简介
Splay是二叉搜索树的一种,也是平衡树的一种。其复杂度低的原因在于每次查找一个节点的时候,树都会重构使得深度降低,然后以后再访问周围的节点就会很快,不容易被卡。
既然是二叉搜索树,所以其每个节点最多只有2个子节点,且左儿子节点的值一定比它小,右儿子节点的值一定比它大。
例如:

节点结构
#define ls(x) T[x].ch[0]
#define rs(x) T[x].ch[1]
#define fa(x) T[x].fa
#define root T[0].ch[1]
struct node {
int fa; //父节点
int ch[2]; //0代表左儿子,1代表右儿子
int val; //权值
int rec; //这个权值的节点出现的次数
int size; //子节点的数量(包含这个点)
};
基本操作
ident
获取一个节点x是它父亲节点的哪个儿子
int ident(int x) {
return T[fa(x)].ch[0] == x ? 0 : 1;
}
update
更新一个节点x的值
void update(int x) {
T[x].size = T[ls(x)].size + T[rs(x)].size + T[x].rec;
}
rotate
把一个节点x和它的父亲节点交换位置。
假设有树:

把X和Y互换位置后:
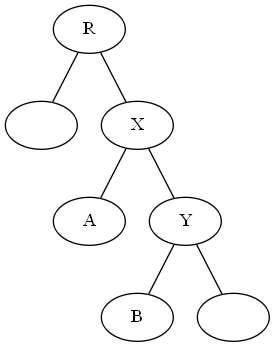
也可以描述为:
- B成为Y的哪个儿子与X是Y的哪个儿子是一样的
- Y成为X的哪个儿子与X是Y的哪个儿子是相反的
- X成为R的哪个儿子与Y是R的哪个儿子是一样的
void connect(int x, int fa, int how) {
T[fa].ch[how] = x;
T[x].fa = fa;
}
void rotate(int x) {
int Y = fa(x), R = fa(Y);
int Yson = ident(x), Rson = ident(Y);
connect(T[x].ch[Yson ^ 1], Y, Yson);
connect(Y, x, Yson ^ 1);
connect(x, R, Rson);
update(Y);
update(x);
}
splay
把一个节点x搬到to位置
为了方便操作,先把to赋值为to的父亲节点
to = fa(to);
int y = fa(x);
这时要分三种情况:
-
to是x的父亲节点
此时直接把x旋转上去即可
if (T[y].fa == to) rotate(x); -
x和x的父亲的父亲在一条直线上
此时应先把Y旋转上去,再把X旋转上去。(这里存疑,为啥直接旋转两次x就会T呢)
2020/10/25答疑,因为连续旋转两次x会形成直链,而直链是搜索树退化的关键原因。先旋转y再旋转x就能有效地避免直链
if (ident(x) == ident(y)) rotate(y), rotate(x); -
x和它父亲的父亲不在一条直线上
直接旋转两次x
rotate(x), rotate(x);
void splay(int x, int to) {
to = fa(to);
while (fa(x) != to) {
int y = fa(x);
if (T[y].fa == to)
rotate(x);
else if (ident(x) == ident(y))
rotate(y), rotate(x);
else
rotate(x), rotate(x);
}
}
newnode
新建节点:
int newnode(int v, int f) {
T[++tot].fa = f;
T[tot].rec = T[tot].size = 1;
T[tot].val = v;
return tot;
}
Insert
插入节点:
根据二叉搜索树的性质,找到节点要插入的位置,然后把它旋转到根节点的位置。
void Insert(int x) {
int now = root;
if (root == 0) {
newnode(x, 0); root = tot; }
else {
while (1) {
T[now].size++;
if (T[now].val == x) {
T[now].rec++;
splay(now, root);
return;
}
int nxt = x < T[now].val ? 0 : 1;
if (!T[now].ch[nxt]) {
int p = newnode(x, now);
T[now].ch[nxt] = p;
splay(p, root);
return;
}
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
}
}
find
找到值为x的节点
根据二叉搜索树的性质进行查找,很简单,不赘述。
值得注意的是,在查找完成后,此节点将被旋转到根节点的位置。
int find(int x) {
int now = root;
while (1) {
if (!now) return 0;
if (T[now].val == x) {
splay(now, root);
return now;
}
int nxt = x < T[now].val ? 0 : 1;
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
}
delete
删除节点
当查找到节点x的时候,他已经被旋转到根节点了,所以此时我们不需关心他的父亲节点的情况。
那么有以下四种情况:
1.此节点的出现次数大于1
直接把出现次数和子树大小-1即可。
2.此节点没有左右儿子
此节点为根,且没有子节点,那么删除后就成了一颗空树。
3.此节点没有左儿子
直接把右儿子设置为根节点
之所以不考虑只有右儿子的情况是因为第4种情况会把左儿子中的值最大的节点设置为根节点,所以有没有右儿子都一样。
4.既有左儿子,又有右儿子
在左儿子里找到值最大的节点,设置成根节点。
void delet(int x) {
int pos = find(x);
if (!pos) return;
if (T[pos].rec > 1) {
T[pos].rec--, T[pos].size--;
return;
} else {
if (!T[pos].ch[0] && !T[pos].ch[1]) {
root = 0;
return;
} else if (!T[pos].ch[0]) {
root = T[pos].ch[1];
T[root].fa = 0;
return;
} else {
int left = T[pos].ch[0];
while (T[left].ch[1]) left = T[left].ch[1];
splay(left, T[pos].ch[0]);
connect(T[pos].ch[1], left, 1);
connect(left, 0, 1); //
update(left);
}
}
}
rank
找到值为x的节点的排名
排名也等于左儿子子树的大小+1
int rak(int x) {
// int now = root, ans = 0;
// while (1) {
// if (T[now].val == x) return ans + T[T[now].ch[0]].size + 1;
// int nxt = x < T[now].val ? 0 : 1;
// if (nxt == 1) ans = ans + T[T[now].ch[0]].size + T[now].rec;
// now = T[now].ch[nxt];
// }
return T[ls(find(x))].size + 1;
}
arand
查询排名为x的值
用tem_num记录该节点以及左子树的节点数量,如果左子树的数量<x<tem_num,那么当前节点的权值就是答案。否则就根据二叉搜索树的性质继续搜索。
int arank(int x) {
int now = root;
while (1) {
int tem_num = T[now].size - T[T[now].ch[1]].size;
if (T[T[now].ch[0]].size < x && x <= tem_num) {
splay(now, root);
return T[now].val;
}
if (x < tem_num)
now = T[now].ch[0];
else
now = T[now].ch[1], x -= tem_num;
}
}
lower
求x的前驱,即小于x的最大值
编译一遍即可。
int lower(int x) {
int now = root, ans = -INF;
while (now) {
if (T[now].val < x) ans = max(ans, T[now].val);
int nxt = x <= T[now].val ? 0 : 1; //这里需要特别注意
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
return ans;
}
upper
求x的后继,即大于x的最小值
同样是遍历一遍即可。
int upper(int x) {
int now = root, ans = INF;
while (now) {
if (T[now].val > x) ans = min(ans, T[now].val);
int nxt = x < T[now].val ? 0 : 1;
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
return ans;
}
完整代码
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define m_p make_pair
#define p_i pair<int, int>
#define _for(i, a) for(register int i = 0, lennn = (a); i < lennn; ++i)
#define _rep(i, a, b) for(register int i = (a), lennn = (b); i <= lennn; ++i)
#define outval(a) cout << "Debuging...|" << #a << ": " << a << "\n"
#define mem(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define mem0(a) memset(a, 0, sizeof(a))
#define fil(a, b) fill(a.begin(), a.end(), b);
#define scl(x) scanf("%lld", &x)
#define sc(x) scanf("%d", &x)
#define pf(x) printf("%d\n", x)
#define pfl(x) printf("%lld\n", x)
#define abs(x) ((x) > 0 ? (x) : -(x))
#define PI acos(-1)
#define lowbit(x) (x & (-x))
#define dg if(debug)
#define nl(i, n) (i == n - 1 ? "\n":" ")
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
// typedef __int128 LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const int maxn = 100005;
const int maxm = 1000005;
const int maxp = 30;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const double eps = 1e-8;
const double e = 2.718281828;
int debug = 0;
inline int read() {
int x(0), f(1); char ch(getchar());
while (ch<'0' || ch>'9') {
if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }
return x * f;
}
#define ls(x) T[x].ch[0]
#define rs(x) T[x].ch[1]
#define fa(x) T[x].fa
#define root T[0].ch[1]
struct node {
int fa; //父节点
int ch[2]; //0代表左儿子,1代表右儿子
int val; //权值
int rec; //这个权值的节点出现的次数
int size; //子节点的数量(包含这个点)
} T[maxn];
int tot = 0, pointnum = 0;
void update(int x) {
T[x].size = T[ls(x)].size + T[rs(x)].size + T[x].rec; }
int ident(int x) {
return T[fa(x)].ch[0] == x ? 0 : 1; }
void connect(int x, int fa, int how) {
T[fa].ch[how] = x;
T[x].fa = fa;
}
void rotate(int x) {
int Y = fa(x), R = fa(Y);
int Yson = ident(x), Rson = ident(Y);
connect(T[x].ch[Yson ^ 1], Y, Yson);
connect(Y, x, Yson ^ 1);
connect(x, R, Rson);
update(Y);
update(x);
}
void splay(int x, int to) {
to = fa(to);
while (fa(x) != to) {
int y = fa(x);
if (T[y].fa == to)
rotate(x);
else if (ident(x) == ident(y))
rotate(y), rotate(x);
else
rotate(x), rotate(x);
}
}
int newnode(int v, int f) {
T[++tot].fa = f;
T[tot].rec = T[tot].size = 1;
T[tot].val = v;
return tot;
}
void Insert(int x) {
int now = root;
if (root == 0) {
newnode(x, 0); root = tot; }
else {
while (1) {
T[now].size++;
if (T[now].val == x) {
T[now].rec++;
splay(now, root);
return;
}
int nxt = x < T[now].val ? 0 : 1;
if (!T[now].ch[nxt]) {
int p = newnode(x, now);
T[now].ch[nxt] = p;
splay(p, root);
return;
}
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
}
}
int find(int x) {
int now = root;
while (1) {
if (!now) return 0;
if (T[now].val == x) {
splay(now, root);
return now;
}
int nxt = x < T[now].val ? 0 : 1;
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
}
void delet(int x) {
int pos = find(x);
if (!pos) return;
if (T[pos].rec > 1) {
T[pos].rec--, T[pos].size--;
return;
} else {
if (!T[pos].ch[0] && !T[pos].ch[1]) {
root = 0;
return;
} else if (!T[pos].ch[0]) {
root = T[pos].ch[1];
T[root].fa = 0;
return;
} else {
int left = T[pos].ch[0];
while (T[left].ch[1]) left = T[left].ch[1];
splay(left, T[pos].ch[0]);
connect(T[pos].ch[1], left, 1);
connect(left, 0, 1); //
update(left);
}
}
}
int rak(int x) {
return T[ls(find(x))].size + 1;
}
int arank(int x) {
int now = root;
while (1) {
int tem_num = T[now].size - T[T[now].ch[1]].size;
if (T[T[now].ch[0]].size < x && x <= tem_num) {
splay(now, root);
return T[now].val;
}
if (x < tem_num)
now = T[now].ch[0];
else
now = T[now].ch[1], x -= tem_num;
}
}
int lower(int x) {
int now = root, ans = -inf;
while (now) {
if (T[now].val < x) ans = max(ans, T[now].val);
int nxt = x <= T[now].val ? 0 : 1; //这里需要特别注意
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
return ans;
}
int upper(int x) {
int now = root, ans = inf;
while (now) {
if (T[now].val > x) ans = min(ans, T[now].val);
int nxt = x < T[now].val ? 0 : 1;
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
int N = read();
while (N--) {
int opt = read(), x = read();
if (opt == 1)
Insert(x);
else if (opt == 2)
delet(x);
else if (opt == 3)
printf("%d\n", rak(x));
else if (opt == 4)
printf("%d\n", arank(x));
else if (opt == 5)
printf("%d\n", lower(x));
else if (opt == 6)
printf("%d\n", upper(x));
}
return 0;
}
模板
#define ls(x) T[x].ch[0]
#define rs(x) T[x].ch[1]
#define fa(x) T[x].fa
#define root T[0].ch[1]
struct node {
int fa; //父节点
int ch[2]; //0代表左儿子,1代表右儿子
int val; //权值
int rec; //这个权值的节点出现的次数
int size; //子节点的数量(包含这个点)
} T[maxn];
int tot = 0, pointnum = 0;
void update(int x) {
T[x].size = T[ls(x)].size + T[rs(x)].size + T[x].rec; }
int ident(int x) {
return T[fa(x)].ch[0] == x ? 0 : 1; }
void connect(int x, int fa, int how) {
T[fa].ch[how] = x;
T[x].fa = fa;
}
void rotate(int x) {
int Y = fa(x), R = fa(Y);
int Yson = ident(x), Rson = ident(Y);
connect(T[x].ch[Yson ^ 1], Y, Yson);
connect(Y, x, Yson ^ 1);
connect(x, R, Rson);
update(Y);
update(x);
}
void splay(int x, int to) {
to = fa(to);
while (fa(x) != to) {
int y = fa(x);
if (T[y].fa == to)
rotate(x);
else if (ident(x) == ident(y))
rotate(y), rotate(x);
else
rotate(x), rotate(x);
}
}
int newnode(int v, int f) {
T[++tot].fa = f;
T[tot].rec = T[tot].size = 1;
T[tot].val = v;
return tot;
}
void Insert(int x) {
int now = root;
if (root == 0) {
newnode(x, 0); root = tot; }
else {
while (1) {
T[now].size++;
if (T[now].val == x) {
T[now].rec++;
splay(now, root);
return;
}
int nxt = x < T[now].val ? 0 : 1;
if (!T[now].ch[nxt]) {
int p = newnode(x, now);
T[now].ch[nxt] = p;
splay(p, root);
return;
}
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
}
}
int find(int x) {
int now = root;
while (1) {
if (!now) return 0;
if (T[now].val == x) {
splay(now, root);
return now;
}
int nxt = x < T[now].val ? 0 : 1;
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
}
void delet(int x) {
int pos = find(x);
if (!pos) return;
if (T[pos].rec > 1) {
T[pos].rec--, T[pos].size--;
return;
} else {
if (!T[pos].ch[0] && !T[pos].ch[1]) {
root = 0;
return;
} else if (!T[pos].ch[0]) {
root = T[pos].ch[1];
T[root].fa = 0;
return;
} else {
int left = T[pos].ch[0];
while (T[left].ch[1]) left = T[left].ch[1];
splay(left, T[pos].ch[0]);
connect(T[pos].ch[1], left, 1);
connect(left, 0, 1); //
update(left);
}
}
}
int rak(int x) {
return T[ls(find(x))].size + 1;
}
int arank(int x) {
int now = root;
while (1) {
int tem_num = T[now].size - T[T[now].ch[1]].size;
if (T[T[now].ch[0]].size < x && x <= tem_num) {
splay(now, root);
return T[now].val;
}
if (x < tem_num)
now = T[now].ch[0];
else
now = T[now].ch[1], x -= tem_num;
}
}
int lower(int x) {
int now = root, ans = -inf;
while (now) {
if (T[now].val < x) ans = max(ans, T[now].val);
int nxt = x <= T[now].val ? 0 : 1; //这里需要特别注意
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
return ans;
}
int upper(int x) {
int now = root, ans = inf;
while (now) {
if (T[now].val > x) ans = min(ans, T[now].val);
int nxt = x < T[now].val ? 0 : 1;
now = T[now].ch[nxt];
}
return ans;
}