“当你越来越优秀的时候就会遇见越来越好的人。”你好,我是梦阳辰,和我一起加油吧!
【问题提出】
之前我们连接数据库,都会执行一次创建和断开Connection对象的操作,这样频繁的操作十分影响数据库的访问效率,并且增加了代码量。
这就好比,你开一个饭店,当客人来了,你招一个服务员为客人提供服务,当客人走了,你就把服务员开了。
文章目录
01.为什么要数据库连接池
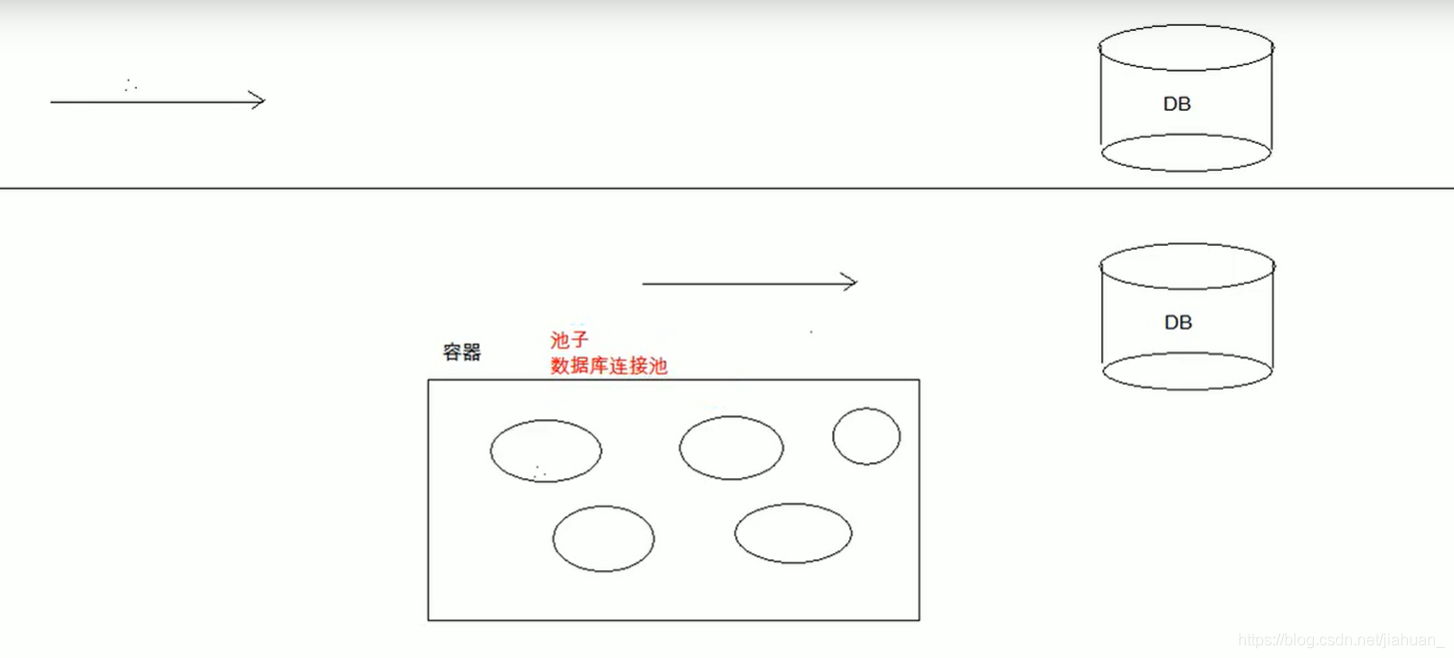
为了避免频繁的创建数据库连接,数据库连接池应运而生。数据库连接池负责分配、管理和释放数据库连接。它允许应用程序重复使用现有的数据库连接,而不是重新建立。
数据库连接池在初始化的时候创建一定数量的数据库连接放到数据库连接池中,当应用程序访问时向连接池申请一个Connection。如果有空闲的Connection,则将其返回,否则创建新的Connection。使用完毕后,连接池会将该Connection收回,交付给其它线程使用,以减少创建数据库连接的次数,提高数据库访问的效率。
数据库连接池
概念:其实就是一个容器(集合),存放数据库连接的容器。
特点:节约了资源,用户访问高效。
02.数据库连接池的实现
标准接口:DataSource接口
在javax.sql包下。
为了获取数据库连接对象,JDBC提供了javax.sql。DataSource接口,他负责与数据库建立连接,并定义了返回值为Connection对象的方法。
1.方法:
获取连接: Connection getConnection() Connection getConnection(String username, String password) 归还连接:如果连接对象Connection时是从连接池中获取的, 那么调用Connection.close()方法,则不会再关闭连接了。 而是归还连接
2.一般我们不去实现它,由数据库厂商来实现。
通常把实现了DataSource接口的类称为数据源,数据源存储了所有建立数据库连接的信息。数据源中包含数据库连接池。
常用的
03.C3P0:数据库连接池技术
步骤:
1.导入jar包:c3p0-0.9.5.2.jar mchange-commons-java-0.2.12.jar
2.定义配置文件(自动加载)
名称:c3p0.properties 或者 c3p0-config.xml
路径:直接将文件放在src目录下。
3.创建核心对象,数据库连接池对象 ComboPooledDataSource
DataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
4.获取数据库连接对象
Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
5.剩下操作跟基本操作相同。
@WebServlet("/C3p0ServletTest1")public class C3p0ServletTest1 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
//1.创建数据库连接池对象
DataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstat = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//2.获取连接对象
conn = ds.getConnection();
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from student where sex =?";
//4.获取执行sql的对象
pstat = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstat.setString(1, "男");
//5.执行sql
rs = pstat.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
String sequence = rs.getString("sequence");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String sex = rs.getString("sex");
out.println("<p>" + sequence + " " + name + " " + sex + "<p>");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
if(pstat!=null){
try {
pstat.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws
ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}}
04.Druid:数据库连接池实现技术
Druid由阿里巴巴提供。
步骤:
1.导入jar包:druid-1.0.9.jar。
2.定义配置文件:
是proporties形式。
名称:可以交任意名称,可以放在任意目录下(需要手动加载)
3.获取数据库连接池对象:通过工厂类来获取
DruidDataSourceFactory
4.获取连接
5.其他的步骤相同
@WebServlet("/DruidServletTest1")public class DruidServletTest1 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
DataSource ds = null;
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstat = null;
//1.加载配置文件
Properties pro = new Properties();
InputStream is = DruidServletTest1.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
pro.load(is);
//2.获取连接池对象
try {
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
//5.获取连接
conn = ds.getConnection();
//3.定义sql
String sql = "update student set name=? where birthday=?";
//4.获取执行sql的对象
pstat = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstat.setString(1, "梦阳辰");
pstat.setString(2,"1999-10-18");
//5.执行sql
int count = pstat.executeUpdate();
if(count>0){
out.print("修改成功!");
}else{
out.print("修改失败!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(pstat!=null){
try {
pstat.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}}
2.定义工具类,简化开发
定义一个JDBCUtils类。
提供方法:
1.获取连接的方法:通过数据库连接池获取。
2.释放资源
3.获取连接池的方法。
/**
* Druid连接池的工具类
*/public class JdbcUtils {
//1.定义成员变量DateaSource
private static DataSource ds;
static {
try{
//1.加载配置文件
Properties pro = new Properties();
InputStream is = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
pro.load(is);
//2.获取DataSource
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取连接
*/
public static Connection getConntion() throws SQLException {
return ds.getConnection();
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
public static void close(Statement stmt,Connection conn){
/* if(stmt!=null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){//归还连接
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}*/
close(null,stmt,conn);
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement stmt, Connection conn){
if(rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(stmt!=null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){//归还连接
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 获取连接池
*/
public static DataSource getDataSource(){
return ds;
}}
05.Spring JDBC
JDBC已经能够满足大部分用户最基本的需求,但是在使用JDBC时,必须自己来管理数据库资源如:获取 PreparedStatement,设置SQL语句参数,关闭连接等步骤。JdbcTemplate就是Spring对JDBC的封装,目的是使 JDBC更加易于使用。JdbcTemplate是Spring的一部分。 JdbcTemplate处理了资源的建立和释放。他帮助我们避免一些常见的错误,比如忘了总要关闭连接。他运行核心的JDBC工作流,如Statement的建立和执行,而我们只需 要提供SQL语句和提取结果。
JDBC的工具类,目的是为了简化开发步骤。
Spring框架对JDBC的简单框架,提供了一个JdbcTemplate对象简化JDBC的开发。
步骤:
1.导入jar包。
2.创建JdbcTemplate对象,依赖于数据源DataSource。
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(ds);
3.调用JdbcTemplate的方法来完成CRUD的操作。
update():执行DML语句(insert,update,delete)。 queryForMap():查询结果将结果封装为map集合。结果只能为1条, 列名为key,值为value queryForList():查询结果将结果集封装为list集合。 先将数据封装为一个Map集合,再将Map集合转载到List集合中 query():查询结果,将结果封装为JavaBean对象。(重点) 一般我们使用BeanPropertyRowMapper实现类。 可以完成到JavaBean的自动封装。 new BeanPropertyRowMapper<类型>(类型.class) queryForObject:查询结果,将结果封装为对象。 一般用于聚合函数的查询
update()练习:
@WebServlet("/jdbcTemplateServletTest1")public class jdbcTemplateServletTest1 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
//1.导入jar包
//2.创建JdbcTemplate对象
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
//定义sql
String sql = "insert into student(sequence,sex,name,birthday) values(?,?,?,?)";
//调用方法
int count = template.update(sql,"101000","男","张三","2020-11-19");
out.print(count);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}}
queryForMap()练习:
@WebServlet("/jdbcTemplateServletTestl2")public class jdbcTemplateServletTestl2 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
String sql = "select * from student where id = ?";
//只能封装1条
Map<String,Object> map =template.queryForMap(sql,1);
out.print(map);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}}
queryForList()练习:
@WebServlet("/jdbcTemplateServletTestl2")public class jdbcTemplateServletTestl2 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
String sql = "select * from student where id > ?";
List<Map<String,Object>> list =template.queryForList(sql,1);
for(Map<String,Object> StringObjectMap:list){
out.print("<p>"+StringObjectMap+"</p>");
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}}
将Map转换成JSON格式:
String sql="select * from student where id > ?"; List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql,1); Map<String, Object> map = maps.get(2); JSONObject jsonObject=new JSONObject(map); System.out.println(jsonObject.toJSONString());
query练习:
@WebServlet("/jdbcTemplateServletTest2")public class jdbcTemplateServletTest2 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
String sql = "select * from student ";
List<Student> list = template.query(sql, new RowMapper<Student>() {
@Override
public Student mapRow(ResultSet rs, int i) throws SQLException {
Student student = new Student();
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String sequence = rs.getString("sequence");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String sex = rs.getString("sex");
Date birthday = rs.getDate("birthday");
student.setId(id);
student.setSequence(sequence);
student.setName(name);
student.setSex(sex);
student.setBirthday(birthday);
return student;
}
});
for(Student student :list){
out.print(student);
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}}
存在的问题:虽然我们用了Spring JDBC类,通过query练习但是我们并没有实现简化代码,跟以前差不多,那是因为我们自己去实现了 RowMapper接口, 其实JdbcTemplate已经帮我们实现了,我们直接使用就好了。
改进后:
@WebServlet("/JdbcTemplateServletTest3")public class JdbcTemplateServletTest3 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
String sql = "select * from student ";
List<Student> list = template.query(sql,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Student>(Student.class));
for(Student student:list){
out.print(list);
}
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}}
@WebServlet("/JdbcTemplateServletTest3")public class JdbcTemplateServletTest3 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
String sql = "select * from student where id =?";
//将查询结果封装成了java对象
List<Student> list = template.query(sql,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Student>(Student.class),"1");
out.print(list.get(0).getName());
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}}
注意JavaBean类,如果属性定义为基本类型,在查询数据库时,如果字段为空,会报错,可以将JavaBean属性基本类型改为引用数据类型。
queryForObject练习:
@WebServlet("/JdbcTemplateServletTest3")public class JdbcTemplateServletTest3 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
String sql ="select count(id) from student";
Long total = template.queryForObject(sql,Long.class);
out.print(total);
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request,response);
}}
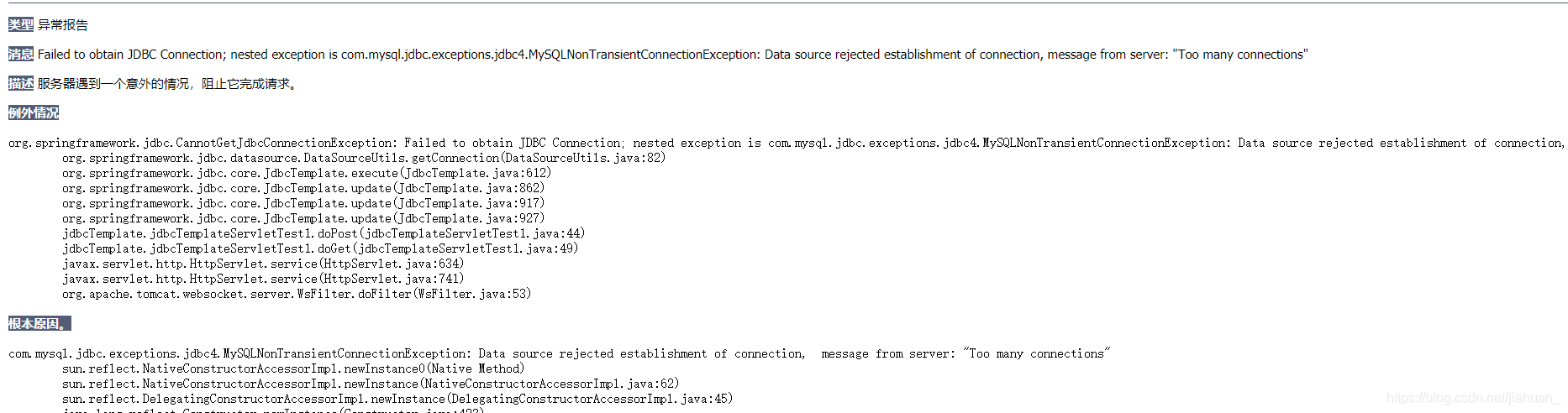
【提出问题】
如果这里不使用自定义工具类JdbcUtils得到连接池,而是直接获取连接池,多次访问后,则会出现too many connection情况。
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
06.登录案例
登录页面:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Insert title here</title><script src="../../case43/res/js/jquery.min.js"></script><style type="text/css">
p{
color:red;
}</style></head><body>
<form class="fm">
<div>
<label>账号:</label>
<input type="text" name="userName" id="userName">
</div>
<div>
<label>密码:</label>
<input type="password" name="passWord" id="passWord">
</div>
<input type="button" id="btn" value="确认">
</form>
<p id="p"></p>
<script>
$(function(){
$("#btn").click(function(){
var dataFm = $(".fm").serialize();
$.post(
"/teaching/com/teaching/homeWork/Check1",
dataFm,
function(data){
var json =JSON.parse(data);
if(json.success){
window.location.href= json.url;
}else{
$("#p").html("账号或密码错误!");
}
}
);
});
});
</script></body></html>
工具类:
/**
* Druid连接池的工具类
*/public class JdbcUtils {
//1.定义成员变量DateaSource
private static DataSource ds;
static {
try{
//1.加载配置文件
Properties pro = new Properties();
InputStream is =JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
pro.load(is);
//2.获取DataSource
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取连接
*/
public static Connection getConntion() throws SQLException {
return ds.getConnection();
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
public static void close(Statement stmt,Connection conn){
close(null,stmt,conn);
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement stmt, Connection conn){
if(rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(stmt!=null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){//归还连接
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 获取连接池
*/
public static DataSource getDataSource(){
return ds;
}}
处理request:
@WebServlet("/com/teaching/homeWork/Check1")public class Check1 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet()
*/
public Check1() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
* response)
*/
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String userName = request.getParameter("userName");
String passWord = request.getParameter("passWord");
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
//因为teaching表没有账号和密码字段,为了减少时间,默认将name作为账号,sequence作为密码
String sql = "select * from student where name = ? and sequence = ?";
//将查询结果封装成了java对象,如果没有执行成功会报异常(则会存在问题)
Student student = null;
try {
student =template.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Student>(Student.class),userName,passWord);
} catch (EmptyResultDataAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//Student student = template.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Student>(Student.class),userName,passWord);
if(student!=null&&userName.equals(student.getName())&&passWord.equals(student.getSequence())) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.setAttribute("userName",student.getName());
session.setAttribute("passWord",student.getSequence());//密码
//设置session存活时间
Cookie id = new Cookie("JSESSIONID",session.getId());
id.setMaxAge(60*60*24*10);//10天
response.addCookie(id); //转发
String url= request.getContextPath()+"/case631/homeWork/html/success.jsp";
request.setAttribute("success",true);
request.setAttribute("url",url);
request.setAttribute("student", student);
String url1 ="/com/teaching/homeWork/Json";
RequestDispatcher rd =request.getRequestDispatcher(url1);
rd.forward(request, response);
}else{//查询失败,转发到登录页面
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setName("null");
student1.setSequence("null");
request.setAttribute("success",false);
request.setAttribute("url","null");
request.setAttribute("student", student1);
String url1 ="/com/teaching/homeWork/Json";
RequestDispatcher rd =request.getRequestDispatcher(url1);
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
* response)
*/
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}}
JavaBean类:
package com.teaching.homeWork;import java.util.Date;/**
* javaBean
*/public class Student {
private Integer id;//为防止数据库字段为空,定义为应用数据类型
private String sequence;
private String name;
private String sex;
private Date birthday;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getSequence() {
return sequence;
}
public void setSequence(String sequence) {
this.sequence = sequence;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", sequence='" + sequence + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}}
response类:
@WebServlet("/com/teaching/homeWork/Json")public class Json extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet()
*/
public Json() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
*/
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
boolean success=(boolean)request.getAttribute("success");
String url=(String)request.getAttribute("url");
Student student = (Student)request.getAttribute("student");
String json="{"+"\""+"success"+"\":"+success+","+"\""+"url"+"\":"+"\""+url+"\""+","+"\""+"userName"+"\":"+"\""+student.getName()+"\""+","+"\""+"userName"+"\":"+"\""+student.getSequence()+"\""+"}";
System.out.print(json);
out.print(json);
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
*/
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}}
登录成功页面:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Insert title here</title></head><body><p><%=request.getSession().getAttribute("userName") %>>欢迎你!</p></body></html>
练习:
1.查询id为1的记录,将其封装为Map集合
2.查询所有记录,将其封装为List
3.查询所有记录,将其封装为Studentt对象的List集合
4.查询总记录数
要成功不需要什么特别的才能,只要把你能做的小事做得好就行了。
