LinkedQueue
前面我们学习了Stack,学习了ArrayList ,学习了Vector,其实Vector和ArrayList一样,都是基于数组实现的List,也就是说都是属于List 阵营的,其主要的区别是在于线程安全上,二者的底层实现都是基于数组的,stack 集合实现了数据结构Stack 的定义,底层依赖Vector 实现也就是数组,对栈顶元素的操作实际上是对数组尾部元素的操作,因为这样可以避免数据的迁移。
也就是说我们是用数组实现的Stack,今天我们学习一个和Stack同样重要的数据结构Queue,前面学习LinkedList 的时候我们注意到了LinkedList它其实实现了Queue 接口的,所以我们可以将LinkedList当做Queue来使用,那么其底层实现就是LinkedList的实现,也就是链表。
Queue 的定义
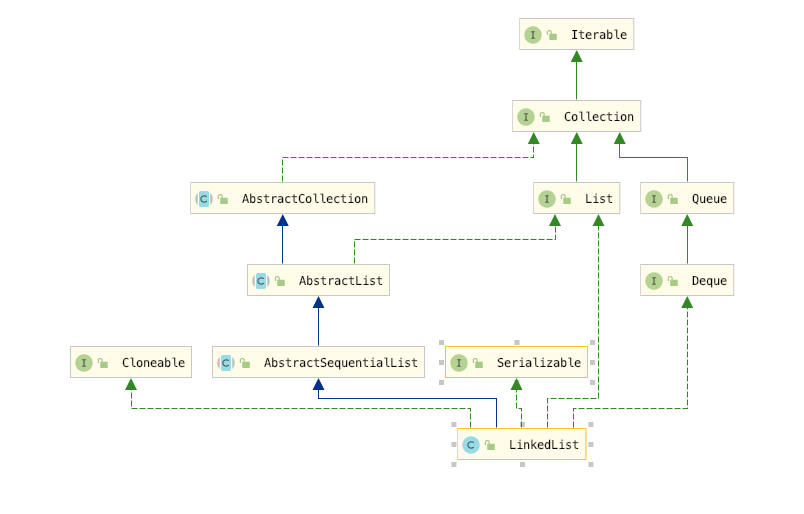
我们看到List ,Set 和 Queue 都是Java 集合框架的顶级接口,虽然我们今天学习的Queue 是基于LinkedList 实现的,但是为了方便理解和梳理整个集合框架我们还是将其划分到Queue 家族,LinkedList实现了Queue接 口,Queue接口窄化了对LinkedList的方法的访问权限(即在方法中的参数类型如果是Queue时,就完全只能访问Queue接口所定义的方法 了,而不能直接访问 LinkedList的非Queue的方法),以使得只有恰当的方法才可以使用。
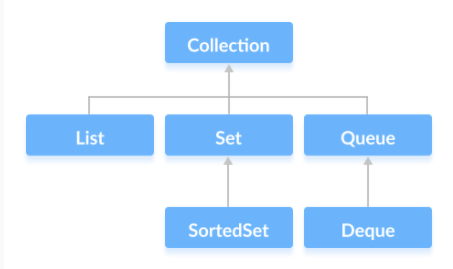
接下来我们看一下 Queue 接口的定义
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> {
// 将指定的元素插入此队列(如果立即可行且不会违反容量限制),在成功时返回 true,如果当前没有可用的空间,则抛出 IllegalStateException。
boolean add(E e);
// 将指定的元素插入此队列(如果立即可行且不会违反容量限制),当使用有容量限制的队列时,此方法通常要优于 add(E),add可能无法插入元素,而只是抛出一个异常。
boolean offer(E e);
// 获取并移除此队列的头。
E remove();
// 获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。
E poll();
// 获取,但是不移除此队列的头。
E element();
// 获取但不移除此队列的头;如果此队列为空,则返回 null。
E peek();
}
Queue使用时要尽量避免Collection的add()和remove()方法,而是要使用offer()来加入元素,使用poll()来获取并移出元素。它们的优点是通过返回值可以判断成功与否,add()和remove()方法在失败的时候会抛出异常。
如果要使用队头元素而不移出该元素,使用element()或者peek()方法。
使用
因为底层是通过LinkedList 来实现的,前面我们又对LinkedList进行了非常详细的学习,所以这里我们就不探究原理什么的了,直接看一下怎么使用
其实队列是一个先进先出的这样一个数据结构,那么我们添加元素只需要插入到链表的尾部,其他的操作都是在链表的头部操作,性能也很高
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating Queue using the LinkedList class
Queue<Integer> numbers = new LinkedList<>();
// offer elements to the Queue
numbers.offer(1);
numbers.offer(2);
numbers.offer(3);
System.out.println("Queue: " + numbers);
// Access elements of the Queue
int accessedNumber = numbers.peek();
System.out.println("Accessed Element peek: " + accessedNumber);
accessedNumber = numbers.element();
System.out.println("Accessed Element element: " + accessedNumber);
// Remove elements from the Queue
int removedNumber = numbers.poll();
System.out.println("Removed Element: " + removedNumber);
System.out.println("Updated Queue: " + numbers);
}
输出
Queue: [1, 2, 3]
Accessed Element peek: 1
Accessed Element element: 1
Removed Element: 1
Updated Queue: [2, 3]
操作的实现
add 和 offer
我们看到本质上offer 还是使用了LinkedList的add 方法,如果你对LinkedList有什么不清楚的话,可以看前面的文章
/**
* Adds the specified element as the tail (last element) of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @since 1.5
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
// 添加到队列的尾部
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
peek 和 element 以及poll 和 remove
之所有将这个三个方法放到一起说是因为这三分方法都是对队列的头部进行操作,这个三个方法的实现基本一样的,poll 因为是要删除队列头部的元素,所以多调用了一步unlinkFirst,也就是在删除之后给"队列选择了新的头领"
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E element() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E poll() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E remove() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
总结
- 这一节的知识很简单,主要就是想告诉大家Queue的实现方式以及它是怎么实现的,注意和Stack 进行对比。
- LinkedList 实现的Queue 是一个无界的队列,所以add 和 offer 方法的效果是一样的,但是remove 和 poll还是有点差异的,poll 使用起来更加安全。