(根据参考文档翻译整理而成,原文有修改)
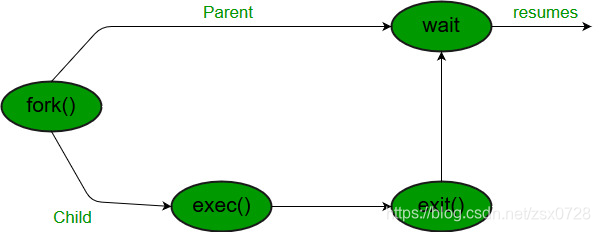
wait()
对 wait() 的调用会阻止调用进程,直到它的一个子进程退出或收到信号为止。子进程终止后,父进程在wait系统调用指令后继续执行。
子进程可能由于以下原因而终止:
- 调用exit();
- 接收到main进程的return值;
- 接收一个信号(来自操作系统或另一个进程),该信号的默认操作是终止。
语法:
// 获取子进程退出状态并返回死掉的子进程ID
pid_t wait(int *stat_loc);
如果任何进程有多个子进程,则在调用 wait() 之后,如果没有子进程终止,则父进程必须处于wait状态。
如果只有一个子进程被终止,那么 wait() 返回被终止的子进程的进程ID。
如果多个子进程被终止,那么 wait() 将获取任意子进程并返回该子进程的进程ID。
wait的目的之一是通知父进程子进程结束运行了,它的第二个目的是告诉父进程子进程是如何结束的。wait返回结束的子进程的PID给父进程。父进程如何知道子进程是以何种方式退出的呢?
答案在传给wait的参数之中。父进程调用wait时传一个整型变量地址给函数。内核将子进程的退出状态保存在这个变量中。如果子进程调用exit退出,那么内核把exit的返回值存放到这个整数变量中;如果进程是被杀死的,那么内核将信号序号存放在这个变量中。这个整数由3部分组成,8个bit记录子进程exit值,7个bit记录信号序号,另一个bit用来指明发生错误并产生了内核映像(core dump)。
如果进程没有子进程,那么 wait() 返回“-1”。
示例:
// C program to demonstrate working of wait()
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
pid_t cpid;
int status;
int high_8, low_7, bit_7;
if (fork()== 0)
{
printf("this is child process, the id is %d\n", getpid());
exit(18); /* terminate child */
}
else
{
printf("status is %d\n", status);
cpid = wait(&status); /* reaping parent */
high_8 = status >> 8; /* 1111 1111 0000 0000 */
low_7 = status & 0x7F; /* 0000 0000 0111 1111 */
bit_7 = status & 0x80; /* 0000 0000 1000 0000 */
printf("status is %d\n", status);
printf("high_8 is %d, low_7 is %d, bit_7 is %d\n", high_8, low_7, bit_7);
}
printf("Parent pid = %d\n", getpid());
printf("Child pid = %d\n", cpid);
return 0;
}
输出:
status is 0
this is child process, the id is 5412
status is 4608
high_8 is 18, low_7 is 0, bit_7 is 0
Parent pid = 5411
Child pid = 5412
在本例中,wait() 将子进程的退出状态存储到status变量中,4608的二进制格式为0001 0010 0000 0000,前8位用10进制表示为18,也就是子进程exit的值。
WIF宏
wait报告的子进程的状态信息不仅仅是子进程的退出状态,也包括:
- 正常/异常终止
- 终止原因
- 退出状态
有关状态的信息,请使用WIF….系列的宏。
- WIFEXITED(status):子级正常退出
WEXITSTATUS(status):子级退出时的返回代码 - WIFSIGNALED(status):子级异常退出
WTERMSIG(status):给出终止信号的代码 - WIFSTOPPED(status):子级被暂停。
WSTOPSIG(status):给出暂停信号的代码。
/*if we want to prints information about a signal */
void psignal(unsigned sig, const char *s);
示例:
// C program to demonstrate working of wait()
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
pid_t cpid;
int status;
int high_8, low_7, bit_7;
if (fork()== 0)
{
printf("this is child process, the id is %d\n", getpid());
exit(18); /* terminate child */
}
else
{
printf("status is %d\n", status);
cpid = wait(&status); /* reaping parent */
high_8 = status >> 8; /* 1111 1111 0000 0000 */
low_7 = status & 0x7F; /* 0000 0000 0111 1111 */
bit_7 = status & 0x80; /* 0000 0000 1000 0000 */
printf("status is %d\n", status);
printf("high_8 is %d, low_7 is %d, bit_7 is %d\n", high_8, low_7, bit_7);
if (WIFEXITED(status))
printf("the child process exit status is %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
else if (WIFSIGNALED(status))
psignal(WTERMSIG(status), "Exit signal");
}
printf("Parent pid = %d\n", getpid());
printf("Child pid = %d\n", cpid);
return 0;
}
输出:

status is 0
this is child process, the id is 2997
status is 4608
high_8 is 18, low_7 is 0, bit_7 is 0
the child process exit status is 18
Parent pid = 2996
Child pid = 2997
在上一个示例的基础上进行修改,可以看到,WEXITSTATUS(status) 的值就是子进程exit的值18,WEXITSTATUS() 简化了high_8的实现。
waitpid()
我们知道如果有多个子进程被终止,那么 wait() 将收获任意子进程,但是如果我们想收获任何特定的子进程,我们将使用 waitpid() 函数。
语法:
pid_t waitpid (child_pid, &status, options);
options参数:
- 如果options为0表示没有选项,则父级必须等待子级终止;
- 如果options为WNOHANG,表示如果子进程不终止,父进程不等待,只需检查并返回waitpid() 。(不阻塞父进程)
- 如果child_pid为 -1,则表示任意子级,这里的 waitpid() 工作方式与 wait() 工作方式相同。
waitpid() 的返回值:
- 如果子级退出,返回子级的pid
- 如果使用 WNOHANG或子级未退出,返回0。
// C program to demonstrate waitpid()
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<unistd.h>
void waitexample()
{
int i, stat;
pid_t pid[5];
for (i=0; i<5; i++)
{
if ((pid[i] = fork()) == 0)
{
sleep(1);
printf("pid is %d\n", getpid());
exit(100 + i);
}
else
{
printf("i is %d, the pid[i] is %d, mypid is %d\n", i, pid[i], getpid());
}
}
// Using waitpid() and printing exit status
// of children.
for (i=0; i<5; i++)
{
pid_t cpid = waitpid(pid[i], &stat, 0);
if (WIFEXITED(stat))
printf("Child %d terminated with status: %d\n",
cpid, WEXITSTATUS(stat));
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
waitexample();
return 0;
}
输出:
i is 0, the pid[i] is 3554, mypid is 3553
i is 1, the pid[i] is 3555, mypid is 3553
i is 2, the pid[i] is 3556, mypid is 3553
i is 3, the pid[i] is 3557, mypid is 3553
i is 4, the pid[i] is 3558, mypid is 3553
pid is 3558
pid is 3557
pid is 3554
Child 3554 terminated with status: 100
pid is 3556
pid is 3555
Child 3555 terminated with status: 101
Child 3556 terminated with status: 102
Child 3557 terminated with status: 103
Child 3558 terminated with status: 104
由输出可知,父进程3553创建了5个子进程,并等待子进程运行结束后退出,其中子进程执行顺序是随机的。
参考文档
[1]Kadam Patel.Wait System Call in C[EB/OL].https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wait-system-call-c/,2019-11-01.