netty是异步非阻塞通信领域的经典之作,优点分为内存模型、线程模型、任务调度,通过对源码的研究可以跟深入理解设计,提高java水平.
如果理解有错的地方希望大家能指出。
分析的顺序是整体看各对象的关系,在每个对象具体研究
以netty提供的EchoServer为切入点吧,
//配置服务器参数
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
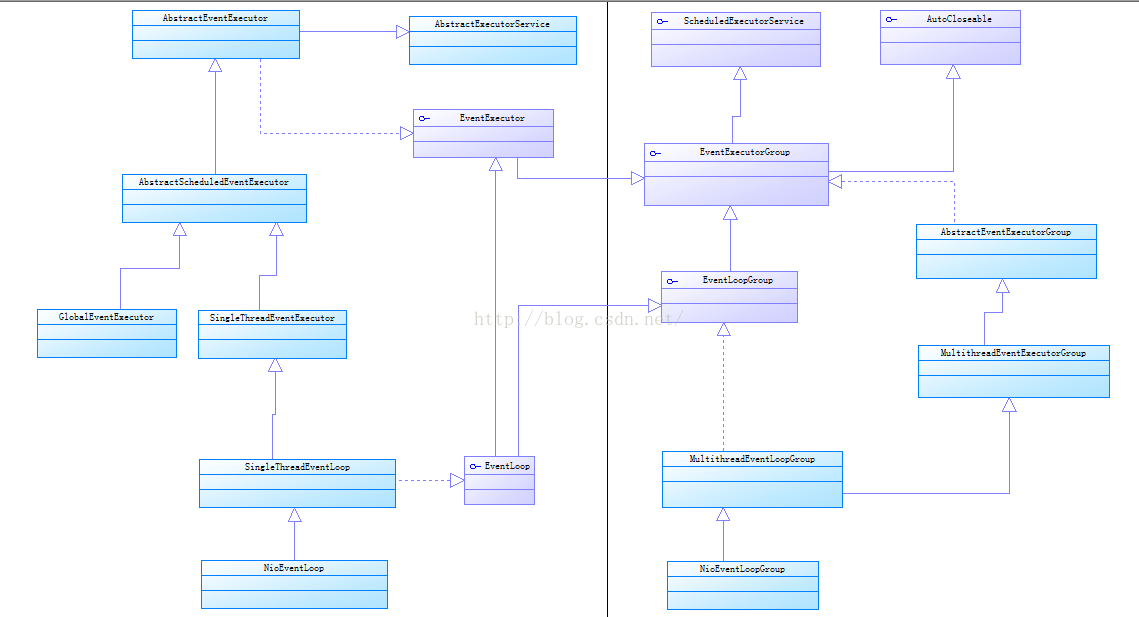
先围绕着EventLoopGroup来分析一下所有关联的对象
先看下它的结构
EventLoopGroup继承EventExecutorGroup,EventExecutorGroup继承ScheduledExecutorService,说明它是个延迟或定期执行的任务的ExecutorService,另一个java.lang.AutoCloseable为1.7新加的特性用于try-with-resources块自动关闭资源的
EventExecutorGroup通过next()方法能获取EventExecutor,EventExecutorGroup用来管理EventExecutor
public interface EventExecutorGroup extends ScheduledExecutorService, AutoCloseable {
boolean isShuttingDown();
Future<?> shutdownGracefully(); //给调用EventExecutor发送关闭信号,此方法被调用后isShuttingDown()为返回true,关闭Executor前确保没有task被提交,如何确保?里面有个'the quiet period',什么意思?此方法替代ScheduledExecutorService的shutdown(),因为ExecutorService的shutdown无法保证能够停止正在处理的活动执行任务,但是会尽力尝试
Future<?> shutdownGracefully(long quietPeriod, long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
Future<?> terminationFuture(); //通知所有EventExecutor结束任务
EventExecutor next();
...
}
EventLoopGroup是针对Channel的EventExecutorGroup,用于注册Channel,对next()做了重写,新加2个方法,注册channel和promise
public interface EventLoopGroup extends EventExecutorGroup {
@Override
EventLoop next();
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel);
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel, ChannelPromise promise);
}
EventExecutor也是一种EventExecutorGroup,它的next()返回的是自己
public interface EventExecutor extends EventExecutorGroup {
@Override
EventExecutor next(); //next返回的自己
@Override
<E extends EventExecutor> Set<E> children(); //返回包含自己的unmodifiable 独立set
EventExecutorGroup parent(); //返回当前EventExecutor的父EventExecutorGroup
boolean inEventLoop();//判断当前线程Thread#currentThread()是否允许在event loop中
boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread); //判断指定Thread是否在event loop中
EventExecutor unwrap(); //返回包装WrappedEventExecutor下的底层的EventExecutor,如果不是WrappedEventExecutor返回本身
<V> Promise<V> newPromise(); //返回一个新的Promise
<V> ProgressivePromise<V> newProgressivePromise(); //返回一个新的ProgressivePromise
<V> Future<V> newSucceededFuture(V result); //创建一个标记为succeeded的Futrue,isSuccess()方法返回true,所有添加在此Futrue上的FutureListener都被触发notify,FutureListener继承java.util.EventListener
<V> Future<V> newFailedFuture(Throwable cause);//创建一个标记为failed的Futrue,isSuccess()方法返回false,所有添加在此Futrue上的FutureListener都被触发notify,FutureListener继承java.util.EventListener
}
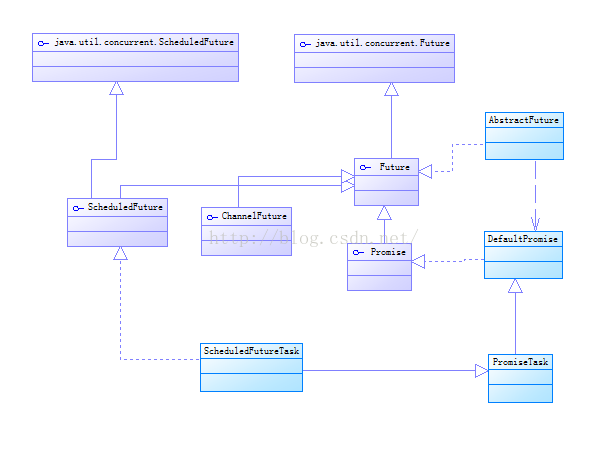
Promise结构关系看图
Futrue接口,异步操作结果
public interface Future<V> extends java.util.concurrent.Future<V> {
boolean isSuccess(); //IO操作完成返回true
boolean isCancellable(); //操作是否能被取消
Throwable cause(); //返回IO操作失败的异常原因
Future<V> addListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener); //给当前Future添加监听,当Future的isDone()为true是立即出发监听
Future<V> addListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);//批量添加监听
Future<V> removeListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener);//移除当前Future监听,不在给监听发送通知
Future<V> removeListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);//批量移除
Future<V> sync() throws InterruptedException;//Waits for this future until it is done,and rethrows the cause of the failure if this future failed
Future<V> syncUninterruptibly(); //Waits for this future until it is done,and rethrows the cause of the failure if this future failed
Future<V> await() throws InterruptedException; //等待当前Future完成
Future<V> awaitUninterruptibly(); //Waits for this future to be completed without interruption
boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; //设置超时时间
boolean await(long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException; //超时时间毫秒单位
boolean awaitUninterruptibly(long timeout, TimeUnit unit); //非打扰的等待,死等...
boolean awaitUninterruptibly(long timeoutMillis);
V getNow();//非阻塞获取结果,Future没完成返回null,null也可能是返回值,所以要先通过isDone()确定null的意义
@Override
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning); //成功取消正在运行的任务会抛出CancellationException
}
Promise接口,一个可写的特殊Future
public interface Promise<V> extends Future<V> {
Promise<V> setSuccess(V result); //能设置Future的Success,通知所有监听,如果Future已经完成或者失败抛出IllegalStateException
boolean trySuccess(V result);//
Promise<V> setFailure(Throwable cause);
boolean tryFailure(Throwable cause);
boolean setUncancellable(); //标记Future不能取消
@Override
Promise<V> addListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener);
@Override
Promise<V> addListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);
@Override
Promise<V> removeListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener);
@Override
Promise<V> removeListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);
@Override
Promise<V> await() throws InterruptedException;
@Override
Promise<V> awaitUninterruptibly();
@Override
Promise<V> sync() throws InterruptedException;
@Override
Promise<V> syncUninterruptibly();
}
ProgressiveFuture属于Future,用于标记操作过程
public interface ProgressiveFuture<V> extends Future<V> {
@Override
ProgressiveFuture<V> addListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener);
@Override
ProgressiveFuture<V> addListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);
@Override
ProgressiveFuture<V> removeListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener);
@Override
ProgressiveFuture<V> removeListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);
@Override
ProgressiveFuture<V> sync() throws InterruptedException;
@Override
ProgressiveFuture<V> syncUninterruptibly();
@Override
ProgressiveFuture<V> await() throws InterruptedException;
@Override
ProgressiveFuture<V> awaitUninterruptibly();
}
ProgressivePromise可写的ProgressiveFuture
public interface ProgressivePromise<V> extends Promise<V>, ProgressiveFuture<V> {
ProgressivePromise<V> setProgress(long progress, long total); //设置当前操作进度,通知GenericProgressiveFutureListener干活
boolean tryProgress(long progress, long total); //试图设置进度,通知GenericProgressiveFutureListener,如果操作已经完成或者进度超了,this method does nothing but returning {@code false}.
@Override
ProgressivePromise<V> setSuccess(V result);
@Override
ProgressivePromise<V> setFailure(Throwable cause);
@Override
ProgressivePromise<V> addListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener);
@Override
ProgressivePromise<V> addListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);
@Override
ProgressivePromise<V> removeListener(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>> listener);
@Override
ProgressivePromise<V> removeListeners(GenericFutureListener<? extends Future<? super V>>... listeners);
@Override
ProgressivePromise<V> await() throws InterruptedException;
@Override
ProgressivePromise<V> awaitUninterruptibly();
@Override
ProgressivePromise<V> sync() throws InterruptedException;
@Override
ProgressivePromise<V> syncUninterruptibly();
}
GenericFutureListener监听Future结果,异步结果被通知到Future#addListener(GenericFutureListener)进来的listener
public interface GenericFutureListener<F extends Future<?>> extends EventListener {
//@param future 被回调的Future
void operationComplete(F future) throws Exception;//跟Future有关的操作完成时调用
}
以上是几个主要的接口功能定义,下面看具体实现
下面看EventLoopGroup的实现类NioEventLoopGroup,NioEventLoopGroup结合Channel用做Nio Selector,AbstractEventExecutorGroup抽象类对EventExecutorGroup做了一次代理,通过next()把调度任务转到EventExecutor
部分代码
public abstract class AbstractEventExecutorGroup implements EventExecutorGroup {
@Override
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
return next().submit(task);
}
@Override
public <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result) {
return next().submit(task, result);
}
@Override
public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
return next().submit(task);
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return next().schedule(command, delay, unit);
}
...
}
下面看下new NioEventLoopGroup(1);够着到底干了哪些事
public class NioEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventLoopGroup {
...
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nEventLoops) {
this(nEventLoops, (Executor) null);
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nEventLoops, Executor executor) {
this(nEventLoops, executor, SelectorProvider.provider());
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nEventLoops, Executor executor, final SelectorProvider selectorProvider) {
super(nEventLoops, executor, selectorProvider);
}
...
}
空的Excutor,并在这创建了SelectorProvider,接着调用父类的构造
public abstract class MultithreadEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventExecutorGroup implements EventLoopGroup {
private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS;
static {
DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt(
"io.netty.eventLoopThreads", Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2));
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.eventLoopThreads: {}", DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS);
}
}
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nEventLoops, Executor executor, Object... args) {
super(nEventLoops == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nEventLoops, executor, args);
}
...
}
构造NioEventLoopGroup传入的nEventLoops数量不传就是取系统设置io.netty.eventLoopThreads,没有就默认cpu数*2,此处的args为SelectorProvider.provider()选择器服务类,接着看父类MultithreadEventExecutorGroup
public abstract class MultithreadEventExecutorGroup extends AbstractEventExecutorGroup {
...
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nEventExecutors, Executor executor, Object... args) {
this(nEventExecutors, executor, false, args);
}
private MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nEventExecutors,
Executor executor,
boolean shutdownExecutor,
Object... args) {
if (nEventExecutors <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
String.format("nEventExecutors: %d (expected: > 0)", nEventExecutors));
}
if (executor == null) { //NioEventLoopGroup构造时传入的executor为空,此处将创建系统默认Executor
executor = newDefaultExecutorService(nEventExecutors); //此处的ThreadFacotroy产生的ForkJoinWorkerThread
shutdownExecutor = true; //系统默认的Executor将会在任务执行完毕后关闭
}
children = new EventExecutor[nEventExecutors];
if (isPowerOfTwo(children.length)) {
chooser = new PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser();
} else {
chooser = new GenericEventExecutorChooser();
}
for (int i = 0; i < nEventExecutors; i ++) {
boolean success = false;
try {
children[i] = newChild(executor, args); //子类实现具体的EventExecutor,传入的executor为ForkJoinPool,args为SelectorProvider
success = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: Think about if this is a good exception type
throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);
} finally {
if (!success) { //只要发现有创建失败的,之前创建的都shutdown
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
children[j].shutdownGracefully();
}
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {//再次检查等待打断任务
EventExecutor e = children[j];
try {
while (!e.isTerminated()) {
e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {
// Let the caller handle the interruption.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
final boolean shutdownExecutor0 = shutdownExecutor;
final Executor executor0 = executor;
//创建terminationListener
final FutureListener<Object> terminationListener = new FutureListener<Object>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Object> future) throws Exception {
if (terminatedChildren.incrementAndGet() == children.length) {
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
if (shutdownExecutor0) {
// This cast is correct because shutdownExecutor0 is only try if
// executor0 is of type ExecutorService.
((ExecutorService) executor0).shutdown();
}
}
}
};
//每个EventExecutor都添加这个监听EventListener
for (EventExecutor e: children) {
e.terminationFuture().addListener(terminationListener);
}
//浅拷贝一份EventExecutor
Set<EventExecutor> childrenSet = new LinkedHashSet<EventExecutor>(children.length);
Collections.addAll(childrenSet, children);
readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet);
}
protected ExecutorService newDefaultExecutorService(int nEventExecutors) {
return new DefaultExecutorServiceFactory(getClass()).newExecutorService(nEventExecutors);
}
//2的指数
private static boolean isPowerOfTwo(int val) {
return (val & -val) == val;
}
private interface EventExecutorChooser {
EventExecutor next();
}
//指定2种选择方式的原因?
private final class PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser implements EventExecutorChooser {
@Override
public EventExecutor next() {
return children[childIndex.getAndIncrement() & children.length - 1];
}
}
private final class GenericEventExecutorChooser implements EventExecutorChooser {
@Override
public EventExecutor next() {
return children[Math.abs(childIndex.getAndIncrement() % children.length)];
}
}
}
上面创建Executor的方式new DefaultExecutorServiceFactory(getClass()).newExecutorService(nEventExecutors),DefaultExecutorServiceFactory创建ForkJoinPool,默认为netty nio ,epoll 事件轮训提供支持,创建出来的线程都是Thread.MAX_PRIORITY优先级比较高
public final class DefaultExecutorServiceFactory implements ExecutorServiceFactory {
...
public ExecutorService newExecutorService(int parallelism) {
ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory threadFactory =
new DefaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory(namePrefix + '-' + executorId.getAndIncrement());
return new ForkJoinPool(parallelism, threadFactory, DefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler.INSTANCE, true);
}
//ThreadFactory,线程工厂
private static final class DefaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory implements ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory {
private final AtomicInteger idx = new AtomicInteger();
private final String namePrefix;
DefaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory(String namePrefix) {
this.namePrefix = namePrefix;
}
@Override
public ForkJoinWorkerThread newThread(ForkJoinPool pool) {
// Note: The ForkJoinPool will create these threads as daemon threads.
ForkJoinWorkerThread thread = new DefaultForkJoinWorkerThread(pool);
thread.setName(namePrefix + '-' + idx.getAndIncrement());
thread.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); //Thread.MAX_PRIORITY
return thread;
}
}
//实现FastThreadLocalAccess,通过ThreadLocal获取
private static final class DefaultForkJoinWorkerThread
extends ForkJoinWorkerThread implements FastThreadLocalAccess {
private InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap;
DefaultForkJoinWorkerThread(ForkJoinPool pool) {
super(pool);
}
@Override
public InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap() {
return threadLocalMap;
}
@Override
public void setThreadLocalMap(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
this.threadLocalMap = threadLocalMap;
}
}
}
ForkJoinPool继承java.util.concurrent.AbstractExecutorService,后面在分析doug lea大神写的类
我们在回到NioEventLoopGroup看下如何创建的EventLoop
@Override
protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {
return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, (SelectorProvider) args[0]);
}
直接new的NioEventLoop,下片文章开始围绕 NioEventLoop分析