最少)。即生成树为包含无向图G所有顶点的极小连通子图。一个图的极小连通子图恰为一个无回路的连通图。也就是说,若在图中任意添加一条边,就会出现回路;若在图中去掉任何一条边,都会使之成为非连通图。
对非连通图,由各个连通分量的生成树组成的集合称为生成森林。
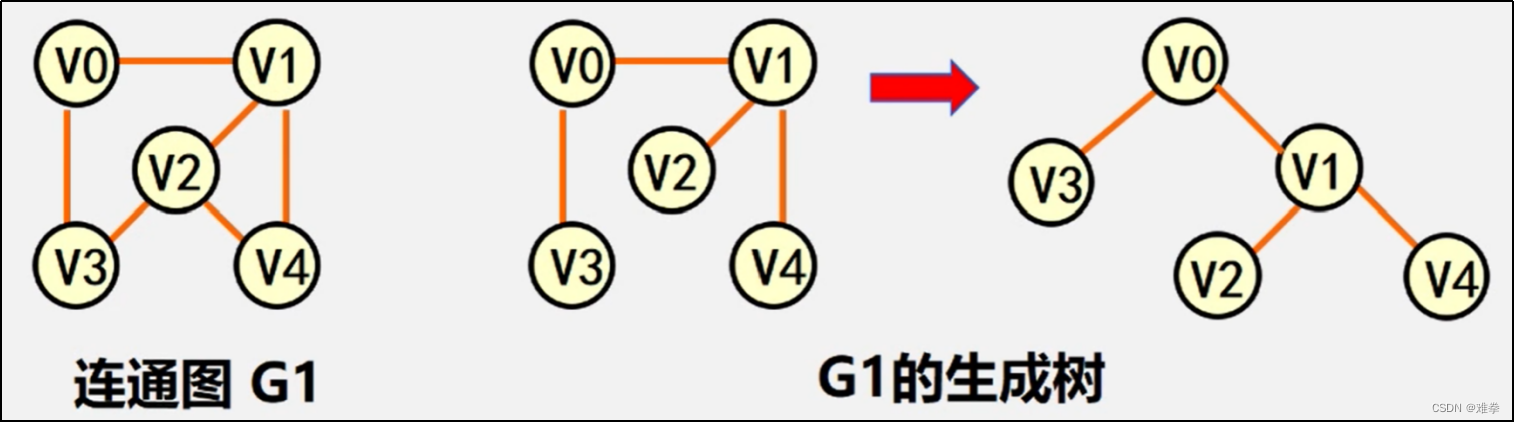
因此,一棵具有n个顶点的生成树有仅有n-1条边,但有n-1条边的图不一定是生成树。同一个图可以有不同的生成树,例如对于图6.15 (a)而言,图6.15 (b)、图6.15 (c)所示都是它的生成树。
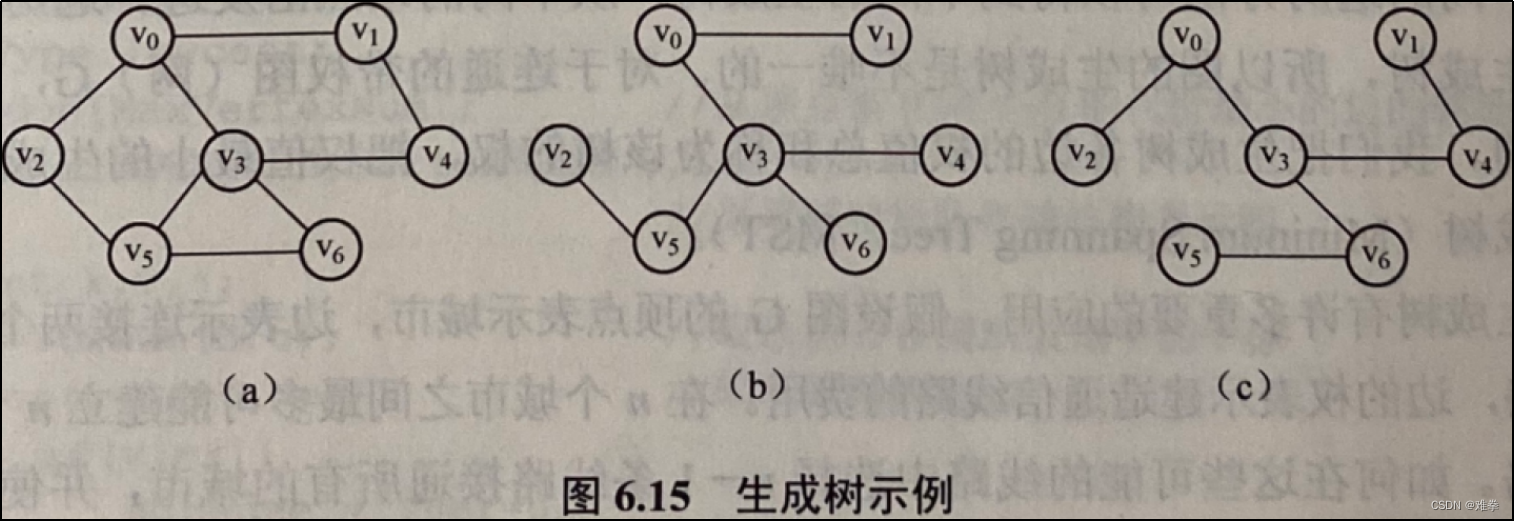
| 生成树:所有顶点均由边连接在一起,但不存在回路的图。
·生成树的顶点个数与图的顶点个数相同; ·生成树是图的极小连通子图,去掉一条边则非连通; ·一个有n个顶点的连通图的生成树有n-1条边; ·在生成树中再加一条边必然形成回路。
|
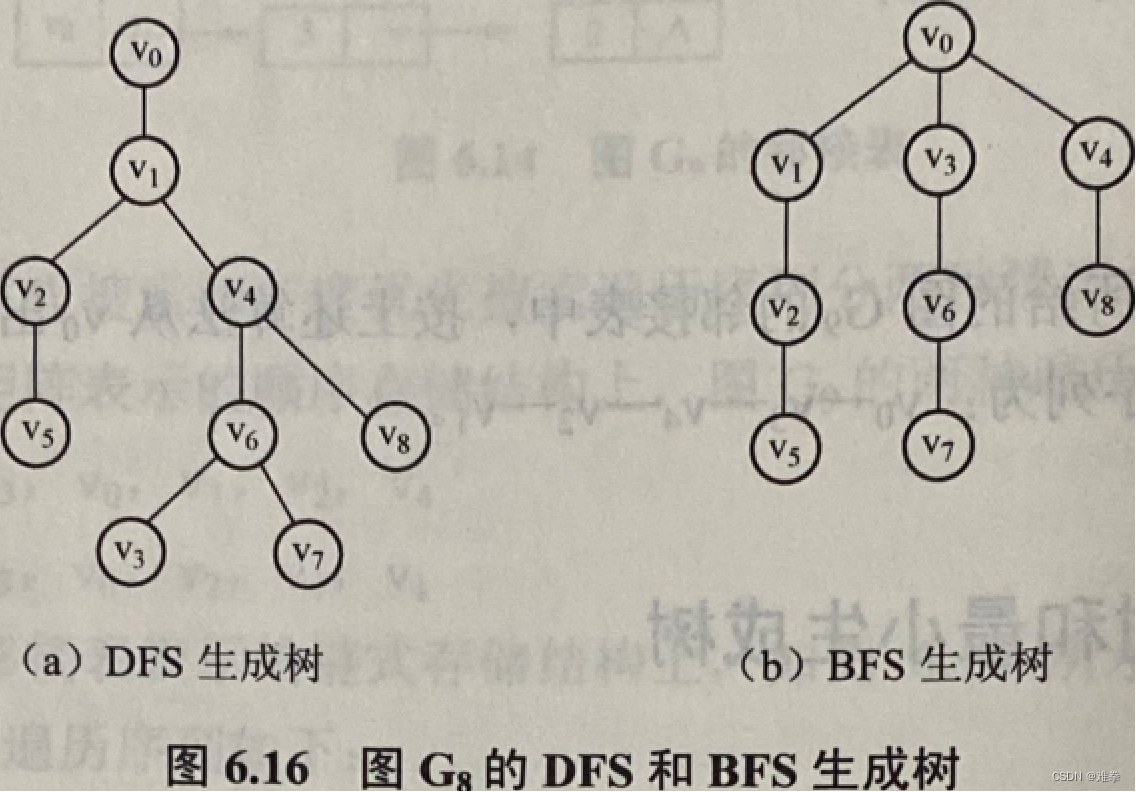
那么,对于给定的连通图,如何求得其生成树呢?设图G=(V, E)是一个具有n个顶点的连通图,从G的任一顶点(源点)出发,做一次深度优先搜索或广度优先搜索,就可以将G中的所有n个顶点都访问到。显然,在这两种遍历搜索方法中,从一个已访问过的顶点vi搜索到一个未曾访问过的邻接点vj必定要经过G中的一条边(vi,vj),而这两种搜索方法对图中的n个顶点都仅访问一次,因此除初始出发点外,对其余n-1个顶点的访问一共要经过G中的n-1条边,这n-1条边将G中n个顶点连接成包含G中所有顶点的极小连通子图。可见它是G的一棵生成树,其源点就是生成树的根。通常,我们把由深度优先搜索所得的生成树称之为深度优先生成树,简称为DFS生成树;而由广度优先搜索所得的生成树称之为广度优先生成树,简称为BFS生成树。例如,从图G8的顶点Vo出发,所得的DFS生成树和BFS生成树如图6.16所示。
从连通图的观点出发,针对无向图而言,生成树又可定义为:若从图的某顶点出发,可以系统地访问到图的所有顶点,则遍历时经过的边和图的所有顶点所构成的子图,称为该图的生成树。此定义对有向图同样适用。
显然,若G是强连通图,则从其中任一顶点v出发,都可以访问遍历G中的所有顶点,从而得到以v为根的生成树。若图G是有根的有向图,设根为v,则从根v出发也可以完成对G的遍历,因而也能得到以v为根的生成树。
无向图生成树算法实现--设图G=(V,E)是个连通图,当从图任意一点出发遍历图G时,将边集E(G)分成两个集合T(G)和B(G)。其中T(G)是遍历图时所经过的边的集合,B(G)遍历图时未经过的边的集合。显然,G1(V,T)是图G的极小连通子图。即子图G1是连通图G的生成树。

6.4.2.最小生成树
采用不同的遍历方法可以得到不同的生成树,从不同的顶点出发进行遍历也可以得到不同的生成树,所以图的生成树是不唯一的。对于连通的带权图(网) G,其生成树也是带权的。我们把生成树各边的权值总和称为该树的权,把权值最小的生成树称为图的最小生成树(Mininum Spanning Tree, MST)也叫做最小代价生成树。
最小生成树有许多重要的应用。假设图G的顶点表示城市,边表示连接两个城市之间的通信线路,边的权表示建造通信线路的费用。在n个城市之间最多可能建立n (n-1) 12条通信线路。如何在这些可能的线路中选择n-1条线路接通所有的城市,并使通信网的总建造费用达到最小?这个问题就是构造最小生成树的问题。
最小生成树有一个非常重要的性质,简称为MST性质:假设N= (V, {E})是一个连通网, U是顶点集V的一个非空子集,若(u, v)是一条具有最小权值的边,其中u∈U, v∈V-U,则必存在一棵包含边(u, v)的最小生成树。
| MST性质解释: 在生成树的构造过程中,图中n个顶点分属两个集合: ·已落在生成树上的顶点集:U ·尚未落在生成树上的顶点集:V-U 接下来则应在所有连通U中顶点和V-U中顶点的边中选取权值最小的边。 |
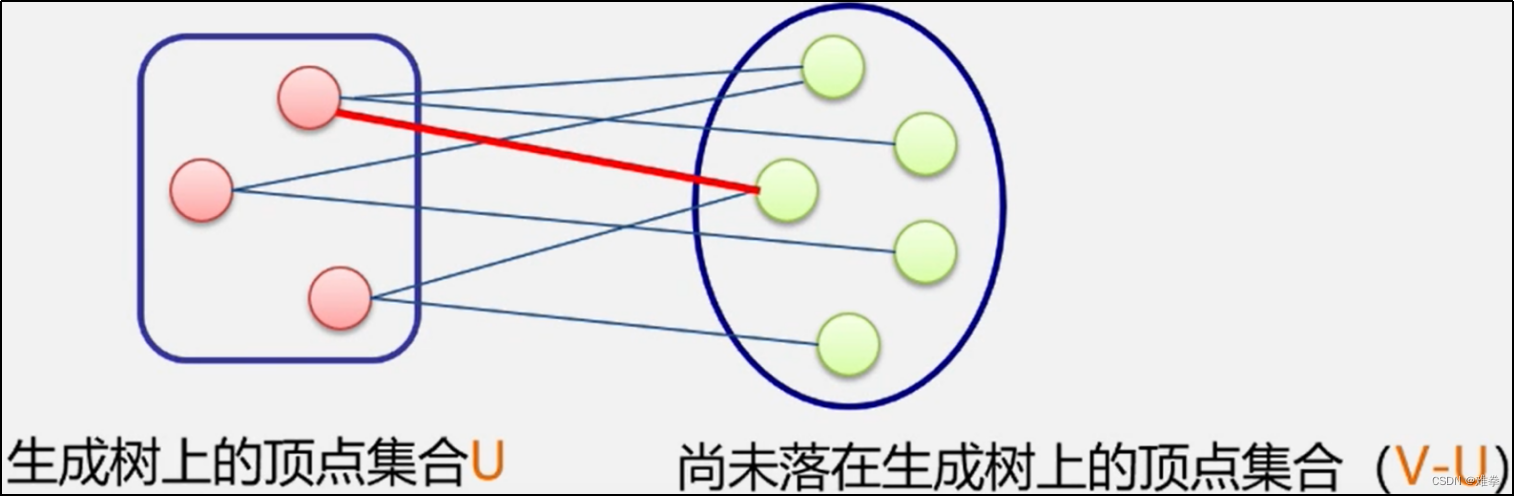
MST性质证明:用反证法,假设连通网N的任何一棵最小生成树都不包含边(u, v)。设T是连通网上的一棵最小生成树,当把边(u, v)加入到T中时,由生成树的定义知,T中必存在一条包含(u, v)的回路。而另一方面,由于T是生成树,则在T上必存在另一条边(u', v'),其中u'∈U, v'∈V-U,且u和u'之间、v和 v'之间均有路径相通。删去边(u', v'),便可消除上述回路,同时得到另一棵包含边(u, v)生成树T'。因为(u, v)的代价不大于(u', v')的代价,所以T'的代价也不大于T的代价。这与假设矛盾,因此命题成立。
以下仅讨论无向图的最小生成树。构造最小生成树可有多种算法,其中多数算法利用了MST性质。常用的算法只有两种,即普里姆算法和克鲁斯卡尔算法。
1..普例姆(Prim)算法
假设G= (V, G),是一个具有n个顶点的连通网, T= (U, TE)是G的最小生成树,其中U是T的顶点集, TE是T的边集, U和TE的初值均为空。算法开始时,首先从V中任取一个顶点(假定取v1),将它并入U中,此时U={ v1}。然后只要U是V的真子集(即U⊂V),就从那些一个端点已在T中,另一个端点仍在T外的所有边中,找一条最短(即权值最小)边,假定为(vi, vj),其中vi∈U, vj∈V-U,并把该边(vi, vj)和顶点vj分别并入T的边集TE和顶点集U,如此进行下去,每次往生成树里并入一个顶点和一条边,直到n-1次后把所有n个顶点都并入到生成树T的顶点集中,此时U=V, TE中包含有n-1条边, T就是最后得到的最小生成树。
普例姆算法的实现借助一个辅助数组,辅助数组单个元素结构如下:
| struct MinWeight { int adjvex; int weight; }; |
数组MinWeight[]的下标对应为邻接矩阵中顶点元素在邻接矩阵数组中的下标,adjvex记录邻接矩阵中邻接点在邻接矩阵数组中的下标,weight记录当前顶点与邻接点边的权值。
普例姆算法的实现一:
普例姆算法另外还需要一个动态数组存储已经访问过的顶点,即上文中提到的生成树U中顶点的集合。实现思路如下(完整代码在6.2.1小节封装):
1.初始化数组MinWeight[],创建一个新的空邻接矩阵用来存放最小生成树;
2.随机放入一个顶点到动态数组中,这里默认将第一个顶点放入动态数组中;
3.遍历动态数组中的顶点元素,比较顶点元素与图中未被访问的顶点形成的边的权值,取最小的那个权值的边,存入数组MinWeight[]中;
4.从数组MinWeight[]中取出权值最小的那个元素,将顶点、邻接点与权值数据存入新的空邻接矩阵中,初始化数组MinWeight[]。
5.将新访问到的顶点存入动态数组中,重复3-5步骤,重复次数为邻接矩阵顶点数n-1。
| struct MinWeight { int adjvex; int weight; }; struct AMGraph* pinmAMGraph(struct AMGraph* aMGraph) { if (aMGraph == NULL || aMGraph->graph == NULL) { printf("邻接矩阵--图,不存在!\n"); return NULL; } struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph = aMGraph->graph; struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* initEmptyAMGraph(int isdigraph, int size); struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* minTree = initEmptyAMGraph(aMGraph->isdigraph, aMGraph->graph->vertexNum); minTree->vertex = graph->vertex; minTree->vertexNum = graph->vertexNum; minTree->edgeNum = graph->edgeNum; void pinmMinTree(struct AMGraph* aMGraph, struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* minTree); pinmMinTree(aMGraph, minTree); struct AMGraph* minGraph = malloc(sizeof(struct AMGraph)); if (minGraph == NULL) { printf("邻接矩阵--%s图生成最小生成树内存不足!\n", aMGraph->isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } minGraph->isdigraph = aMGraph->isdigraph; minGraph->graph = minTree; return initAMGraphTail(minGraph); } struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* initEmptyAMGraph(int isdigraph, int size) { struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct AdjacentMatrixGraph)); if (graph == NULL) { printf("开辟%s图空间失败,内存空间不足!\n", isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } graph->vertex = NULL; graph->vertexNum = 0; graph->edge = NULL; graph->edgeNum = 0; int** edge = malloc(sizeof(int*) * size); if (edge == NULL) { printf("开辟%s图顶点空间失败,内存空间不足!\n", isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } graph->edge = edge; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { int* rowEdge = malloc(sizeof(int) * size); if (rowEdge == NULL) { printf("开辟%s图边空间失败,内存空间不足!\n", isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } graph->edge[i] = rowEdge; for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { if (isdigraph) { graph->edge[i][j] = INT_MAX; } else { graph->edge[i][j] = 0; } } } return graph; } void pinmMinTree(struct AMGraph* aMGraph, struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* minTree) { struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph = aMGraph->graph; int size = graph->vertexNum; struct MinWeight* cacheArray = malloc(sizeof(struct MinWeight) * size); if (cacheArray == NULL) { printf("邻接矩阵--%s图记录最小生成树内存不足!\n", aMGraph->isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return; } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { cacheArray[i].adjvex = -1; cacheArray[i].weight = -1; } struct ArrayList* vertexArray = initArrayList(size); int in = 0; vertexArray->insert(0, &in, vertexArray); int** edge = graph->edge; for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) { int lenght = vertexArray->size(vertexArray); for (int j = 0; j < lenght; j++) { int minWeight = INT_MAX, * vertex = vertexArray->get(j, vertexArray), adjvex = -1; for (int k = 0; k < size; k++) { int compareVertex(void* firstData, void* secondData); if (edge[*vertex][k] > 0 && edge[*vertex][k] < minWeight && vertexArray->getData(&k, compareVertex, vertexArray) == NULL) { minWeight = edge[*vertex][k]; adjvex = k; } } cacheArray[*vertex].adjvex = adjvex; cacheArray[*vertex].weight = minWeight; } int* adjvex = malloc(sizeof(int)); if (adjvex == NULL) { printf("邻接矩阵--%s图记录最小生成树内存不足!\n", aMGraph->isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return; } *adjvex = -1; int minWeight = INT_MAX, vertex = -1; for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { if (cacheArray[j].weight < minWeight && cacheArray[j].weight != -1) { vertex = j; *adjvex = cacheArray[j].adjvex; minWeight = cacheArray[j].weight; } cacheArray[j].adjvex = -1; cacheArray[j].weight = -1; } minTree->edge[*adjvex][vertex] = minWeight; minTree->edge[vertex][*adjvex] = minWeight; vertexArray->insert(0, adjvex, vertexArray); } } int compareVertex(void* firstData, void* secondData) { int* first = firstData; int* second = secondData; if (*first == *second) { return 1; } return 0; } |
普例姆算法的实现二:
辅助数组数组MinWeight[],记录从U到V-U具有最小代价的边(轻边)。对每个顶点v∈V-U,在辅助数组中存在一个分量MinWeight[v],它包括两个域,其中weight存储该边上的权值, vertex域存储该边的依附在U中的顶点。
算法实现步骤:
1.创建一个新的空邻接矩阵用来存放最小生成树;
2.创建数组MinWeight[],初始化数组MinWeight[],从第一个顶点的索引vertexIndex开始,所有与索引vertexIndex连接的边,根据邻接点的索引值在数组MinWeight[]记录边的权值。、
3.找出数组MinWeight[]中最小权值的边,存入新建的空邻接矩阵中,从该边的邻接点开始,重新查找以该邻接点为顶点的边的权值,比较数组MinWeight[]中对应邻接点的权值,若比数组MinWeight[]中的权值小,则将新的边更新记录到数组MinWeight[]中。重复执行第3步骤,直至遍历完所有的的顶点(一般遍历顶点数n-1次)。
根据分析,可得求最小生成树的普里姆算法的具体描述如下:
| struct AMGraph* pinmAMGraph(struct AMGraph* aMGraph) { if (aMGraph == NULL || aMGraph->graph == NULL) { printf("邻接矩阵--图,不存在!\n"); return NULL; } struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph = aMGraph->graph; struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* initEmptyAMGraph(int isdigraph, int size); struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* minTree = initEmptyAMGraph(aMGraph->isdigraph, aMGraph->graph->vertexNum); minTree->vertex = graph->vertex; minTree->vertexNum = graph->vertexNum; minTree->edgeNum = graph->edgeNum; void pinmCreateMinTree(struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph, struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* minTree, int vertexIndex); pinmCreateMinTree(graph, minTree, 0); struct AMGraph* minGraph = malloc(sizeof(struct AMGraph)); if (minGraph == NULL) { printf("邻接矩阵--%s图生成最小生成树内存不足!\n", aMGraph->isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } minGraph->isdigraph = aMGraph->isdigraph; minGraph->graph = minTree; return initAMGraphTail(minGraph); } struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* initEmptyAMGraph(int isdigraph, int size) { struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct AdjacentMatrixGraph)); if (graph == NULL) { printf("开辟%s图空间失败,内存空间不足!\n", isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } graph->vertex = NULL; graph->vertexNum = 0; graph->edge = NULL; graph->edgeNum = 0; int** edge = malloc(sizeof(int*) * size); if (edge == NULL) { printf("开辟%s图顶点空间失败,内存空间不足!\n", isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } graph->edge = edge; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { int* rowEdge = malloc(sizeof(int) * size); if (rowEdge == NULL) { printf("开辟%s图边空间失败,内存空间不足!\n", isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } graph->edge[i] = rowEdge; for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { if (isdigraph) { graph->edge[i][j] = INT_MAX; } else { graph->edge[i][j] = 0; } } } return graph; } struct MinWeight { int adjvex; int weight; }; void pinmCreateMinTree(struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph, struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* minTree, int vertexIndex) { int size = graph->vertexNum; struct MinWeight* minWeightArray = malloc(sizeof(struct MinWeight) * size); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (i != vertexIndex) { minWeightArray[i].adjvex = vertexIndex; if (graph->edge[i][vertexIndex] == 0) { minWeightArray[i].weight =INT_MAX; } else { minWeightArray[i].weight = graph->edge[i][vertexIndex]; } } } minWeightArray[vertexIndex].weight = 0; int findMinWeight(struct MinWeight* minWeightArray, int size); for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) { vertexIndex = findMinWeight(minWeightArray, size); minTree->edge[vertexIndex][minWeightArray[vertexIndex].adjvex] = minWeightArray[vertexIndex].weight; minTree->edge[minWeightArray[vertexIndex].adjvex][vertexIndex] = minWeightArray[vertexIndex].weight; minWeightArray[vertexIndex].weight = 0; for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { if (graph->edge[vertexIndex][j] < minWeightArray[j].weight && graph->edge[vertexIndex][j] > 0) { minWeightArray[j].adjvex = vertexIndex; minWeightArray[j].weight = graph->edge[j][vertexIndex]; } } } } int findMinWeight(struct MinWeight* minWeightArray, int size) { int minWeight = INT_MAX, index = -1; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (minWeightArray[i].weight < minWeight && minWeightArray[i].weight > 0) { minWeight = minWeightArray[i].weight; index = i; } } return index; } |
分析上述算法可知,对于具有n个顶点的无向网络,第一个进行初始化的循环语句的频度为n,第二个循环语句的频度为n-1,其中有两个内循环,其频度分别为n-1和n,因此,普里姆算法的时间复杂度是O(n2),与网中边数无关。
【6.3】利用普里姆算法,给出求图6.17(a)所示的无向网络的最小生成树的过程。
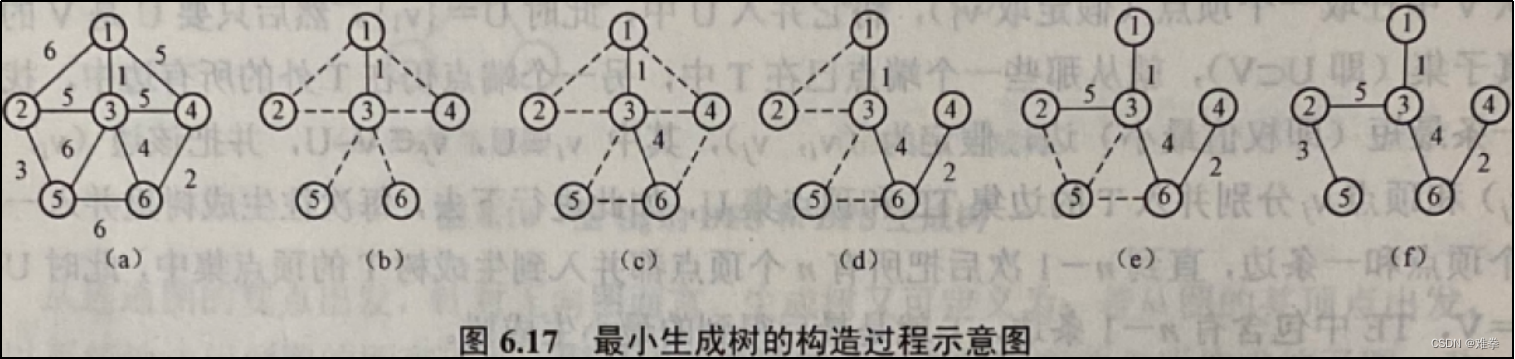
运用6.2.1小节封装的代码输入图6.17(a)所示的无向网络,生成最小生成树:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "AMGraph.h" int main() { //struct AMGraph* graph = initAMGraph(1, NULL); //struct AMGraph* graph = initAMGraph(0, "D:/Graph.temp"); struct AMGraph* graph = readAMGraphByDisk(0, "D:/Graph.temp"); graph->print(graph); graph = graph->pinm(graph); graph->print(graph); graph->breadthFirstSearch(graph); printf("\n"); graph->depthFirstSearch(graph); return 0; } |
运行结果:
| 邻接矩阵--无向图读出磁盘D:/Graph.temp保存的数据! 邻接矩阵--无向图结构: 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 0 6 1 5 0 0 2 6 0 5 0 3 0 3 1 5 0 5 6 4 4 5 0 5 0 0 2 5 0 3 6 0 0 6 6 0 0 4 2 6 0 邻接矩阵--无向图结构: 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 0 5 0 3 0 3 1 5 0 0 0 4 4 0 0 0 0 0 2 5 0 3 0 0 0 0 6 0 0 4 2 0 0 广度优先遍历邻接矩阵--无向图: 1 3 2 6 5 4 深度优先遍历邻接矩阵--无向图! 1 3 2 5 6 4 |
可以看到生成的最小生成树结构与图6.17(f)一致。
根据普利姆算法实现二分析:算法一开始取U={1},然后到V-U中找一条代价最小且依附于顶点1的边,(u0, v0) = (1, 3),将v0=3加入集合U中,修改辅助数组中的值。使MinWeight[3].weight=0,以表示顶点3已并入U,由于边(3, 6)上的权值是一条最小且依附于顶点集中顶点的边,因此修改MinWeight[6]的值,依此类推,直到U-V,其过程如表6.1所示。为了绘图的方便,顶点的序号仍从1开始顺序编排。
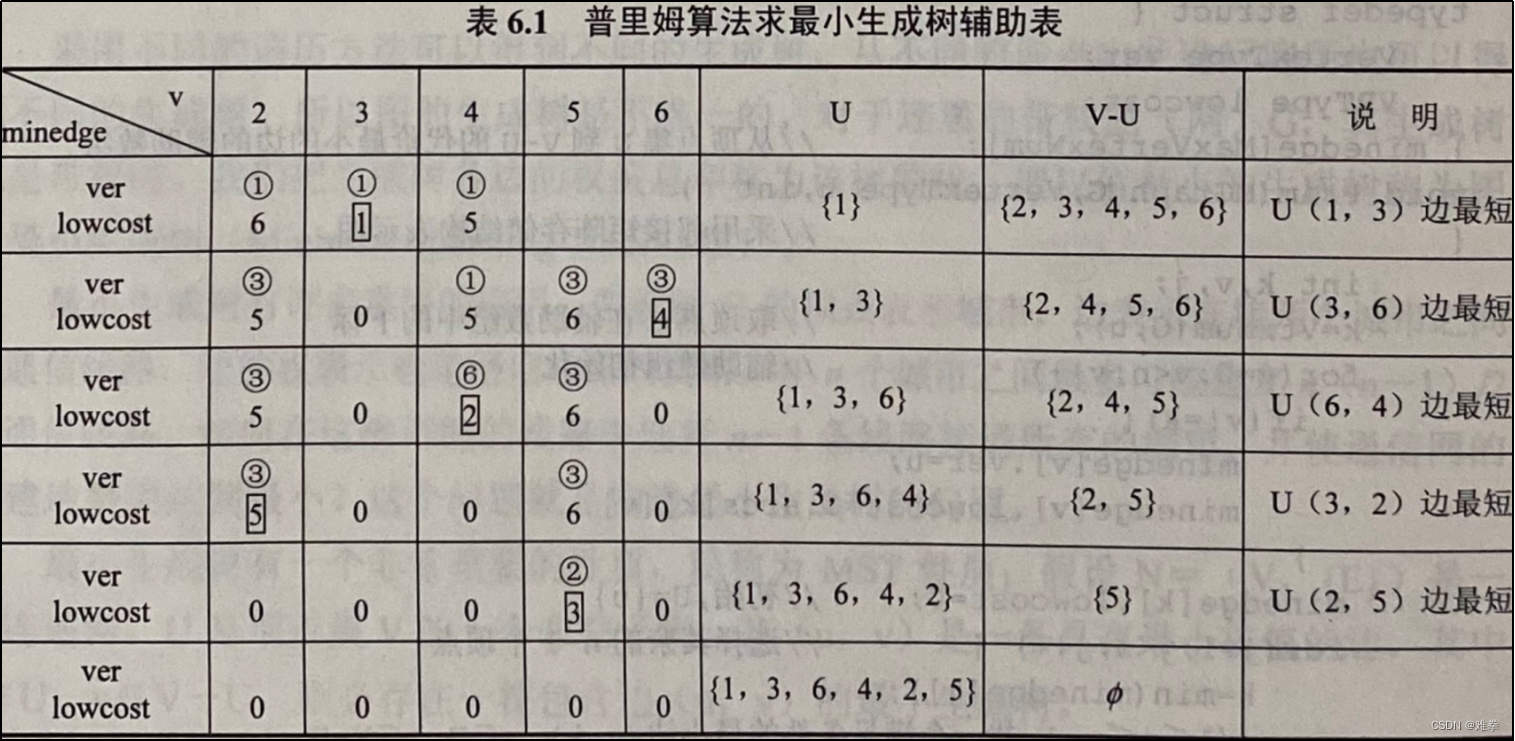
不难看出,普里姆算法构造一棵最小生成树的过程是从一个顶点U={u0}作初始状态,不断增大与U中顶点相邻且最小代价的边的另一个顶点,不断扩大U集合直至U=V。
在表6.1中用方框括起来的数字表示当前行中边权值最小的数据,因而选取由它上方的圆圈框起来的顶点与其列中最上方的邻接顶点所构成的边,此边也就是所谓的轻边。由此表不难画出图的最小生成树,如图6.17,所示。
2.克鲁斯卡尔(Kruskal)算法
假设G= (V, E)是一个具有n个顶点的连通网, T= (U, TE)是G的最小生成树, U的初值等于V,即包含有G中的全部顶点。T的初始状态是只含有n个顶点而无边的森林T= (V, Φ)。
该算法的基本思想是:将图G中的边按权值从小到大的顺序依次选取E中的边(u,v),若选取的边使生成树T不形成回路,则把它并入TE中,保留作为T的一条边;若选取的边使生成树T形成回路,则将其舍弃,如此进行下去直到TE中包含n-1条边为止,此时的T即为最小生成树。 例如,按克鲁斯卡尔算法构造图6.17 (a)所示的最小生成树的过程如图6.18所示。,在图6.18中,按权值递增顺序依次考虑边(1, 3), (4, 6), (2, 5), (3, 6), (1, 4),(2, 3), (3, 4), (1, 2), (5, 6)和(3, 5),因为前四条边上的权值最小,而且又满足不在同一个连通分量上(不形成回路)的条件,所以依次将它们加入到T中。接着要考虑当前权值最小的边(1, 4),因该边的两个端点在同一个连通分量上(即形成回路),故舍去这条边。然后再选择边(2, 3)加入到T中,便得到要求的一棵最小生成树。
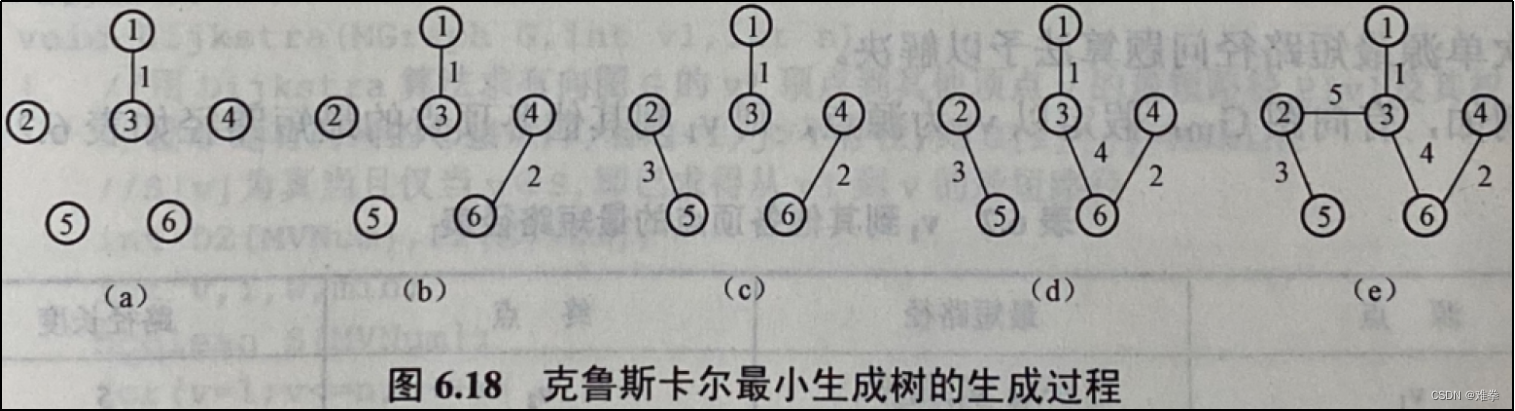
下面给出克鲁斯卡尔算法的抽象描述:
| Kruskal(G) { //求连通网G的一颗MST T=(V,Φ) //初始化T为只含有n个顶点而无边的森林,按权值升序对边集E中的边进行排序,结果存入E[0...e-1]中 for (i=0; i<e; i++) { //e为图G中边总数 取第i条边(u,v); if(u和v分别属于两棵不同的树) then T=T∪{(u,v)}; if(T已经是一棵树) then return T; } //end of for return T; } |
上述克鲁斯卡尔算法的初始化时间为O(n);对边的排序需要时间O(eloge);在for循环中,至多对e条边各扫描一次,而每次选择最小代价的边仅需要O(loge)的时间,这是可以证明的。因此,整个for循环需要的执行时间为O(eloge),从而克鲁斯卡尔算法的时间复杂度为O(eloge)。
克鲁斯卡尔算法实现思路:
1.新建一个空的邻接矩阵存储最小生成树;
2.遍历无向图中所有的边,按照权值大小排好序,存入一个数组中;
3.取出排好序的数组中最小权值的那条边先放入新建的空的邻接矩阵中;
3.遍历排好序的数组,依次取出当前数组中最小权值的边,如果边两端的顶点在新邻接矩阵中找不到回路,就将当前的边取出来放入新邻接矩阵中,如果在新邻接矩阵中能找到回路,则丢弃这条边,直至遍历完排好序的数组为止。
| struct AMGraph* kruskalAMGraph(struct AMGraph* aMGraph) { if (aMGraph == NULL || aMGraph->graph == NULL) { printf("邻接矩阵--图,不存在!\n"); return NULL; } struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph = aMGraph->graph; struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* initEmptyAMGraph(int isdigraph, int size); struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* minTree = initEmptyAMGraph(aMGraph->isdigraph, aMGraph->graph->vertexNum); minTree->vertex = graph->vertex; minTree->vertexNum = graph->vertexNum; minTree->edgeNum = graph->edgeNum; void kruskalMinTree(struct AMGraph* aMGraph, struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* minTree); kruskalMinTree(aMGraph, minTree); struct AMGraph* minGraph = malloc(sizeof(struct AMGraph)); if (minGraph == NULL) { printf("邻接矩阵--%s图生成最小生成树内存不足!\n", aMGraph->isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } minGraph->isdigraph = aMGraph->isdigraph; minGraph->graph = minTree; return initAMGraphTail(minGraph); } struct ASCWeight { int vertex; int adjvex; int weight; }; void kruskalMinTree(struct AMGraph* aMGraph, struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* minTree) { struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph = aMGraph->graph; int size = graph->edgeNum; struct ASCWeight* getSortASCWeight(struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph, int isdigraph); struct ASCWeight* weightArray = getSortASCWeight(graph, aMGraph->isdigraph); minTree->edge[weightArray[0].vertex][weightArray[0].adjvex] = weightArray[0].weight; int isLoop(struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* minTree, int vertex, int adjvex); for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) { if (!isLoop(minTree, weightArray[i].vertex, weightArray[i].adjvex)) { minTree->edge[weightArray[i].vertex][weightArray[i].adjvex] = weightArray[i].weight; minTree->edge[weightArray[i].adjvex][weightArray[i].vertex] = weightArray[i].weight; } } free(weightArray); weightArray = NULL; } struct ASCWeight* getSortASCWeight(struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph, int isdigraph) { int edgeSize = graph->edgeNum, size = graph->vertexNum; struct ASCWeight* weightArray = malloc(sizeof(struct ASCWeight) * edgeSize); if (weightArray == NULL) { printf("邻接矩阵--%s图生成最小生成树构建辅助数组内存不足!\n", isdigraph ? "有向" : "无向"); return NULL; } int** edge = graph->edge, index = 0; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { for (int j = i; j < size; j++) { if (edge[i][j] > 0 && edge[i][j] < INT_MAX) { weightArray[index].vertex = i; weightArray[index].adjvex = j; weightArray[index].weight = edge[i][j]; index++; } } } void sortWeightArray(struct ASCWeight* weightArray, int size); sortWeightArray(weightArray, index); return weightArray; } void sortWeightArray(struct ASCWeight* weightArray, int size) { int flag = 0; struct ASCWeight* temp = malloc(sizeof(struct ASCWeight)); if (temp == NULL) { printf("生成最小生成数,排序临时分配空间失败,内存不足!"); return; } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < size - 2 - i; j++) { if (weightArray[j].weight > weightArray[j + 1].weight) { flag = 0; temp->vertex = weightArray[j].vertex; temp->adjvex = weightArray[j].adjvex; temp->weight = weightArray[j].weight; weightArray[j].vertex = weightArray[j + 1].vertex; weightArray[j].adjvex = weightArray[j + 1].adjvex; weightArray[j].weight = weightArray[j + 1].weight; weightArray[j + 1].vertex = temp->vertex; weightArray[j + 1].adjvex = temp->adjvex; weightArray[j + 1].weight = temp->weight; } else { flag++; } } if (flag == (size - 2 - i)) { break; } flag = 0; } free(temp); temp = NULL; } // -1:成功; -2:回参表示回路/入参表示空值; -3:异常; >=0:顶点索引 int recursionAMGraph(int* visited, int index, struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph, int (*execute)(struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph, int index), int adjvex) { if (adjvex == -2) { if (!execute(graph, index)) return index; } else if (adjvex == index) { return -2; } // printf("%s ", graph->vertex[index]); visited[index] = 1; for (int i = 0; i < (int)graph->vertexNum; i++) { if (!visited[i] && graph->edge[index][i] > 0 && graph->edge[index][i] != INT_MAX) { int result = recursionAMGraph(visited, i, graph, execute, adjvex); if (result != -1) { return result; } } } return -1; } int isLoop(struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* minTree, int vertex, int adjvex) { int size = minTree->vertexNum; int* visited = malloc(sizeof(int) * size); if (visited == NULL) return 1; memset(visited, 0, sizeof(int) * size); int verifyLoop(struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph, int index); int isAdjvex = recursionAMGraph(visited, vertex, minTree, verifyLoop, adjvex); if (isAdjvex == -2) { return 1; } return 0; } int verifyLoop(struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph, int index) { return 1; } |
上述算法为核心算法,完整算法见6.2.1小节封装的完整代码。
测试结果:
| 邻接矩阵--无向图读出磁盘D:/Graph.temp保存的数据! 邻接矩阵--无向图结构: 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 0 6 1 5 0 0 2 6 0 5 0 3 0 3 1 5 0 5 6 4 4 5 0 5 0 0 2 5 0 3 6 0 0 6 6 0 0 4 2 6 0 邻接矩阵--无向图结构: 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 0 5 0 3 0 3 1 5 0 0 0 4 4 0 0 0 0 0 2 5 0 3 0 0 0 0 6 0 0 4 2 0 0 广度优先遍历邻接矩阵--无向图: 1 3 2 6 5 4 深度优先遍历邻接矩阵--无向图! 1 3 2 5 6 4 |
算法执行结果与图6.18一致无误。
由于一个网(带权图)中会有权值相同的边,所以从不同的顶点出发,可以得到不同的最小生成树。
3.两种算法比较
| 算法 |
普里姆算法 |
克鲁斯卡尔算法 |
| 思想 |
选择点 |
选择边 |
| 时间复杂度 |
O(n2)(n为顶点数) |
O(eloge)(e为边数) |
| 适应范围 |
稠密图 |
稀疏图 |
6.5.最短路径
在交通网络中,常常会提出许多这样的问题:两地之间是否有路相通,在有多条通路的情况下,哪一条最近,哪一条花费最少,等等。交通网络可以用带权图表示,图中顶点表示城镇,边表示两城镇之间的道路,边上的权值可表示两城镇间的距离、交通费用或途中所需的时间等。上述这些问题就是在带权图中求最短路径的问题。此时的路径长度的度量不再是路径上边的数目,而是路径上边的权值之和。本节将讨论的是带权有向图(又称有向网),并称路径上的第一个顶点为源点,最后一个顶点为终点。
在有向网中A点(源点)到达B点(终点)的多条路径中,寻找一条各边权值之和最小的路径,即最短路径。
最短路径问题:
第一类问题:两点间最短路径
第二类问题:某源点到其他各点最短路径
6.5.1.迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)
最短路径问题的提法很多,在这里仅讨论单源最短路径问题:从某个源点S∈V到G中其余各顶点的最短路径。对于求多源点的最短路径问题,可以用每个顶点作为源点调用一次单源最短路径问题算法予以解决。
最短路径与最小生成树不同,路径上不一定包含n个顶点,也不一定包含n-1条边。
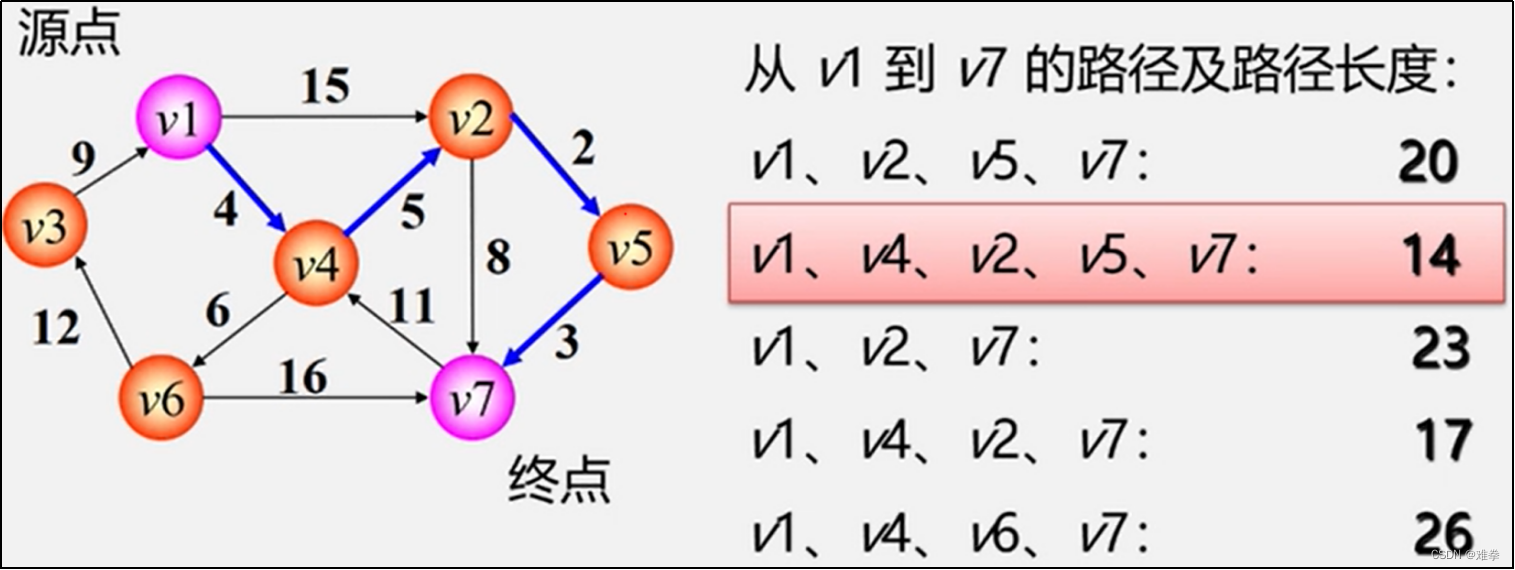
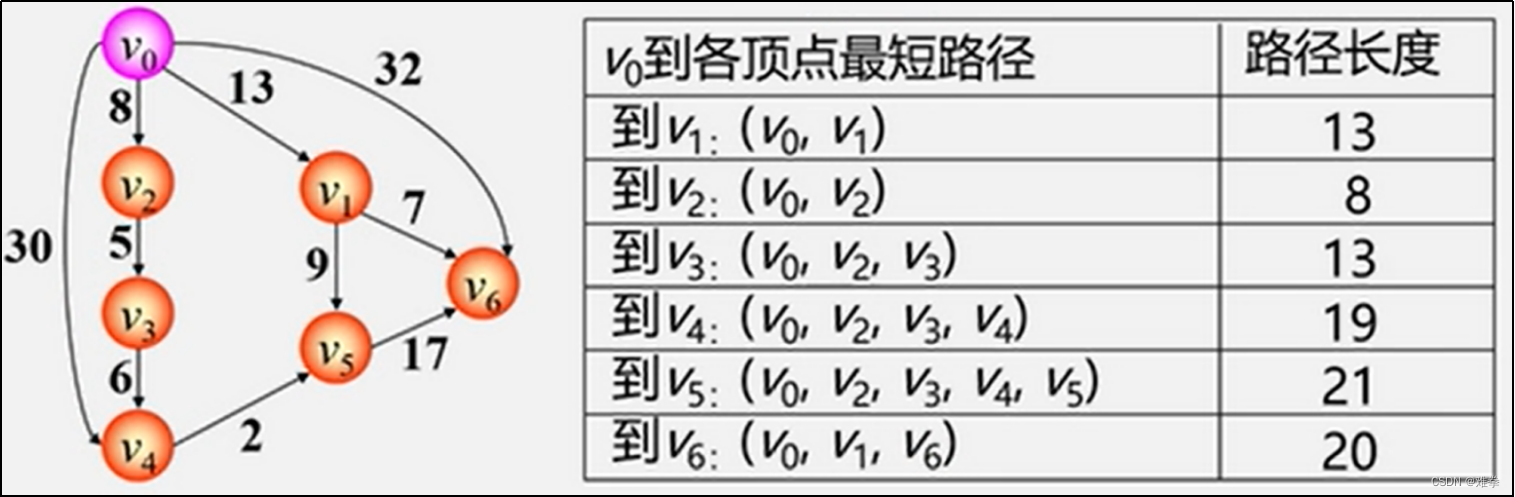
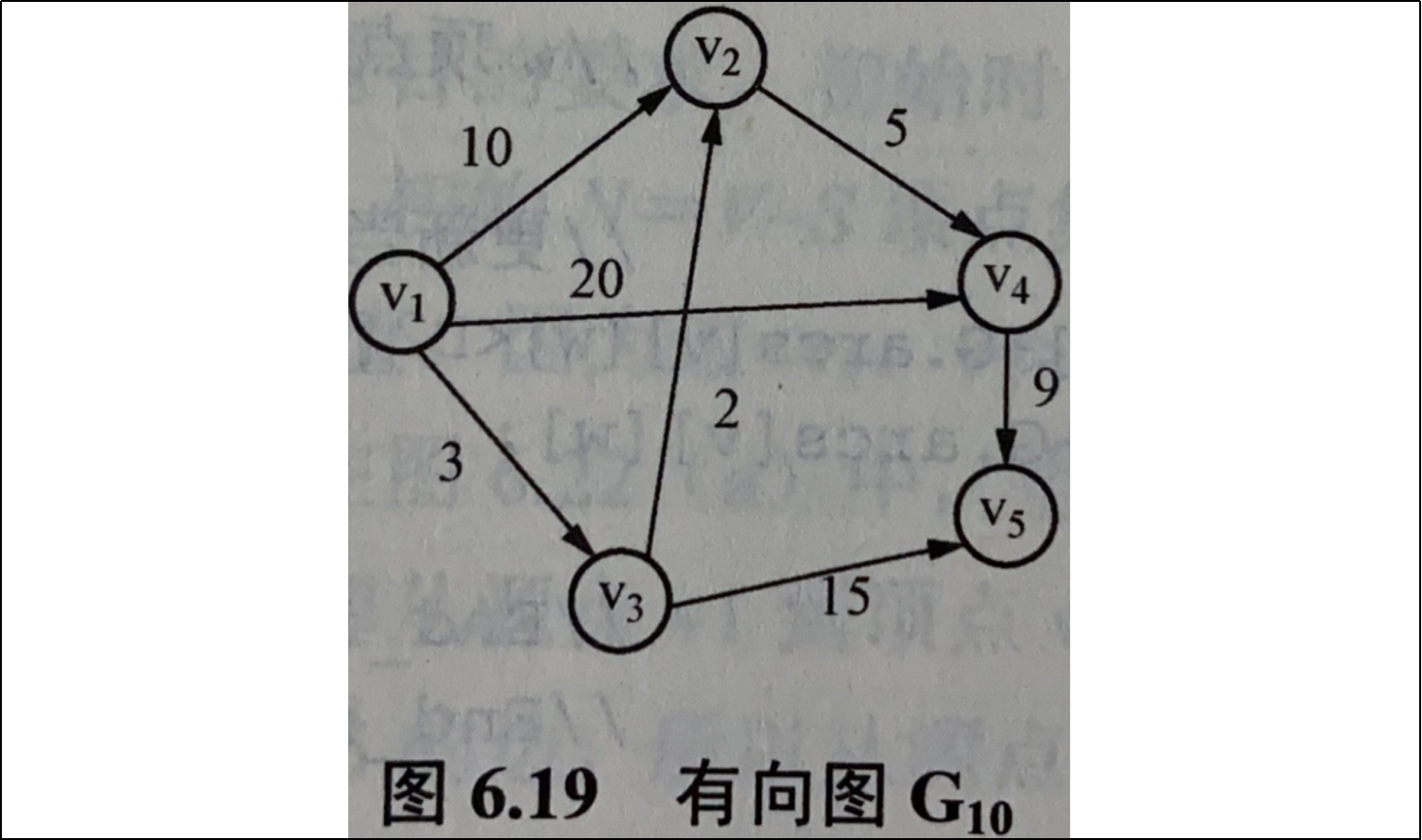
例如,有向图G10,假定以v1为源点,则v1到其他各顶点的最短路径如表6.2所示。
如图6.19所示,从图G10可看出,顶点v1到v4的路径有3条(v1,v2, v4),(v1, v4), (v1,v3,v2, v4),其路径长度分别为15、20和10,因此, v1到v4的最短路径为 (v1,v3,v2, v4)。
那么,如何求得给定有向图的单源最短路径呢?迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)提出了按路径长度递增的顺序产生诸顶点的最短路径算法,称之为迪杰斯特拉算法。
Dijistra算法原理:
1.初始化:先找出从源点v0到各终点vk的直达路径(v0,vk),即通过一条弧到达的路径,无法直接到达的路径标记无穷大;
2.选择:从这些路径中找出一条长度最短的路径(v0,u);
3.更新:然后对其余各条路径进行适当调整;若在图中存在弧(u,vk),且(v0,u)+(u,vk)<(v0,vk),则以路径(v0,u,vk)替代(v0,vk)。
4.在调整后的各条路径中,再找长度最短的路径,以此类推。
迪杰斯特拉算法数据存储结构:
| struct Dijkstra { int* vertex; int isMinPath; int priorVertex; int weight; }; |
struct Dijkstra:描述迪杰斯特拉记录的每个顶点元素信息。
vertex:是一个数组记录求最短路径时经过的顶点,按顺序存储。这个数组是一个指针,所有的顶点共享这个数组中的数据信息。
isMinPath:标记是否已经是最短路径。
priorVertex:标记当前顶点的前驱顶点在vertex数组中的下标索引。
weight:从源顶点到当前顶点的最短路径权值之和。
迪杰斯特拉算法求最短路径的实现思想:
1.创建迪杰斯特拉数据结构数组Dijkstra[],数组长度为有向图G=(V, E)的顶点个数。新建一个vertex[]顶点数组,长度仍然是顶点的个数。
2.初始化数组Dijkstra[],数组中每个元素的vertex参数都指向vertex[]顶点数组。标记isMinPath为0,表示未访问过当前顶点。前驱priorVertex标记当前访问的顶点下标。weight权值取graph->edge[i][j](i当前访问的顶点元素在邻接矩阵中的下标,j表示其它顶点元素的下标),graph->edge[i][j]表示有向边<i,j>的权。若不存在有向边<i,j>,则graph->edge[i][j]的权为无穷大(假定取值为int类型最大值)。
3.在数组Dijkstra[]中根据第一个访问的顶点元素下标找到数组中的元素,标记isMinPath为1,表示已访问过当前顶点(即上文提到的已访问集合U中),将权值weight设置为0,因为源点到源点自己没有权值。将当前第一个访问的顶点元素下标存入vertex[]顶点数组中(所有Dijkstra[].vertex共享这个数据)。
4.从数组Dijkstra[]取出权值最小的顶点信息,标记isMinPath为1,表示已访问过当前顶点(添加到已访问集合U中),从当前顶点开始到未被访问过的顶点路径中,比较是否因为新顶点的加入出现了更短的路径,如果有更短路径则更新路径,并标记当前顶点为前驱priorVertex。
5.重复3-4步骤,直至所有顶点都被访问过,即求得了源顶点到图中其它顶点的最短路径。
| void dijkstraAMGraph(struct AMGraph* aMGraph) { if (aMGraph == NULL || aMGraph->graph == NULL) { printf("邻接矩阵--图,不存在!\n"); return; } struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph = aMGraph->graph; int size = graph->vertexNum; struct Dijkstra* dijkstra = malloc(sizeof(struct Dijkstra) * size); int* vertex = malloc(sizeof(int) * size); if (dijkstra == NULL || vertex == NULL) { printf("构建Dijkstra数组失败,内车内空间不足!\n"); return; }
int index = 0, vertexIndex = 0; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { dijkstra[i].vertex = vertex; dijkstra[i].isMinPath = 0; dijkstra[i].weight = graph->edge[index][i]; if (dijkstra[i].weight < INT_MAX && dijkstra[i].weight > 0) { dijkstra[i].priorVertex = index; } else { dijkstra[i].priorVertex = -1; } } dijkstra[index].vertex[vertexIndex++] = index; dijkstra[index].isMinPath = 1; dijkstra[index].weight = 0; for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) { int minWeight = INT_MAX, minVertex = -1; for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { if (!dijkstra[j].isMinPath && dijkstra[j].weight < minWeight) { minWeight = dijkstra[j].weight; minVertex = j; } } dijkstra[index].vertex[vertexIndex++] = minVertex; dijkstra[minVertex].isMinPath = 1; for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { if (!dijkstra[j].isMinPath && dijkstra[minVertex].weight + graph->edge[minVertex][j] > 0 && dijkstra[minVertex].weight + graph->edge[minVertex][j] < dijkstra[j].weight) { dijkstra[j].priorVertex = minVertex; dijkstra[j].weight = dijkstra[minVertex].weight + graph->edge[minVertex][j]; } } } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (dijkstra[i].priorVertex == -1) continue; vertexIndex = 0; printf("顶点"); while (1) { int searchIndex = dijkstra[i].vertex[vertexIndex]; printf("%s+", graph->vertex[searchIndex]); if (searchIndex == dijkstra[i].priorVertex) { printf("%s=权值:%d\n", graph->vertex[i], dijkstra[i].weight); break; } vertexIndex++; } } } |
注释:完整算法见6.2.1小节邻接矩阵封装。
例如,如图6.19所示的图G10的带权邻接矩阵如图6.20所示。
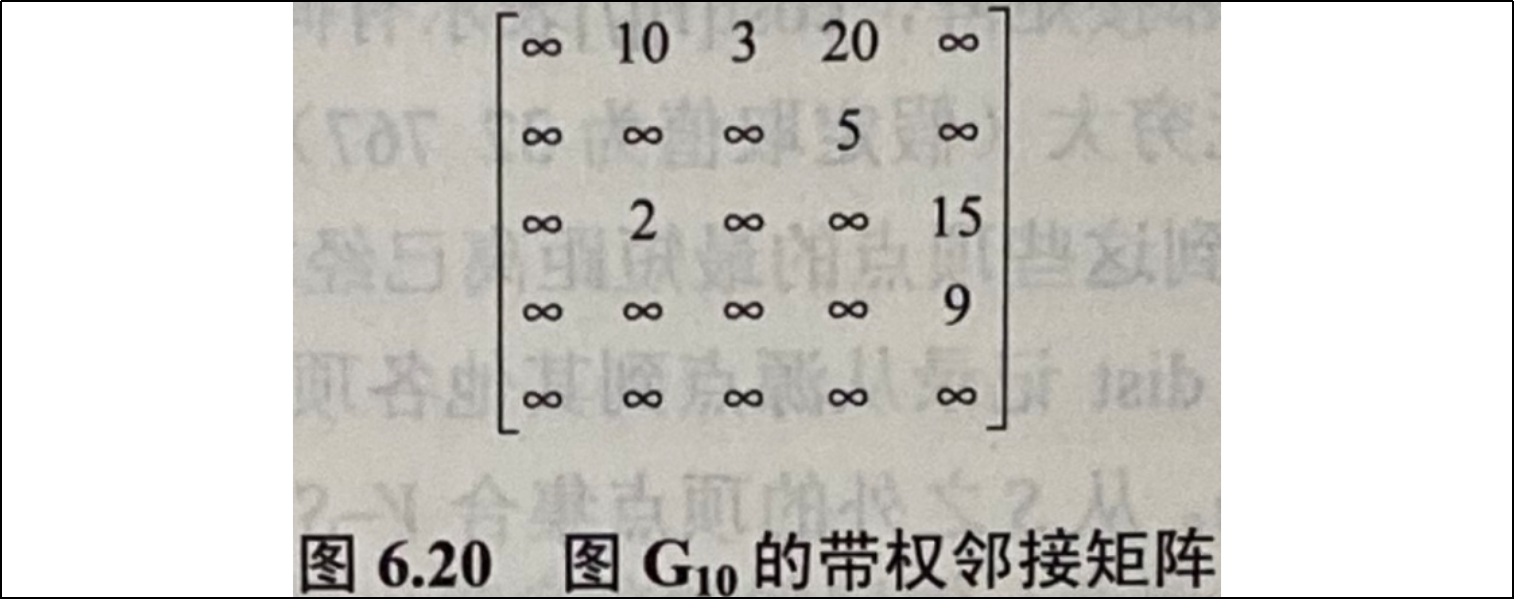
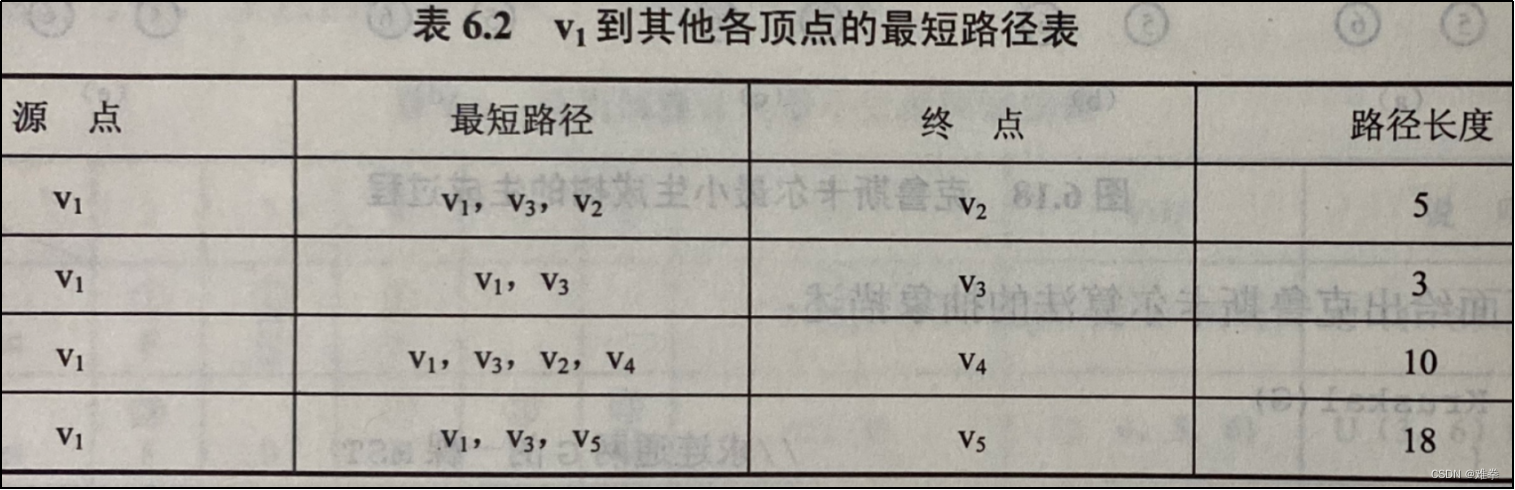
若对G10执行上述迪杰斯特拉算法,则从v1到其余个项顶点的最短路径描述如下:
| 邻接矩阵--无向图读出磁盘D:/Graph.temp保存的数据! 邻接矩阵--无向图结构: V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V1 ∞ 10 3 20 ∞ V2 ∞ ∞ ∞ 5 ∞ V3 ∞ 2 ∞ ∞ 15 V4 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ 9 V5 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ 顶点V1+V3+V2=权值:5 顶点V1+V3=权值:3 顶点V1+V3+V2+V4=权值:10 顶点V1+V3+V5=权值:18 |
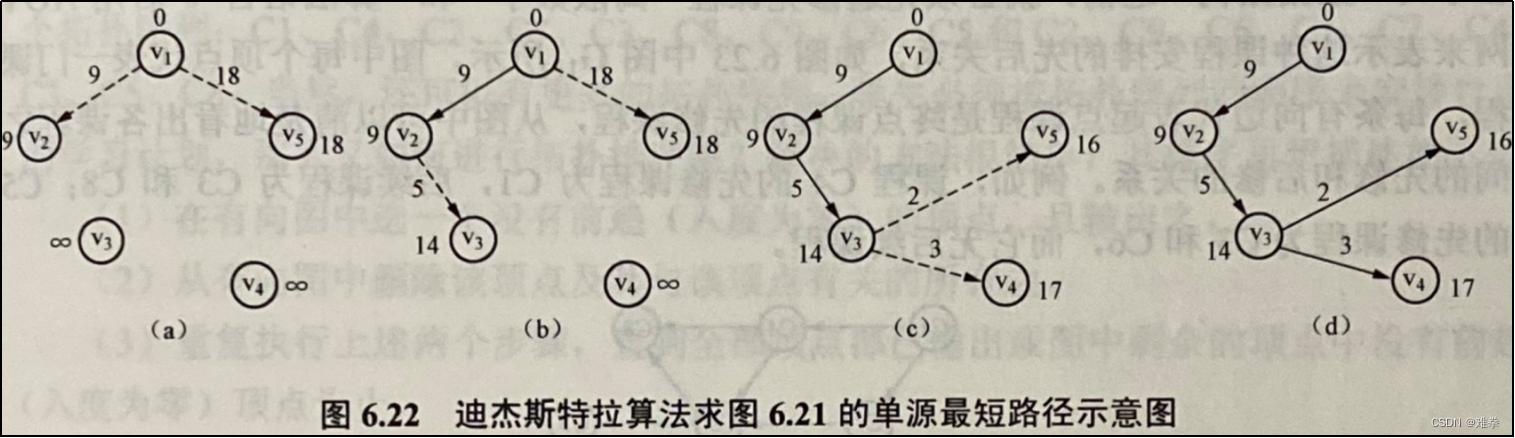
【例6.4】已知有向图如图6.21所示,根据迪杰斯特拉算法画出求从源点v1开始的单源最短路径的过程示意图以及算法的动态执行情况。

分析:按迪杰斯特拉算法及题目的要求,初始时记录从源点到该顶点存在最短路径的顶点数组vertex[]中只有一个源点v1,初始N=V-S顶点集中vj (j=2, 3, 4, 5)的估计距离Dijkstra[j].weight均为有向边<v1, vj>上的权值。因为边<v1, v3>和边<v1, v4>不存在,所以Dijkstra[3].weight=Dijkstra[4].weight=∞,如图6.22 (a)所示。在图6.22 (a)中,当前顶点数组vertex[]中顶点v2的估计距离Dijkstra[2].weight=9最小,故将其加入到vertex[]集中,即从源点v1到顶点v2的最短路径已找到,其长度为9。因为顶点v2到顶点v3有一条权为5的边,所以从源点v1,到v3且中间经过顶点v2的新路径<1, 2, 3>的长度是14,它小于顶点v3的原估计距离∞,因此必须将顶点v3的估计距离Dijkstra[3].weight调整为14,顶点v4、v5的原估计距离没有因为新顶点v3的产生而减小,故无需调整,如图6.22 (b)所示。在当前vertex[]顶点集中顶点v3的估计距离Dijkstra[3].weight=14最小,故将其加入到数组vertex[]中;又因为新加入vertex[]的顶点v3到顶点v4有一条权为3的边,所以从源点v1到顶点v4中间经过的新路径<1, 2, 3, 4>的长度是17,它小于顶点v4的原估计值∞,因此必须将顶点v4的估计距离Dijkstra[4].weight调整为17,而顶点v3到顶点v5有一条权为2的边,那么从源点v1到顶点v5中间经过的新路径<1, 2, 3, 5>的长度是16,它小于顶点v5的原估计值18,因此将顶点v5的估计距离Dijkstra[5].weight调整为16,如图6.22 (c)所示。最后将顶点v5、v4加入到数组vertex[]中,如图6.22 (d)所示。
6.5.2.弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法
算法思想:
· 逐个顶点试探
· 从vi到vj的所有可能存在的路径中
· 选出一条长度最短的路径
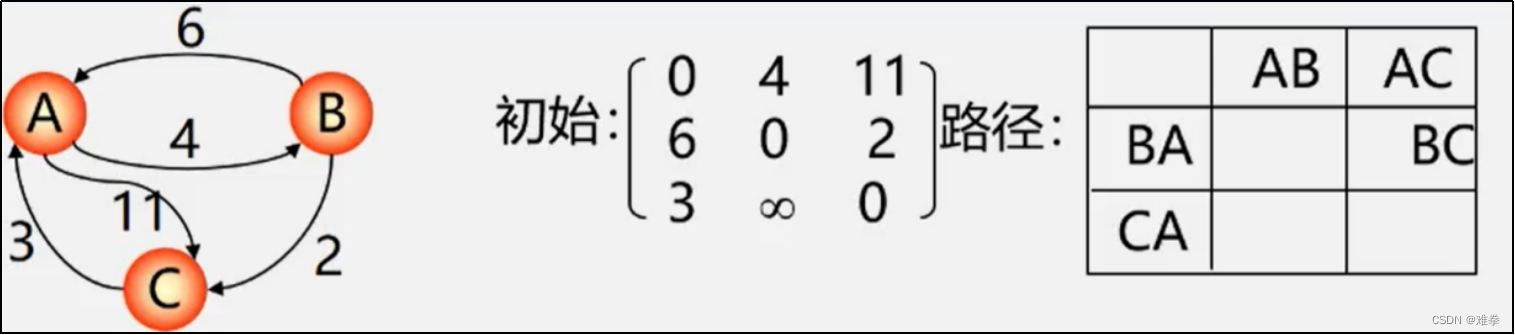
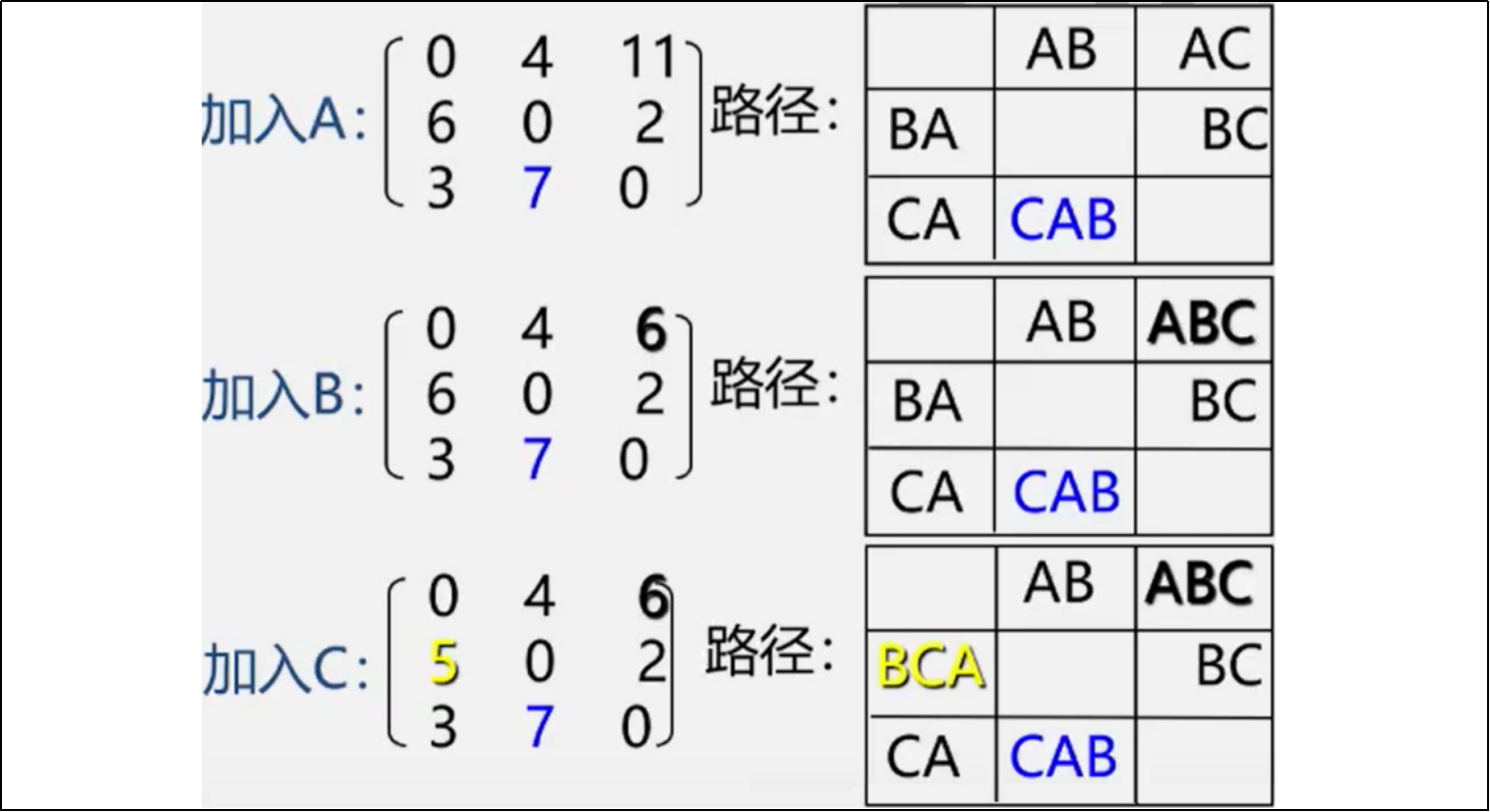
求最短路径步骤:
初始时设置一个n阶方阵,令其对角线元素为0,若存在弧<vi,vj>,则对应元素的权值,否则为∞。
逐步试着在原直接路径中增加中间顶点,若加入中间顶点后路径变短,则修改之;否则,维持原值。所有顶点试探完毕,算法结束。
弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法矩阵中单个元素数据结构存储当前顶点间的最小边的权以及路径:
| struct Floyd { int capacity; int* vertex; int size; int weight; }; |
capacity:vertex数组的最大容量;
vertex:当前最短路径经过的顶点数组;
size:vertex数组中存储的顶点数量;
weight:当前最小边的权值和。
弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法实现步骤:
1.初始化一个n阶方阵,存储有向图边的权值信息(相当于复制了邻接矩阵);
2.依次加入一个顶点,遍历n阶方阵中每个元素在加入了新的顶点后,源顶点与目标顶点之间是否存在更短的路径,如果存在,则跟新一条带新顶点的路径;
3.重复执行步骤2,直至尝试往n阶方阵中加入所有顶点为止。
| // int元素类型数组拷贝功能 暂时放在这里 将来找到新位置了 过来迁移 copyIntArray(int* source, int index, int* taget, int start, int lenght) { for (int i = index, j = start; i < index + lenght; i++, j++) { taget[j] = source[i]; } } struct Floyd { int capacity; int* vertex; int size; int weight; }; void floydAMGraph(struct AMGraph* aMGraph) { if (aMGraph == NULL || aMGraph->graph == NULL) { printf("邻接矩阵--图,不存在!\n"); return; } struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph = aMGraph->graph; int size = graph->vertexNum; struct Floyd** initFloydArray(struct AMGraph* aMGraph); struct Floyd** floydArray = initFloydArray(aMGraph); int** edge = graph->edge; for (int v = 0; v < size; v++) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { if (i == j) continue; if (floydArray[i][v].weight + floydArray[v][j].weight < floydArray[i][j].weight && floydArray[i][v].weight + floydArray[v][j].weight > 0) { memset(floydArray[i][j].vertex, -1, sizeof(int) * floydArray[i][j].capacity); copyIntArray(floydArray[i][v].vertex, 0, floydArray[i][j].vertex, 0, floydArray[i][v].size); floydArray[i][j].size = floydArray[i][v].size; copyIntArray(floydArray[v][j].vertex, 0, floydArray[i][j].vertex, floydArray[i][j].size, floydArray[v][j].size); floydArray[i][j].size = floydArray[i][j].size + floydArray[v][j].size; floydArray[i][j].weight = floydArray[i][v].weight + floydArray[v][j].weight; } } } } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { printf("顶点%s到其它顶点的最短距离:\n", graph->vertex[i]); for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { if (i == j) continue; int lenght = floydArray[i][j].size, vertexIndex = 0;; while (vertexIndex < lenght) { int searchIndex = floydArray[i][j].vertex[vertexIndex]; printf("%s+", graph->vertex[searchIndex]); vertexIndex++; if (vertexIndex == lenght) { if (floydArray[i][j].weight == INT_MAX) { printf("%s=权值:∞\n", graph->vertex[j]); } else { printf("%s=权值:%d\n", graph->vertex[j], floydArray[i][j].weight); } } } } printf("\n"); } return; } struct Floyd** initFloydArray(struct AMGraph* aMGraph) { struct AdjacentMatrixGraph* graph = aMGraph->graph; int size = graph->vertexNum; struct Floyd** floydArray = malloc(sizeof(struct Floyd*) * size); if (floydArray == NULL) { printf("Floyd算法开辟矩阵内存空间不足!\n"); return; } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { struct Floyd* floyd = malloc(sizeof(struct Floyd) * size); if (floyd == NULL) { printf("Floyd算法开辟矩阵行内存空间不足!\n"); return; } floydArray[i] = floyd; for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { int* vertex = malloc(sizeof(int) * size); if (vertex == NULL) { printf("Floyd算法开辟矩阵元素内存空间不足!\n"); return; } memset(vertex, -1, size); floyd[j].vertex = vertex; floyd[j].capacity = size; floyd[j].size = 0; floyd[j].weight = graph->edge[i][j]; if (i == j) { floyd[j].weight = 0; } else { vertex[floyd[j].size++] = i; } } } return floydArray; } |
弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法的时间复杂度比较大,为O(n3)
6.6.拓扑排序
通常,在实现一项较大的工程时,经常会将该工程划分为若干个子工程,我们把这些子工程称为活动。在整个工程中,有些子工程必须在其他相关子工程完成之后才能开始。也就是说,一个子工程的开始是以它的所有前序子工程的结束为先决条件的,但有些子工程没有先决条件,可以安排在任何时间开始。为了形象地反映出整个工程中各个子工程之间的先后关系,可用一个有向图来表示,图中的顶点代表活动(子工程),图中的有向边代表活动的先后关系,即有向边的起点活动是终点活动的前趋活动,只有当起点活动完成以后,其终点活动才能进行。
用一个有向图表示一个工程的各子工程及其相互制约的关系,用顶点表示活动、弧表示活动间先后关系的有向无环图(DAG)称为顶点活动网(Directed/daɪˈrɛktɪd/ Acyclic/ˌeɪˈsaɪklɪk/ Graph, DAG),简称AOV(Acyclic/ˌeɪˈsaɪklɪk/ On Vertex Network)网。用弧表示活动,顶点表示活动的开始或结束事件,称这种有向图为边活动网,简称AOE(Acyclic/ˌeɪˈsaɪklɪk/ On Edge)。
在AOV网中,若从顶点vi到顶点vj有一条有向路径,则顶点vi是vj的前趋, vj是vi的后继。若<vi, vj>是网中一条弧,则顶点vi是vj的直接前趋, vj是vi的直接后继。在AOE网中<vi, vj>表示活动,vi表示开始,vj表示结束。
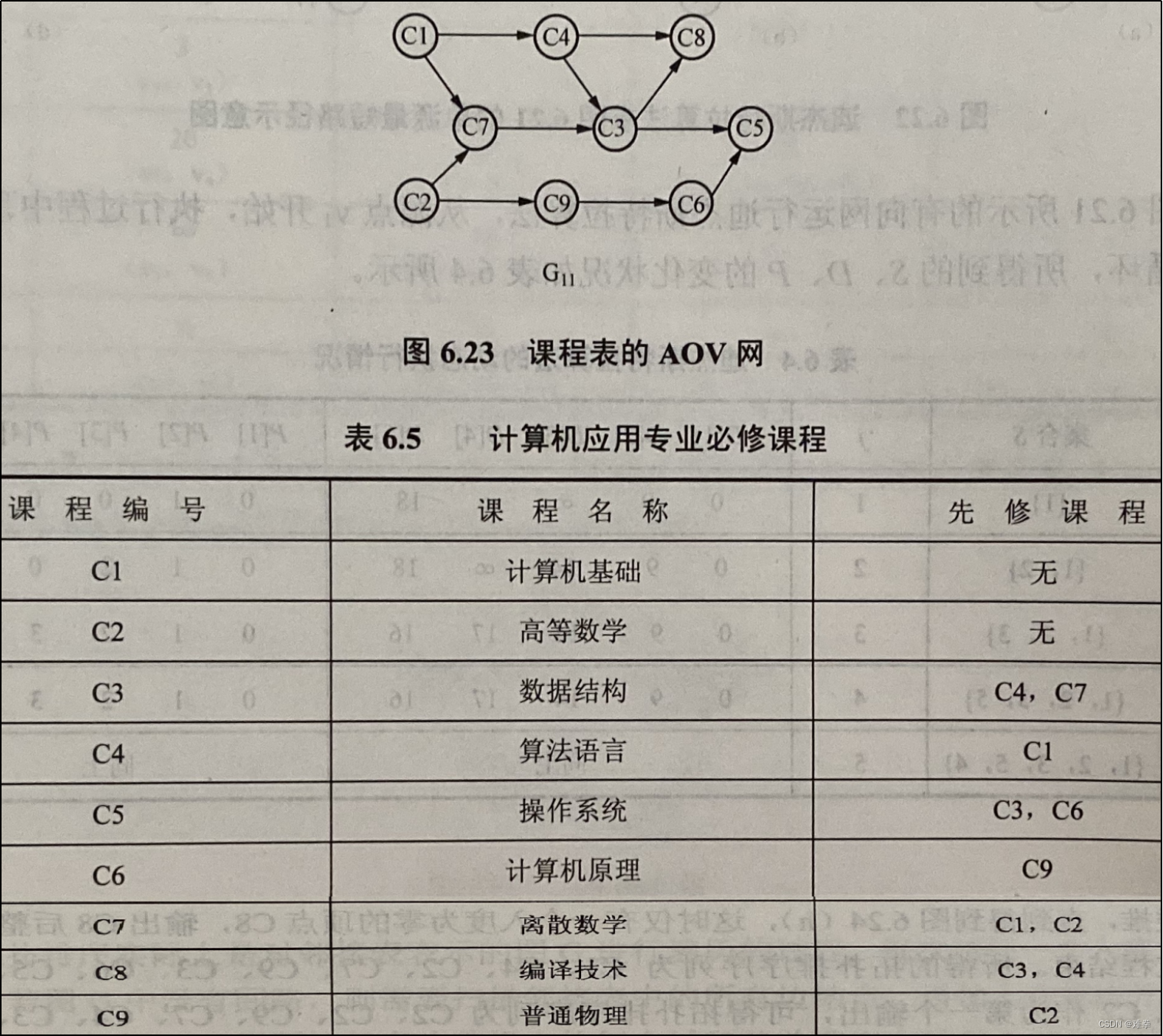
例如,一个计算机应用专业的学生必须修完一系列基本课程(如表6.5所示),其中有些课程是基础课,它们独立于其他课程,如“高等数学”,它无需先选修其他课程;而在学习“数据结构”之前,就必须先选修完课程“离散数学”和“算法语言”。若用AOV网来表示这种课程安排的先后关系,如图6.23中图G11所示。图中每个顶点代表一门课程,每条有向边代表起点课程是终点课程的先修课程,从图中可以清楚地看出各课程之间的先修和后修的关系。例如,课程C4的先修课程为C1,后续课程为C3和C8; C5的先修课程为C3和C6,而它无后续课程。
对于一个有向无环图(Directed/daɪˈrɛktɪd/ Acyclic/ˌeɪˈsaɪklɪk/ Graph, DAG),若将G中所有顶点排成一个线性序列,使得图中任意一对顶点u和v,若<u, v>∈E (G),则u在线性序列中出现在v之前,这样的线性序列称为拓扑序列。也就是说,在AOV网中,若不存在回路(即环),所有活动可排成一个线性序列,使得每个活动的所有前趋活动都排在该活动的前面,此序列就是拓扑序列。由AOV网构造拓扑序列的过程称为拓扑排序。
在AOV网中,不应该出现有向环(即回路),因为存在环即意味着某项活动以自己为先决条件。若设计出这样的流程,工程就将无法进行。因此,对给定的AOV网,应首先判定网中是否存在环。检测的方法是对有向图构造其顶点的拓扑序列,若网中所有顶点都在它的拓扑序列中,则该AOV网必定不存在环。
AOV网的拓扑序列不是唯一的。例如,对图G11进行拓扑排序,至少可得到如下两个拓扑序列: C1、C4、C2、C7,、C3、C8、C9、C6、C5和C2、C9、C6、C1、C7、C4、C3、 C5、C8。当然,还可以有更多的拓扑序列。学生必须按拓扑序列的顺序来安排自己的学习计划,那么又如何进行拓扑排序呢?解决的方法很简单,其排序思想描述如下:
(1)在有向图中选一个没有前趋(入度为零)的顶点,且输出之。
(2)从有向图中删除该顶点及其与该顶点有关的所有边。
(3)重复执行上述两个步骤,直到全部顶点都已输出或图中剩余的顶点中没有前趋(入度为零)顶点为止。
(4)输出剩余的无前趋结点。例如,以图6.23所示的AOV网为例,画出拓扑排序过程如图6.24所示。
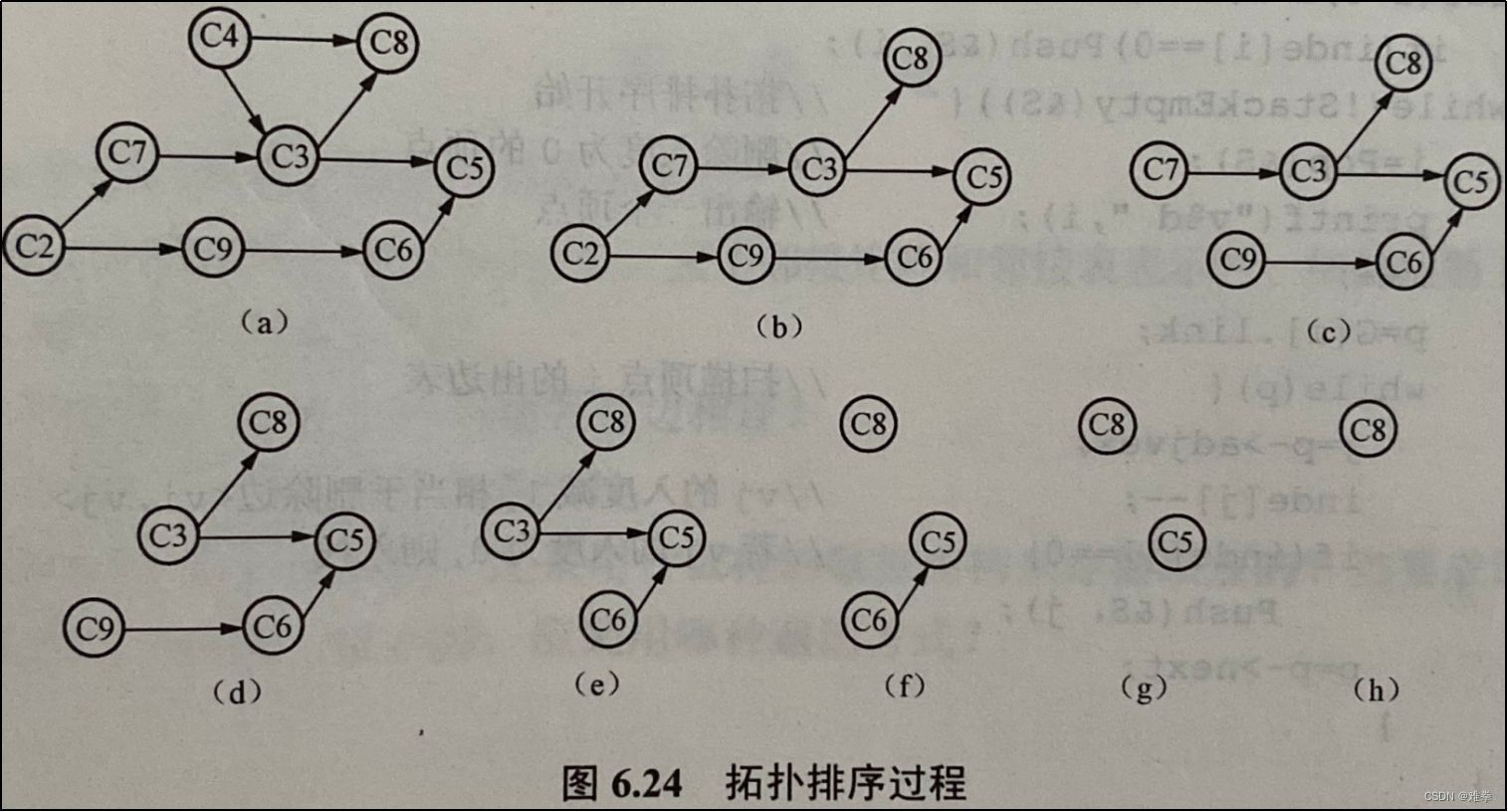
图6.23中顶点C1和C2的入度均为零,可以输出任何一个。若先输出C1,则在删除相应的边后便得到图6.24 (a),该图中C4、C2的入度数为零,输出C4,则得图6.24 (b),依此类推,直到得到图6.24 (h),这时仅有一个入度为零的顶点C8,输出C8后整个拓扑排序过程结束。所得的拓扑排序序列为C1、C4、C2、C7、C9、C3、C6、C5、C8,如果以C2作为第一个输出,可得拓扑排序序列为C2、C1、C9、C7、C4、C3、C6、C8、C5。
十字链表拓扑排序算法:
1.遍历十字链表中顶点数组,找出一个入边为空的顶点,先输入顶点;
2.当前顶点如果有出边,沿着出边释放掉出边上每条边的内存,每次是释放前找到当前边的入边链,从链中删除当前的边,然后再释放这条边;如果入边链是头结点,即释放后对应的顶点入边链为空,如果此时对应的顶点也没有出边,则输出这个顶点;
3.重复步骤1和2直至遍历结束,一共遍历最大顶点个数次,最后输出的顶点数量如果与图中顶点数量一致,则说明图中没有回路。
| void topologyOLGraph(struct OLGraph* oLGraph) { if (oLGraph == NULL || oLGraph->graph == NULL) { #ifdef PRINT printf("十字链表不存在!"); #endif return; } struct OrthogonalListGraph* graph = oLGraph->graph; int size = graph->vertexNum; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (graph->vertex[i]->firstEdgeIn == NULL && graph->vertex[i]->outNodeSize > 0) { printf("顶点%s-->", graph->vertex[i]->data); struct EdgeNode* firstOut = graph->vertex[i]->firstEdgeOut; struct EdgeNode* prior = NULL; graph->vertex[i]->firstEdgeOut = NULL; while (firstOut != NULL) { prior = firstOut; firstOut = firstOut->tailLink; prior->tailLink = NULL; // 处理入边表 struct EdgeNode* firstIn = graph->vertex[prior->heahVertex]->firstEdgeIn; struct EdgeNode* priorNode = NULL; if (firstIn != NULL && prior == firstIn) { graph->vertex[prior->heahVertex]->firstEdgeIn = firstIn->heahLink; if (graph->vertex[prior->heahVertex]->firstEdgeOut == NULL && graph->vertex[prior->heahVertex]->firstEdgeIn == NULL) { printf("顶点%s-->", graph->vertex[prior->heahVertex]->data); } free(firstIn); firstIn = NULL; } while (firstIn != NULL) { priorNode = firstIn; firstIn = firstIn->heahLink; if (prior == firstIn) { priorNode->heahLink = firstIn->heahLink; free(firstIn); firstIn = NULL; } } } graph->vertex[i]->outNodeSize = 0; i = -1; } } } |
测试(完整十字链表算法实现见6.2.3小节):
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "OLGraph.h" int main() { struct OLGraph* graph = initOLGraph(); graph->print(graph); graph->topology(graph); return 0; } |
测试结果:
| 请输入有向图的顶点数和边数: 顶点 边。 9 11 请输入9个顶点的值。 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 请输入11条边: 弧尾 弧头 权重 请输入第1条边: C1 C7 1 请输入第2条边: C1 C4 1 请输入第3条边: C4 C3 1 请输入第4条边: C4 C8 1 请输入第5条边: C7 C3 1 请输入第6条边: C3 C8 1 请输入第7条边: C2 C7 1 请输入第8条边: C2 C9 1 请输入第9条边: C9 C6 1 请输入第10条边: C3 C5 1 请输入第11条边: C6 C5 1 十字链表图结构->出边表: 0 C1====[0->3 1]====[0->6 1] 1 C2====[1->6 1]====[1->8 1] 2 C3====[2->4 1]====[2->7 1] 3 C4====[3->2 1]====[3->7 1] 4 C5 5 C6====[5->4 1] 6 C7====[6->2 1] 7 C8 8 C9====[8->5 1] 十字链表图结构->入边表: 0 C1 1 C2 2 C3====[6->2 1]====[3->2 1] 3 C4====[0->3 1] 4 C5====[5->4 1]====[2->4 1] 5 C6====[8->5 1] 6 C7====[0->6 1]====[1->6 1] 7 C8====[3->7 1]====[2->7 1] 8 C9====[1->8 1] 顶点C1-->顶点C2-->顶点C4-->顶点C7-->顶点C3-->顶点C8-->顶点C9-->顶点C6-->顶点C5--> |
邻接表拓扑排序算法需要设置一个含n个元素的一维数组inDegree[],用来保存AOV网中每个顶点的入度值。设一个栈暂存所有入度为零的顶点,以后每次选入度为零的顶点时,只需要做出栈操作即可。算法中删除顶点及其所有边的操作只需要检查出栈的顶点vi的出边表,把每条出边<vi, vj>的终点vj所对应的入度inDegree[j]减1,若vj的入度为零,则将j入栈。因此,拓扑排序算法的具体描述为:
| void topologyALGraph(struct ALGraph* aLGraph) { if (aLGraph == NULL || aLGraph->graph == NULL) { printf("邻接表--%s图不存在!\n", digraphAL ? "有向" : "无向"); return; } struct AdjacencyListGraph* graph = aLGraph->graph; int size = graph->vertexNum; struct SequenceStack* stack = initSequenceStack(); int* inDegree = calloc(size, sizeof(int)); if (inDegree == NULL) { printf("邻接表--%s图拓扑排序开辟辅助数组内存不足!\n", digraphAL ? "有向" : "无向"); return; } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { struct EdgeNode* firstEdge = graph->vertex[j]->firstEdge; while (firstEdge != NULL) { if (firstEdge->adjvex == i) { inDegree[i]++; } firstEdge = firstEdge->next; } } } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (inDegree[i] == 0) { int* index = malloc(sizeof(int)); if (index == NULL) return; *index = i; stack->push(index, stack); } } while (stack->isNotEmpty(stack)) { int* index = stack->top(stack); printf("顶点%s-->", graph->vertex[*index]->data); stack->pop(stack); struct EdgeNode* node = graph->vertex[*index]->firstEdge; struct EdgeNode* prior = NULL; free(index); while(node != NULL) { prior = node; node = node->next; inDegree[prior->adjvex]--; if (inDegree[prior->adjvex] == 0) { int* index = malloc(sizeof(int)); if (index == NULL) return; *index = prior->adjvex; stack->push(index, stack); } free(prior); prior = NULL; } } stack->destroy(stack); } |
测试(完整代码见6.2.2小节封装):
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "ALGraph.h" int main() { struct ALGraph* graph = initALGraph(1, NULL); graph->print(graph); graph->topology(graph); return 0; } |
测试结果:
| 请输入有向图的顶点数和边数: 顶点 边。 9 11 请输入9个顶点的值。 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 请输入11条边: 弧尾 弧头 权重 请输入第1条边: C1 C7 1 请输入第2条边: C1 C4 1 请输入第3条边: C4 C3 1 请输入第4条边: C7 C3 1 请输入第5条边: C3 C8 1 请输入第6条边: C4 C8 1 请输入第7条边: C3 C5 1 请输入第8条边: C2 C7 1 请输入第9条边: C2 C9 1 请输入第10条边: C9 C6 1 请输入第11条边: C6 C5 1 邻接表--有向图结构: 0 C1---->3 1---->6 1 1 C2---->6 1---->8 1 2 C3---->4 1---->7 1 3 C4---->2 1---->7 1 4 C5 5 C6---->4 1 6 C7---->2 1 7 C8 8 C9---->5 1 顶点C2-->顶点C9-->顶点C6-->顶点C1-->顶点C7-->顶点C4-->顶点C3-->顶点C8-->顶点C5--> |
拓扑排序实际上是对邻接表表示的图G进行遍历的过程,每次访问一个入度为0的顶点。若图G中没有回路,则需要扫描邻接表中的所有边结点,再加上在算法开始时,为建立入度数组需要访问表头数组中的每个域和其单链表中的每个结点,所以该算法的时间复杂度为O(n+e)。
6.7.关键路径
用一个有向图表示一个工程的各子工程及其相互制约的关系,用弧表示活动,顶点表示活动的开始或结束事件,称这种有向图为边活动网,简称AOE(Acyclic/ˌeɪˈsaɪklɪk/ On Edge)。
把工程计划表示为边表示活动的网络,即AOE网,用顶点表示事件,弧表示活动,弧的权表示活动持续时间。事件表示在它之前的活动已经完成,在它之后的活动可以开始。

图6.25 边活动网
【例】设一个工程有11项活动,9个事件。事件v1--表示整个工程的开始(源点:入度为0的顶点),事件v9--表示整个工程结束(汇点:出度为0的顶点)。
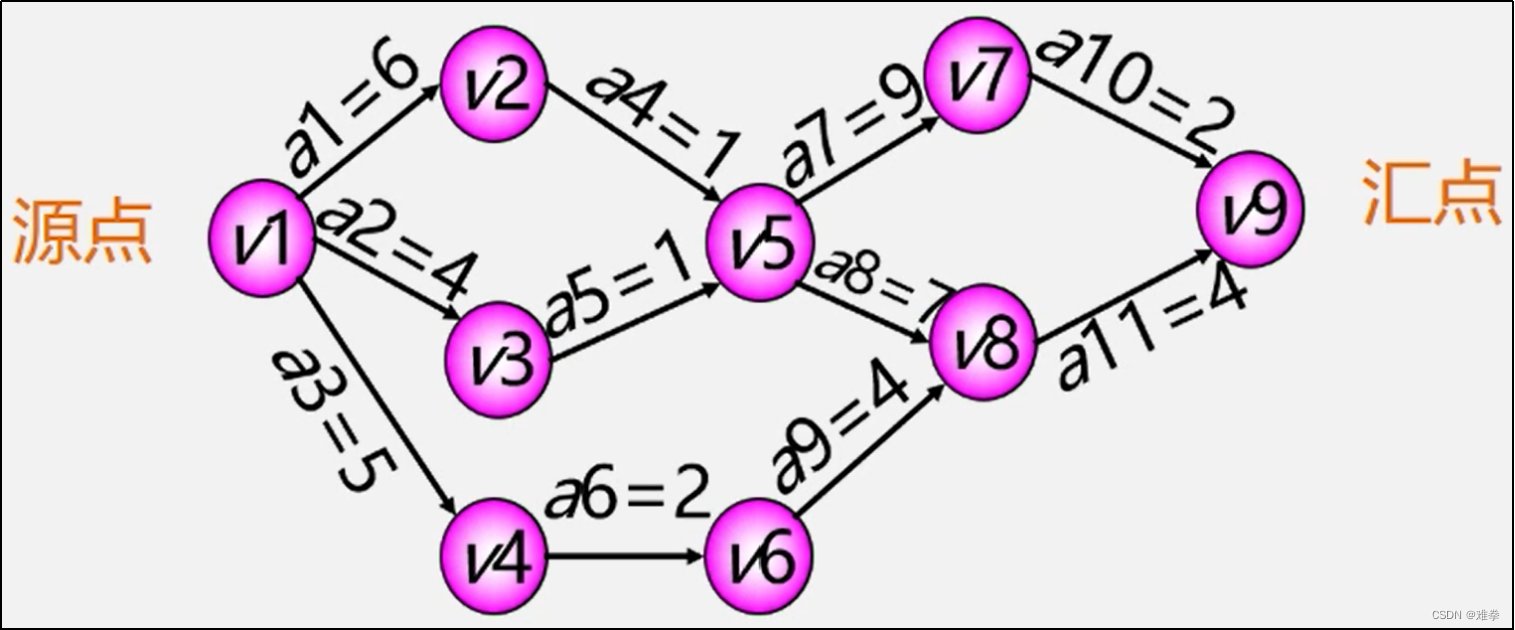
图6.26 AOE网
对于AOE网,我们关心两个问题:
1.完成整个工程至少需要多少时间?
2.那些活动是影响工程进度的关键?
关键路径即路径长度最长的路径。路径长度即路径上各活动持续时间之和。
求关键路径需要定义4各描述量:
1.vertexEarly(vi)--表示事件vi的最早开始时间。这个时间为前一个顶点事件最早开始时间(源点的最早开始时间为0)加上到达这个事件需要的最大权值(时间),即得到事件vi的最早开始时间。

2.vertexLate(vi)--表示事件vi的最迟开始时间。这个时间为从后一个事件反推,后一个事件的最迟开始时间(汇点的最迟开始时间为vertexEarly(vi))减去两个事件间消耗时间最长的活动,得到的余量时间即为vi的最迟开始时间。
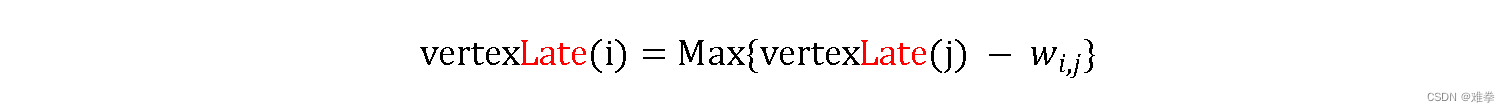
3.early(i)--表示活动ai的最早开始时间。活动ai的最早开始时间为活动ai狐尾事件的最早开始时间,即early(i)=vertexEarly(vi)。
4.late(i)--表示活动ai的最迟开始时间。活动ai的最迟开始时间为活动ai弧头事件的最迟开始时间减去活动ai所需要消耗的时间,为活动ai的最迟开始时间,即vertexLate(vi)-Wai(活动ai权值)。
late(i)-early(i)表示活动ai的时间余量。关键活动表示关键路径上的活动,即late(i)=early(i)的活动。
根据以上理论可以求得图6.26 AOE网事件与活动的最早与最迟开始时间
| 顶点 |
vertexEarly(vi) |
vertexLate(vi) |
||||
| v1 |
0 |
0 |
||||
| v2 |
6 |
6 |
||||
| v3 |
4 |
6 |
||||
| v4 |
5 |
8 |
||||
| v5 |
7 |
7 |
||||
| v6 |
7 |
10 |
||||
| v7 |
16 |
16 |
||||
| v8 |
14 |
14 |
||||
| v9 |
18 |
18 |
||||
| 活动 |
early(i) |
late(i) |
late(i)-early(i) |
|||
| a1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|||
| a2 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
|||
| a3 |
0 |
3 |
3 |
|||
| a4 |
6 |
6 |
0 |
|||
| a5 |
4 |
6 |
2 |
|||
| a6 |
5 |
8 |
3 |
|||
| a7 |
7 |
7 |
0 |
|||
| a8 |
7 |
7 |
0 |
|||
| a9 |
7 |
10 |
3 |
|||
| a10 |
16 |
16 |
0 |
|||
| a11 |
14 |
14 |
0 |
|||
没有时间余量的关键活动有a1、a4、a7、a8、a10、a11,它们构成了关键路径。
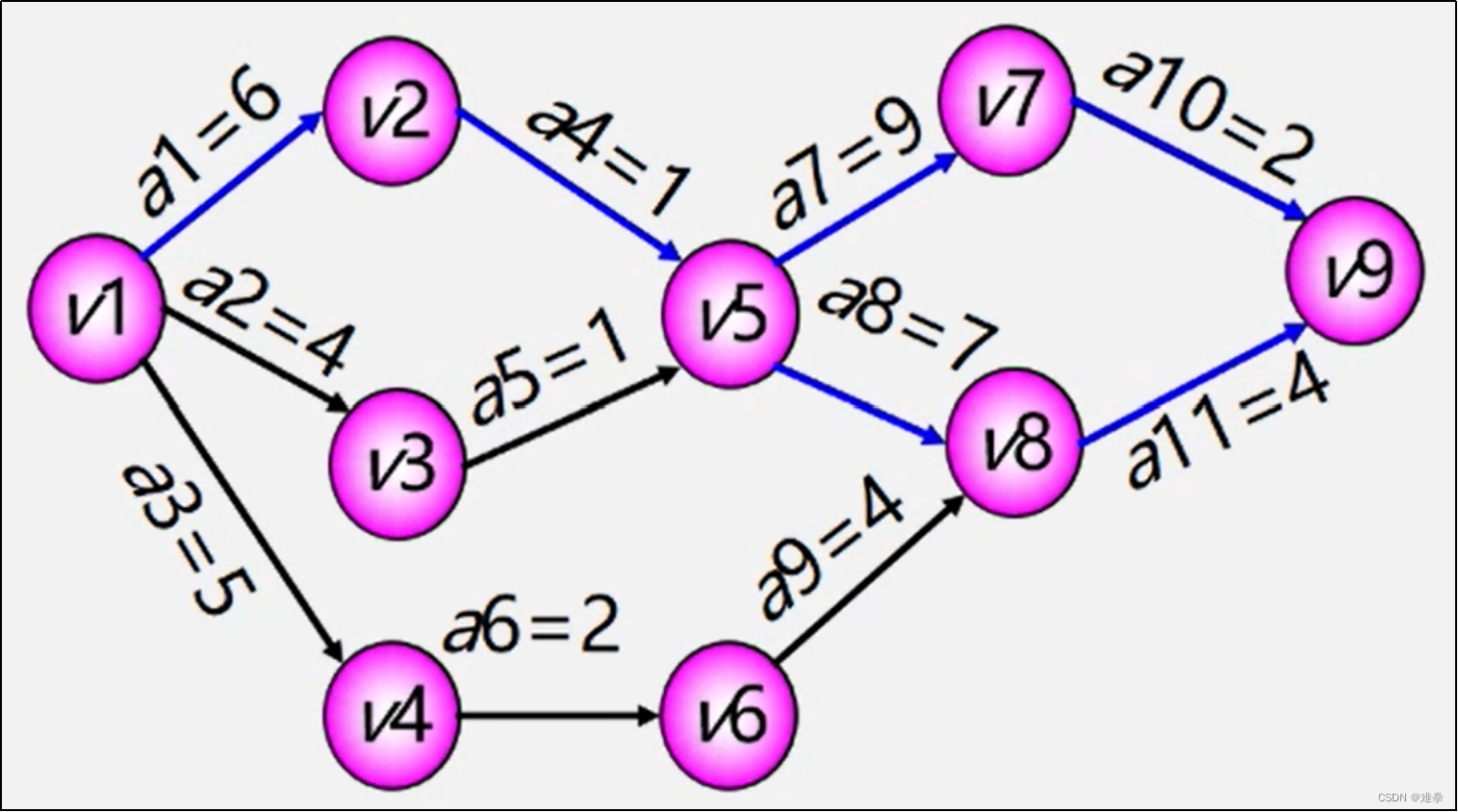
图 6.27中蓝色路径部分即为由关键活动构成的关键路径。
关键路径的算法,事件(顶点)与活动(边)数据存储结构如下:
| struct VertexTime { char* vertex; int vertexEarly; int vertexLate; }; struct EdgeTime { char* edge; int early; int late; int timeMargin; }; |
算法使用十字链表数据结构存储图的信息,实现过程:
1.先找出十字链表的源点与汇点;
2.从源点的出边表开始广度优先遍历图,计算每个顶点(事件)的最早开始时间;
3.从汇点的入边表开始广度优先遍历图,计算每个顶点(事件)的最迟开始时间;
4.根据已经求出的顶点(事件)表最早与最迟开始时间,依次计算每条边(活动)的最早开始时间、最迟开始时间与该边的时间余量。
| void keyPathOLGraph(struct OLGraph* oLGraph) { if (oLGraph == NULL || oLGraph->graph == NULL) { #ifdef PRINT printf("十字链表不存在!"); #endif return; } struct OrthogonalListGraph* graph = oLGraph->graph; int size = graph->vertexNum; int sourceVertex = -1, convergeVertex = -1, count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (graph->vertex[i]->firstEdgeIn == NULL) { sourceVertex = i; count++; } if (graph->vertex[i]->firstEdgeOut == NULL) { convergeVertex = i; count++; } } if (count > 2 && sourceVertex != -1 && convergeVertex != -1) { printf("十字链表中源点与汇点不唯一!\n"); } struct VertexTime* vertexArray = calloc(size, sizeof(struct VertexTime)); struct EdgeTime* edgeArray = malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeTime) * graph->edgeNum); if (vertexArray == NULL || edgeArray == NULL) { printf("求关键路径,内存空间不足!\n"); return; } for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { vertexArray[i].vertexEarly = 0; vertexArray[i].vertexLate = INT_MAX; } void createVertexEarlyBreadth(struct OrthogonalListGraph* graph, struct VertexTime* vertexArray, int sourceVertex); createVertexEarlyBreadth(graph, vertexArray, sourceVertex); vertexArray[convergeVertex].vertexLate = vertexArray[convergeVertex].vertexEarly; void createVertexLateBreadth(struct OrthogonalListGraph* graph, struct VertexTime* vertexArray, int convergeVertex); createVertexLateBreadth(graph, vertexArray, convergeVertex); void createEdgeLateBreadth(struct OrthogonalListGraph* graph, struct VertexTime* vertexArray, struct EdgeTime* edgeArray); createEdgeLateBreadth(graph, vertexArray, edgeArray); printf("事件:\n"); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { printf("顶点%s ", vertexArray[i].vertex); printf("%d ", vertexArray[i].vertexEarly); printf("%d \n", vertexArray[i].vertexLate); } printf("活动:\n"); for (int i = 0; i < graph->edgeNum; i++) { printf("弧%s ", edgeArray[i].edge); printf("early(i)=%d ", edgeArray[i].early); printf("late(i)=%d ", edgeArray[i].late); printf("late(i)-early(i)=%d \n", edgeArray[i].timeMargin); } } struct PathIndex { void* pointer; int index; }; void createVertexEarlyBreadth(struct OrthogonalListGraph* graph, struct VertexTime* vertexArray, int sourceVertex) { struct LinkQueue* queue = initLinkQueue(); struct PathIndex* pathIndex = malloc(sizeof(struct PathIndex)); if (pathIndex == NULL) return; pathIndex->pointer = NULL; pathIndex->index = sourceVertex; queue->push(pathIndex, queue); while (queue->isNotEmpty(queue)) { struct PathIndex* pathIndex = queue->front(queue); struct EdgeNode* edgeOut = graph->vertex[pathIndex->index]->firstEdgeOut; struct EdgeNode* prior = NULL; while (edgeOut != NULL) { prior = edgeOut; edgeOut = edgeOut->tailLink; int vertexEarly = vertexArray[prior->tailVertex].vertexEarly + prior->weight; if (vertexEarly > vertexArray[prior->heahVertex].vertexEarly) { vertexArray[prior->heahVertex].vertexEarly = vertexEarly; vertexArray[prior->heahVertex].vertex = graph->vertex[prior->heahVertex]->data; }
struct PathIndex* vIndex = malloc(sizeof(struct PathIndex)); if (vIndex == NULL) return; vIndex->index = prior->heahVertex; int comparePathIndex(void* first, void* second); if (queue->isNotExist(vIndex, comparePathIndex, queue)) { queue->push(vIndex, queue); } } queue->pop(queue); } queue->destroy(queue); } int comparePathIndex(void* first, void* second) { struct PathIndex* firstIndex = first; struct PathIndex* secondIndex = second; if (firstIndex->index == secondIndex->index) { return 1; } return 0; } void createVertexLateBreadth(struct OrthogonalListGraph* graph, struct VertexTime* vertexArray, int convergeVertex) { struct LinkQueue* queue = initLinkQueue(); struct PathIndex* pathIndex = malloc(sizeof(struct PathIndex)); if (pathIndex == NULL) return; pathIndex->pointer = NULL; pathIndex->index = convergeVertex; queue->push(pathIndex, queue); while (queue->isNotEmpty(queue)) { struct PathIndex* pathIndex = queue->front(queue); struct EdgeNode* edgeIn = graph->vertex[pathIndex->index]->firstEdgeIn; struct EdgeNode* prior = NULL; while (edgeIn != NULL) { prior = edgeIn; edgeIn = edgeIn->heahLink; int vertexLate = vertexArray[prior->heahVertex].vertexLate - prior->weight; if (vertexLate < vertexArray[prior->tailVertex].vertexLate) { vertexArray[prior->tailVertex].vertexLate = vertexLate; } struct PathIndex* vIndex = malloc(sizeof(struct PathIndex)); if (vIndex == NULL) return; vIndex->index = prior->tailVertex; if (queue->isNotExist(vIndex, comparePathIndex, queue)) { queue->push(vIndex, queue); } } queue->pop(queue); } queue->destroy(queue); } void createEdgeLateBreadth(struct OrthogonalListGraph* graph, struct VertexTime* vertexArray, struct EdgeTime* edgeArray) { int size = graph->edgeNum; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { struct EdgeNode* edge = graph->edge[i]; edgeArray[i].edge = edge->edge; edgeArray[i].early = vertexArray[edge->tailVertex].vertexEarly; edgeArray[i].late = vertexArray[edge->heahVertex].vertexLate - edge->weight; edgeArray[i].timeMargin = edgeArray[i].late - edgeArray[i].early; } } |
测试:
| #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS //规避C4996告警 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "OLGraph.h" int main() { struct OLGraph* graph = initOLGraph(); graph->print(graph); graph->keyPath(graph); return 0; } |
测试结果与前一页统计的表中数据一致无误:
| 请输入有向图的顶点数和边数: 顶点 边。 9 11 请输入9个顶点的值。 v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 v6 v7 v8 v9 请输入11条边: 弧尾 弧头 边 权重 请输入第1条边: v1 v2 a1 6 请输入第2条边: v1 v3 a2 4 请输入第3条边: v1 v4 a3 5 请输入第4条边: v2 v5 a4 1 请输入第5条边: v3 v5 a5 1 请输入第6条边: v4 v6 a6 2 请输入第7条边: v6 v8 a9 4 请输入第8条边: v5 v7 a7 9 请输入第9条边: v5 v8 a8 7 请输入第10条边: v8 v9 a11 4 请输入第11条边: v7 v9 a10 2 十字链表图结构->出边表: 0 v1====[0->1 6]====[0->2 4]====[0->3 5] 1 v2====[1->4 1] 2 v3====[2->4 1] 3 v4====[3->5 2] 4 v5====[4->6 9]====[4->7 7] 5 v6====[5->7 4] 6 v7====[6->8 2] 7 v8====[7->8 4] 8 v9 十字链表图结构->入边表: 0 v1 1 v2====[0->1 6] 2 v3====[0->2 4] 3 v4====[0->3 5] 4 v5====[1->4 1]====[2->4 1] 5 v6====[3->5 2] 6 v7====[4->6 9] 7 v8====[5->7 4]====[4->7 7] 8 v9====[7->8 4]====[6->8 2] 事件: 顶点(null) 0 0 顶点v2 6 6 顶点v3 4 6 顶点v4 5 8 顶点v5 7 7 顶点v6 7 10 顶点v7 16 16 顶点v8 14 14 顶点v9 18 18 活动: 弧a1 early(i)=0 late(i)=0 late(i)-early(i)=0 弧a2 early(i)=0 late(i)=2 late(i)-early(i)=2 弧a3 early(i)=0 late(i)=3 late(i)-early(i)=3 弧a4 early(i)=6 late(i)=6 late(i)-early(i)=0 弧a5 early(i)=4 late(i)=6 late(i)-early(i)=2 弧a6 early(i)=5 late(i)=8 late(i)-early(i)=3 弧a9 early(i)=7 late(i)=10 late(i)-early(i)=3 弧a7 early(i)=7 late(i)=7 late(i)-early(i)=0 弧a8 early(i)=7 late(i)=7 late(i)-early(i)=0 弧a11 early(i)=14 late(i)=14 late(i)-early(i)=0 弧a10 early(i)=16 late(i)=16 late(i)-early(i)=0 |
完整代码见6.2.3小节十字链表的数据结构实现。
小结
在图形结构中,结点之间的关系可以是任意的,图中任意两个元素之间都可能相关,因此图比线性表和树形结构复杂。而图的应用极为广泛,特别是近年来图的迅速发展,已渗入到诸如语言学、逻辑学、物理、化学、电信工程、计算机科学以及数学的其他分支中。本章主要从图的概念入手,介绍图的存储结构,讨论图的遍历及有关算法。
在这一章里,重点介绍了图的基本概念和一些重要的图结构上的运算。在实际应用中,图是一种非常重要的抽象数据结构,有着广泛的用途,许多客观事物及其关系可以抽象地用图来表示,这些事物或关系的一些性质就可以通过图的算法进行处理。
本章中的重点是:图的邻接矩阵和邻接表两种存储表示;图的深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索遍历算法、生成树和最小生成树以及Prim和Kruskal算法思想,并能够应用这些算法给出给定图的深度优先、广度优先遍历序列和构造最小生成树。
本章中还介绍了求最短路径的Djkstra算法和拓扑排序算法的基本思想,这些也是需要掌握和理解的内容。