参考ROS教程:http://wiki.ros.org/ROS/Tutorials,通过下面例子,学习如何创建节点和通过topic通信。
创建ROS功能包
在建立的工作空间创建新的功能包:
$ cd ~/dev/catkin_ws/src
$ catkin_create_pkg [package_name] [depend1] [depend2] [depend3]
依赖项包括:
- std_msgs
- roscpp
- rospy
编译功能包
$ cd ~/dev/catkin_ws
$ catkin_make
如果上述步骤能正确执行,结果如下图所示:
创建节点
Writing the Publisher Node
“Node” is the ROS term for an executable that is connected to the ROS network. Here we’ll create a publisher (“talker”) node which will continually broadcast a message.
代码如下:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2008, Morgan Quigley and Willow Garage, Inc.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
* documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* * Neither the names of Stanford University or Willow Garage, Inc. nor the names of its
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
* this software without specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
* AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
* IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
* ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE
* LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
* CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF
* SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS
* INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
* CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)
* ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*/
// %Tag(FULLTEXT)%
// %Tag(ROS_HEADER)%
#include "ros/ros.h"
// %EndTag(ROS_HEADER)%
// %Tag(MSG_HEADER)%
#include "std_msgs/String.h"
// %EndTag(MSG_HEADER)%
#include <sstream>
/**
* This tutorial demonstrates simple sending of messages over the ROS system.
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
/**
* The ros::init() function needs to see argc and argv so that it can perform
* any ROS arguments and name remapping that were provided at the command line.
* For programmatic remappings you can use a different version of init() which takes
* remappings directly, but for most command-line programs, passing argc and argv is
* the easiest way to do it. The third argument to init() is the name of the node.
*
* You must call one of the versions of ros::init() before using any other
* part of the ROS system.
*/
// %Tag(INIT)%
ros::init(argc, argv, "talker");
// %EndTag(INIT)%
/**
* NodeHandle is the main access point to communications with the ROS system.
* The first NodeHandle constructed will fully initialize this node, and the last
* NodeHandle destructed will close down the node.
*/
// %Tag(NODEHANDLE)%
ros::NodeHandle n;
// %EndTag(NODEHANDLE)%
/**
* The advertise() function is how you tell ROS that you want to
* publish on a given topic name. This invokes a call to the ROS
* master node, which keeps a registry of who is publishing and who
* is subscribing. After this advertise() call is made, the master
* node will notify anyone who is trying to subscribe to this topic name,
* and they will in turn negotiate a peer-to-peer connection with this
* node. advertise() returns a Publisher object which allows you to
* publish messages on that topic through a call to publish(). Once
* all copies of the returned Publisher object are destroyed, the topic
* will be automatically unadvertised.
*
* The second parameter to advertise() is the size of the message queue
* used for publishing messages. If messages are published more quickly
* than we can send them, the number here specifies how many messages to
* buffer up before throwing some away.
*/
// %Tag(PUBLISHER)%
ros::Publisher chatter_pub = n.advertise<std_msgs::String>("chatter", 1000);
// %EndTag(PUBLISHER)%
// %Tag(LOOP_RATE)%
ros::Rate loop_rate(10);
// %EndTag(LOOP_RATE)%
/**
* A count of how many messages we have sent. This is used to create
* a unique string for each message.
*/
// %Tag(ROS_OK)%
int count = 0;
while (ros::ok())
{
// %EndTag(ROS_OK)%
/**
* This is a message object. You stuff it with data, and then publish it.
*/
// %Tag(FILL_MESSAGE)%
std_msgs::String msg;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "hello world " << count;
msg.data = ss.str();
// %EndTag(FILL_MESSAGE)%
// %Tag(ROSCONSOLE)%
ROS_INFO("%s", msg.data.c_str());
// %EndTag(ROSCONSOLE)%
/**
* The publish() function is how you send messages. The parameter
* is the message object. The type of this object must agree with the type
* given as a template parameter to the advertise<>() call, as was done
* in the constructor above.
*/
// %Tag(PUBLISH)%
chatter_pub.publish(msg);
// %EndTag(PUBLISH)%
// %Tag(SPINONCE)%
ros::spinOnce();
// %EndTag(SPINONCE)%
// %Tag(RATE_SLEEP)%
loop_rate.sleep();
// %EndTag(RATE_SLEEP)%
++count;
}
return 0;
}
// %EndTag(FULLTEXT)%
代码详解:
关键是设置节点进程的句柄:
ros::Publisher chatter_pub = n.advertise<std_msgs::String>(“chatter”, 1000);
将节点设置成发布者,并将所发布主题和类型的名称告知节点管理器。
Writing the Subscriber Node
代码如下:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2008, Morgan Quigley and Willow Garage, Inc.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
* documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* * Neither the names of Stanford University or Willow Garage, Inc. nor the names of its
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
* this software without specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
* AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
* IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
* ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE
* LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
* CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF
* SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS
* INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
* CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)
* ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*/
// %Tag(FULLTEXT)%
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "std_msgs/String.h"
/**
* This tutorial demonstrates simple receipt of messages over the ROS system.
*/
// %Tag(CALLBACK)%
void chatterCallback(const std_msgs::String::ConstPtr& msg)
{
ROS_INFO("I heard: [%s]", msg->data.c_str());
}
// %EndTag(CALLBACK)%
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
/**
* The ros::init() function needs to see argc and argv so that it can perform
* any ROS arguments and name remapping that were provided at the command line.
* For programmatic remappings you can use a different version of init() which takes
* remappings directly, but for most command-line programs, passing argc and argv is
* the easiest way to do it. The third argument to init() is the name of the node.
*
* You must call one of the versions of ros::init() before using any other
* part of the ROS system.
*/
ros::init(argc, argv, "listener");
/**
* NodeHandle is the main access point to communications with the ROS system.
* The first NodeHandle constructed will fully initialize this node, and the last
* NodeHandle destructed will close down the node.
*/
ros::NodeHandle n;
/**
* The subscribe() call is how you tell ROS that you want to receive messages
* on a given topic. This invokes a call to the ROS
* master node, which keeps a registry of who is publishing and who
* is subscribing. Messages are passed to a callback function, here
* called chatterCallback. subscribe() returns a Subscriber object that you
* must hold on to until you want to unsubscribe. When all copies of the Subscriber
* object go out of scope, this callback will automatically be unsubscribed from
* this topic.
*
* The second parameter to the subscribe() function is the size of the message
* queue. If messages are arriving faster than they are being processed, this
* is the number of messages that will be buffered up before beginning to throw
* away the oldest ones.
*/
// %Tag(SUBSCRIBER)%
ros::Subscriber sub = n.subscribe("chatter", 1000, chatterCallback);
// %EndTag(SUBSCRIBER)%
/**
* ros::spin() will enter a loop, pumping callbacks. With this version, all
* callbacks will be called from within this thread (the main one). ros::spin()
* will exit when Ctrl-C is pressed, or the node is shutdown by the master.
*/
// %Tag(SPIN)%
ros::spin();
// %EndTag(SPIN)%
return 0;
}
// %EndTag(FULLTEXT)%
代码详解:
创建一个订阅者,并从主题获取message为名称的消息数据,处理消息的回调函数为messageCallback:
ros::Subscriber sub = n.subscribe(“chatter”, 1000, chatterCallback);
Now that you have written a simple publisher and subscriber, let’s examine the simple publisher and subscriber.
编译节点
编译之前,我们需要修改一个CMakeLists.txt和package.xml文件。然后,运行:
$ catkin_make [package_name]
接下来执行如下操作:(注意在不同的终端)
$ roscore
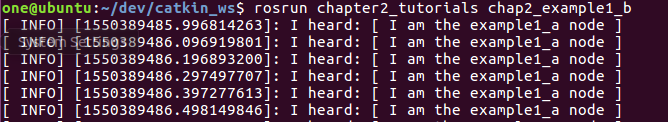
$ rosrun chapter2_tutorials chap2_example1_a
$ rosrun chapter2_tutorials chap2_example1_b
如果tab无法补全,试着先执行这条指令:
($ source ~/dev/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash)
也可以使用rosnode和rostopic命令来查看当前节点的运行状态,尝试使用以下命令:
$ rosnode list
$ rostopic list
$ rqt_graph
上面的操作已经完成了节点之间通信,后续还有更多有趣的操作,今天要讲的就这么多。
最后,通过今天的操作我们也慢慢理解了ROS作为一个机器人的操作系统,其主要思想:
ROS的核心是一个分布式、低耦合的通讯机制。