 版权声明:署名,允许他人基于本文进行创作,且必须基于与原先许可协议相同的许可协议分发本文 (Creative Commons)
版权声明:署名,允许他人基于本文进行创作,且必须基于与原先许可协议相同的许可协议分发本文 (Creative Commons)
学校在拍年度纪念照时,一般要求学生按照 非递减 的高度顺序排列。
请你返回至少有多少个学生没有站在正确位置数量。该人数指的是:能让所有学生以 非递减 高度排列的必要移动人数。

解答:
class Solution {
public int heightChecker(int[] heights) {
int[] copy = Arrays.copyOf(heights, heights.length);
Arrays.sort(copy);
int diff = 0;
for (int count = 0; count < heights.length; count++) {
if (heights[count] != copy[count]) {
diff++;
}
}
return diff;
}
}
思路:
这道题思路是比较简单的,但是这里记录下Arrays的API的回顾:

Arrays在解答LeetCode的数组相关的题中还是比较有用处的 关注它的方法:
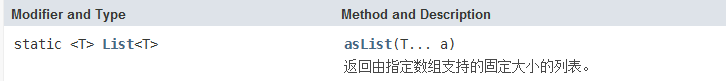
这个可以用于数组转List集合框架
但是需要注意的是
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,2,3,4};
List list = Arrays.asList(a);
System.out.println(list.size()); //1
}
}
期望的输出是 list里面也有4个元素,也就是size为4,然而结果是1.
原因如下:
在Arrays.asList中,该方法接受一个变长参数,一般可看做数组参数,但是因为int[] 本身就是一个类型,所以a变量作为参数传递时,编译器认为只传了一个变量,这个变量的类型是int数组,所以size为1,相当于是List中数组的个数。基本类型是不能作为泛型的参数,按道理应该使用包装类型,但这里缺没有报错,因为数组是可以泛型化的,所以转换后在list中就有一个类型为int的数组
/**
* Returns a fixed-size list backed by the specified array. (Changes to
* the returned list "write through" to the array.) This method acts
* as bridge between array-based and collection-based APIs, in
* combination with {@link Collection#toArray}. The returned list is
* serializable and implements {@link RandomAccess}.
*
* <p>This method also provides a convenient way to create a fixed-size
* list initialized to contain several elements:
* <pre>
* List<String> stooges = Arrays.asList("Larry", "Moe", "Curly");
* </pre>
*
* @param a the array by which the list will be backed
* @return a list view of the specified array
*/
@SafeVarargs
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) {
return new ArrayList<>(a);
}
返回一个受指定数组支持的固定大小的列表。(对返回列表的更改会“直写”到数组。)此方法同 Collection.toArray 一起,充当了基于数组的 API 与基于 collection 的 API 之间的桥梁。返回的列表是可序列化的.
所以,如果是创建多个列表,在传参数时候,最好使用Arrays.copyOf(a)方法,不然,对列表的更改就相当于对数组的更改。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] a = {1,2,3,4};
List list = Arrays.asList(a);
System.out.println(list.size()); //4
}
}
最后提醒,如果Integer[]数组没有赋值的话,默认是null,而不是像int[]数组默认是0。
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
6787783 查看本文章


下面这个用的挺多的,复制数组。解答这道题 就是使用了这个

这个带有范围:

这个则是比较元素

这个是用于排序:
