第二部分面向对象
七、类与对象
7.1 面向过程与面向对象思想
面向过程
定义:当我们在解决一个问题时,会按照预先设定的想法和步骤,一步一步去实现,在这里每一步具体的实现中都需要我们自己去亲自实现和操作。
我们的角色是: 执行者
特点:费时间、费精力、结果也不一定完美
面向对象
定义:当我们在解决一个问题时,可以去找具有相对应的功能的事物帮着我们去解决问题,至于这个事物如何工作,与我们无关,我们只看结果,不关心解决流程。
我们的角色是: 指挥者
特点:节省时间,节省精力,结果相对完美
面向对象和面向过程差异
- 面向对象是一种符合人们思考习惯的思想
- 面向过程中更多的体现是执行者,面向对象中更多的体现是指挥者。
- 面向对象可以将复杂的问题进行简单化,更加贴近真实的社会场景
7.2 类与对象的关系
什么是对象
面向对象编程语言主要是使用对象们来进行相关的编程。对象,万事万物中存在的每一个实例,一个电脑、一个手机、一个人、抖音里的一个短视频、支付宝里的一个交易记录、淘宝里的订单。
如何去描述一个对象的内容?
- 对象的属性:就是对象的相关参数,可以直接用数据来衡量的一些特征用常量|变量来表示(成员变量)
- 对象的行为:就是过将对象的属性进行联动,产生出一系列的动作或行为——函数(成员函数)
什么是类
类是那些具有相同属性特征和行为的对象们的统称。对象就是该类描述下具体存在的一个事物。
7.3 封装与private关键字
封装=包装
常见的封装体现
- 函数
- 类
封装有什么好处? - 提高了安全性
- 向外界隐藏了一些不需要被外界获知的内容
- 提高了代码的复用性
- 也是面向对象的三大特点之一:封装 继承 多态
private关键字,属于权限关键字 public protected 默认不写 private
private可以作用在对象属性和行为上,外界在创建对象后,则不能访问被private修饰的内容
7.4 局部变量与成员变量
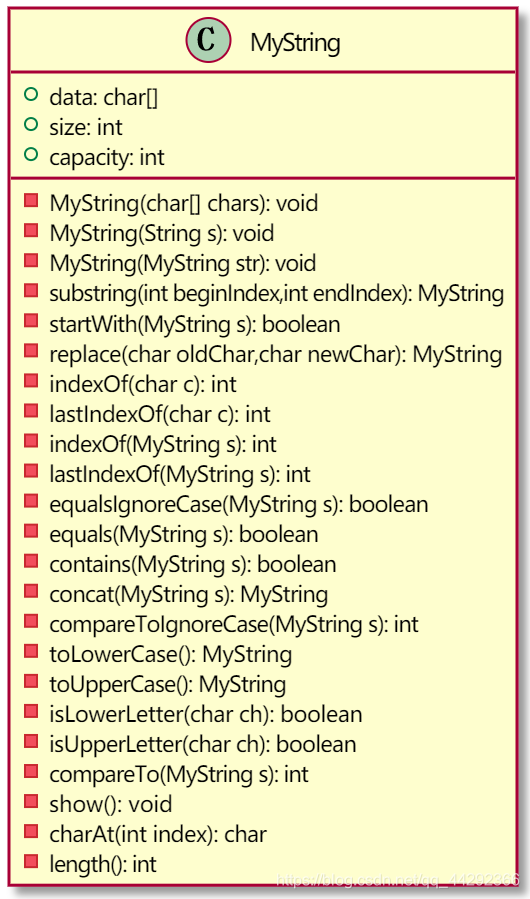
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.setName("小强");
p1.setAge(10);
p1.speak();
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public void speak() {
System.out.println("我是" + name + ",我今年" + age + "岁");
}
public void setName(String name) {
if (name.equals("旺财")) {
this.name = "哈士奇";
} else {
this.name = name;
}
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age < 0) {
this.age = 0;
} else {
this.age = age;
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}
代码执行流程:
- javac 编译Sample.java源代码 生成Sample.class和Person.class两个字节码文件
- 如果java Person ,运行Person字节码文件,则报错,没有主函数不是主类
- 只能java Sample 运行Sample程序
- 将相关的字节码(Sample.class Person.class)文件加载进JVM中内存下的方法区
- 在方法区中Sample字节码所在的区域里,找主函数,将主函数的栈帧加载进栈内存开始运行
- 开始执行主函数的第一句代码,创建Person对象
- 在堆内存中开辟一个空间并分配地址,在该空间中创建成员变量并默认初始化
- 在主函数空间中创建局部变量p1,并将该对象的地址传给p1
- 接着执行主函数第二句代码,调用p1对象的setName方法
- 从方法区中的Person里,将setName函数栈帧加载进栈,主函数暂停运行
- setName进栈后,创建局部变量name(形参),并将实参“小强”这个字符串在字符串常量池中的地址赋予name
- 因为setName成员函数只有一份在方法区中Person所属区间里,之后可以被多个同类对象调用,为了区分到底是哪个对象调用的该方法,所以在每一个成员函数中,都会有一个隐藏的关键字数据 this ,this相当于一个变量来存储当前对象的地址。(当前对象的引用)
- 执行setName中的内容,如果数据没有问题的话,就将局部变量的值赋值个当前对象的成员
变量 - setName函数执行最后一行隐藏的return,表示函数结束并弹栈
- 主函数成为当前栈顶,继续执行
- 执行p1调用setAge函数,从方法区中Person所属空间里找setAge这一段代码,将该函数栈帧加载进栈内存成为新的栈顶,则主函数暂停,该函数运行。先创建形参age的局部变量,接收实
参传来的值10,为了区分对象的调用关系,自带this关键字数据,this存的还是p1的地址,如果age没有问题,则将10传给this所指向的对象中age这个成员变量。setAge执行最后一行隐藏的return,表示函数结束并弹栈 - 主函数称为新的栈顶继续执行,调用p1的speak函数进栈
- 在方法区中Person字节码所属空间里读取speak代码,将该栈帧加载进栈内存中,主函数暂停,该函数执行,无形参只能表示没有形参的局部变量,但是在函数内部也可以创建其他的局部变量,并且有this关键数据存的是p1的地址,然后去打印name和age,由于speak空间中已经没有其他名为name或age的局部变量,所以找不到,接着找this对象中的数据,找到了则打印。直至函数结束并弹栈
- 主函数又称为栈顶,也没有代码了,执行隐藏的return,主函数弹栈,表示程序结束。
局部变量和成员变量有什么区别?
- 生命周期
成员变量随着对象的创建而创建,随着对象的消亡而消失
局部变量随着函数的进栈而创建,随着函数的出栈而消失
- 存储位置
成员变量在堆内存中对象所属空间里
局部变量在栈内存中函数所属空间里
- 定义位置
成员函数在类中,函数外定义
局部变量在函数中定义
- 初始化
成员变量有默认初始化
局部变量必须初始化之后再调用
7.5 构造函数
什么是构造函数:构造函数主要是在创建对象的时候执行的函数,在该函数中也可对成员变量进行一些操作。
构造函数的格式
权限修饰符 类名(参数列表) {
构造函数的代码块
}
- 构造函数没有返回值
- 构造函数的名称必须是类名
- 参数列表可选的,构造函数是可以重载的
- 虽然构造函数没有返回值,还是存在return关键字的
- 当我们的类中没有定义任何构造函数时,会有一个默认隐藏的无参构造函数存在
- 构造函数和成员函数一样,为了区分对象的调用,构造函数自带this关键字数据
构造函数需要注意的问题
- 如果一旦定义其他参数列表的构造函数的话,这个隐藏的无参构造函数就会消失,所建议手写出来
- 构造函数只有在创建对象的时候执行,当对象创建完毕之后,该对象的构造函数则不能执行
- 成员函数只有在对象创建之后才能执行
- 成员函数能否直接调用构造函数?不能够的,报找不到符号错误 会误认为是同名的成员函数
- 构造函数能否直接调用成员函数呢?能够,但是 这些成员函数一般是构造函数的部分代码片段被切割出来了而已,从语意上而言,不属于对象的特有行为(也有特例),所以这些函数长得样子就是
成员函数的样子,但没有必要向外界提供访问,所以加上private - 构造函数能否直接调用构造函数呢?可以,但是必须通过 this(参数列表) ,需要注意的是,构造函数可以单向调用其他构造函数,但坚决不能出现回调。
- 构造函数是在创建对象的时候执行的,可以在期间对成员变量进行初始化,问:setXXX还需要不?看需求,如果后期成员变量需要修改,则提供setXXX修改器
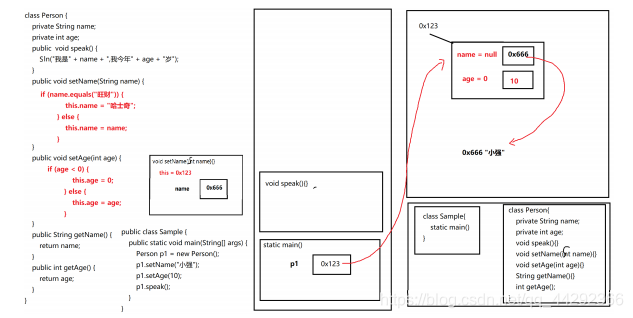
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();//new 构造函数;
p.setName("旺财");
p.setAge(10);
p.speak();
Person p2 = new Person();//new 构造函数;
p2.setName("小强");
p2.setAge(20);
p2.speak();
Person p3 = new Person("如花",40);
p3.speak();
p3.test();
//p3.part();
Car car1 = new Car();
Car car2 = new Car(4);
Car car3 = new Car(4,"红色");
Car car4 = new Car(8,"武士黑",20);
car1.run();
car2.run();
car3.run();
car4.run();
}
}
class Car {
private int wheel = 4;
private String color;
private int weight;
public Car(){
}
public Car(int wheel) {
this(wheel,null,0);
}
public Car(int wheel,String color) {
this(wheel,color,0);
}
public Car(int wheel,String color,int weight) {
this.wheel = wheel;
this.color = color;
this.weight = weight;
//this();//递归构造器调用
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(wheel + ":" + color + ":" + weight);
}
//这个不是重载 Car(int)已经存在了(wheel)
/*
public Car(int weight) {
}
*/
}
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
//这就是隐藏的构造函数
public Person() {
System.out.println("一个Person创建出来了!");
part();
part();
part();
part();
}
//语意
private void part() {
System.out.println("100行代码");
}
public Person(String name,int age) {
System.out.println("一个Person创建出来了!");
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void test() {
Person();//实际上这一段代码并不表示调用无参构造函数
//而表示去调用名字为Person的成员函数!
}
public void Person() {
System.out.println("没想到吧!");
}
public void speak() {
System.out.println(name + ":" + age);
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
关于成员变量初始化的问题
成员变量的初始化经历了三个步骤:默认初始化(大家默认都是0值),显式初始化(大家的值都一样),针对性初始化(大家的值可选)。
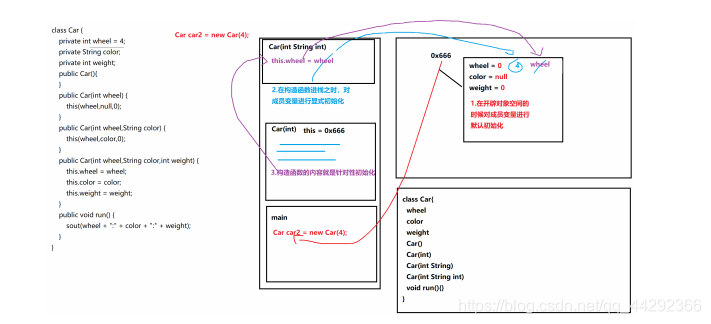
7.6 对象的创建流程及内存图解
示例:定义一个栈

public class Sample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.pop();
System.out.println(stack);
for(int i=1; i<=10;i++){
stack.push(i);
}
System.out.println(stack);
stack.pop();
System.out.println(stack);
System.out.println(stack.peek());
stack.clear();
System.out.println(stack);
System.out.println(stack.peek());
}
}
class Stack{
private int[] data;
private int top = -1;
private static int capacity = 10;
public Stack() {
this(capacity);
}
public Stack(int capacity) {
data = new int[capacity];
}
public void push(int e){
if(size() == data.length) {
reSize(data.length);
}
data[++top] = e;
}
public void reSize(int length){
int[] arr = new int[length * 2];
for(int i=0; i<= top; i++) {
arr[i] = data[i];
}
data = arr;
}
public int pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println(">>>栈为空,弹不出元素了!");
return -1;
}
int e = data[top];
top--;
if(data.length > capacity && size() == data.length / 4) {
reSize(data.length / 2);
}
return e;
}
public void clear(){
top = -1;
data = new int[10];
}
public int peek(){
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println(">>>栈为空,无栈顶元素!");
return -1;
}
return data[top];
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return top == -1;
}
public int size() {
return top + 1;
}
public String toString() {
if(isEmpty()){
return "[]";
}
String s = "[";
for(int i=0; i <= top; i++) {
if(i == top){
s += data[i] + "]";
}else{
s += data[i] + ", ";
}
}
return s;
}
}
示例:模拟吃鸡

public class Sample02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Player p1 = new Player("老王",100);
Player p2 = new Player("老李",100);
p1.shootEnemy(p2);
Gun gun = new Gun();
p1.holdGun(gun);
p1.shootEnemy(p2);
Clip clip = new Clip();
for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) {
clip.pushBullet(new Bullet());
}
p1.loadClip(clip);
for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) {
p1.shootEnemy(p2);
}
p1.shootEnemy(p2);
}
}
//人
class Player{
//人物姓名
private String name;
//人物血值
private int blood;
//人物的枪
private Gun gun;
public Player() {
}
//人物初始化
public Player(String name,int blood){
this(name,blood,null);
}
//人物初始化
public Player(String name,int blood,Gun gun){
this.name = name;
this.blood = blood;
this.gun = gun;
}
//设置枪
public void holdGun(Gun gun) {
this.gun = gun;
}
//攻击敌人
public void shootEnemy(Player enemy) {
if(gun == null) {
System.out.println(">>>玩家信息:没有枪,开P");
}else{
System.out.printf(">>>玩家信息:%s向%s开了一枪\n",name,enemy.name);
gun.shootEnemy(enemy);
}
}
//上弹夹
public void loadClip(Clip clip) {
if(gun == null){
System.out.println(">>>玩家信息:没抢,装不了弹夹");
}else{
gun.loadClip(clip);
}
}
//玩家受到攻击
public void damage(int hurt) {
//血量为0,攻击不了
if(blood == 0) {
System.out.println(">>>玩家信息:" + name + "已经成盒,请勿鞭尸");
}else{
//否则扣血
blood -= hurt;
if(blood > 0){
System.out.println(">>>玩家信息:" + name + "掉血" + hurt + ",剩余" +blood);
}else{
//扣血小于0后,重新赋血值,输出信息
blood = 0;
System.out.println(">>>玩家信息:" + name + "已经成盒");
}
}
}
}
//枪
class Gun{
private Clip clip;
public Gun() {
this(null);
}
//初始化弹夹
public Gun(Clip clip) {
this.clip = clip;
}
//上弹夹
public void loadClip(Clip clip) {
this.clip = clip;
}
//攻击敌人
public void shootEnemy(Player enemy) {
//判断枪是否有弹夹
if(clip == null) {
System.out.println(">>>枪信息:没有弹夹,开了个空枪");
return;
}
//弹夹弹出一颗子弹
Bullet bullet = clip.popBullet();
//弹出子弹为空,则弹夹没有子弹
if(bullet == null) {
System.out.println(">>>枪信息:弹夹没子弹 开了个空枪");
return;
}else{
bullet.hitEnemy(enemy);
}
}
}
//弹夹
class Clip{
//弹夹的容量
private int capacity = 30;
//弹夹剩余的子弹
private int surplus = 0;
//弹夹的子弹容器
private Bullet[] magazine;
public Clip(){
this(30);
}
//初始化子弹容器和弹夹的容量
public Clip(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
magazine = new Bullet[capacity];
}
//装入一颗子弹
public void pushBullet(Bullet bullet) {
//判断弹夹中子弹是否已经装满
if(surplus == capacity) {
System.out.println(">>>弹夹信息:弹夹已满,无法装入子弹");
return;
}else{
magazine[surplus++] = bullet;
showClip();
}
}
//弹出一颗子弹
public Bullet popBullet() {
//判断弹夹中是否有子弹
if(surplus == 0){
System.out.println(">>>弹夹信息:弹夹为空,无法弹出子弹!");
return null;
}else {
//从子弹容器中取出一颗子弹
Bullet bullet = magazine[surplus-1];
//剩余子弹--
surplus--;
showClip();
return bullet;
}
}
public void showClip() {
System.out.printf(">>>弹夹信息:%d/%d\n",surplus,capacity);
}
}
//子弹
class Bullet{
//子弹的伤害
private int hurt;
public Bullet() {
}
//为子弹赋特殊伤害
public Bullet(int hurt) {
this.hurt = hurt;
}
//子弹伤害敌人
public void hitEnemy(Player enemy) {
enemy.damage(hurt);
}
}
7.7 static关键字
静态关键字
主要用于:修饰成员变量(对象的特有属性)和成员函数,变为静态变量和静态函数
静态变量的特点:同类下多个对象之间的共有属性
静态变量的定义时机:在同一类下,多个对象之间有相同的属性和值,那么就可以将该属性和值从成员变量变为静态变量,目的就是为了节省空间。
静态函数的定义时机:当一个成员函数不访问成员时,即可定义为静态函数!
- 静态函数一旦定义出来,可以直接用类名去调用,当然也可以通过创建对象来去调用静态函数!
- 静态优先于对象存在,且在同一类中,静态无法访问非静态(成员),非静态是可以访问静态
- 静态函数中不存在this()
1.当通过对象去调用一个属性时,先找成员,再找静态,最后找父类
2.如果从成员函数中去调用一个属性时,先找局部,再找成员,再找静态,最后找父类
好处:
- 节省堆内存中的空间
- 可以不用费力气去创建对象来调用功能
- 可以对类进行一些初始操作(结合代码块来做)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Chinese c1 = new Chinese();
Chinese c2 = new Chinese();
Chinese c3 = new Chinese();
System.out.println(c1.country);
System.out.println(Chinese.country);
c1.show();
Chinese.show();
/*
Chinese.test();
*/
}
}
class Chinese {
String name;
int age;
static String country;
//静态代码块
static {
country = "China";
System.out.println("init....");
}
Chinese() {
System.out.println("Chinese....");
}
public void test(){
int num = 10;
System.out.println(num + name + country);
}
public static void show() {
/*
//无法从静态上下文中引用非静态 方法 test()
test();
//无法从静态上下文中引用非静态 变量 name
System.out.println("show...." + name);
*/
}
}
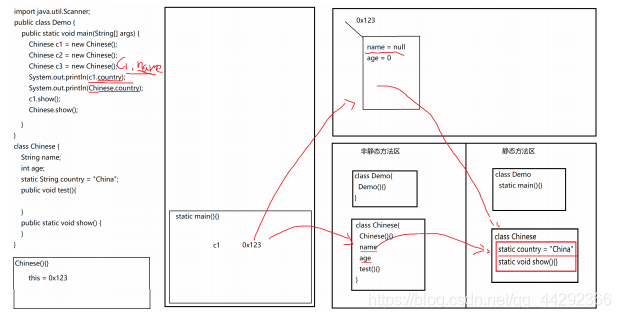
7.8 静态变量与成员变量
存储位置
- 成员变量存储在堆内存中对象所属空间里
- 静态变量存储在静态方法区中对应的字节码空间里
生命周期
- 成员变量随着对象的创建而创建,随着对象的消亡而消亡
- 静态变量随着类的加载而存在,随着程序的结束而消失
所属不同
- 成员变量属于对象的,称之为是对象的特有属性
- 静态变量属于类的,称之为是类的属性,或者叫对象的共有属性
调用方式不同
-
成员变量在外界必须通过创建对象来调用,内部的话成员函数可以直接调用成员变量,但是静态函数不能直接调用成员变量,如果非要在静态函数中调用成员的话,只能创建对象,通过对象来调用
-
静态变量在外界可以通过对象调用,也可以通过类来调用,内部的话静态函数/成员函数可以调用静态变量
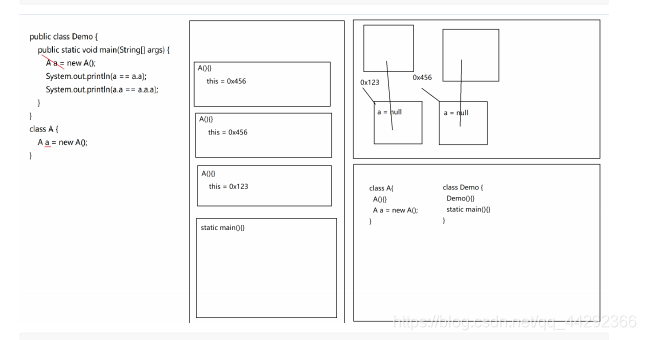
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//StackOverFlowError 栈内存溢出
A a = new A();
System.out.println(a == a.a);
System.out.println(a.a == a.a.a);
}
}
class A {
//OutOfMemoryError 堆内存溢出
int[][] arr = new int[1024][1024];
A a = new A();
}
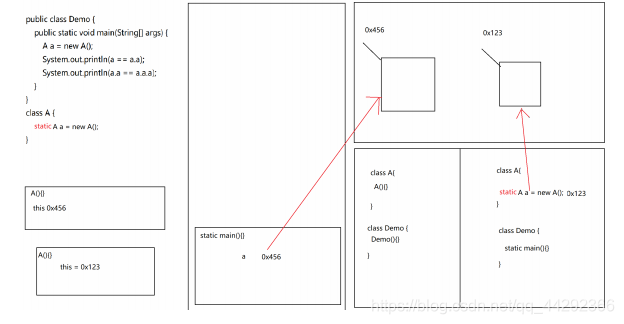
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
System.out.println(a == a.a);
System.out.println(a.a == a.a.a);
}
}
class A {
static A a = new A();
}
编程练习题

public class Demo106{
public static void main(String[] args){
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle();
System.out.println(r1.getArea());
System.out.println(r1.getPermeter());
Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle(4.0,5.0);
System.out.println(r2.getArea());
System.out.println(r2.getPermeter());
}
}
class Rectangle{
private double width = 1;
private double height = 1;
public Rectangle(){
}
public Rectangle(double width,double height){
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public double getArea(){
return width * height;
}
public double getPermeter(){
return 2 * (width + height);
}
}


public class Demo107 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StopWatch sw = new StopWatch();
sw.start();
for(int i = 0; i<1000000; i++){
}
sw.stop();
System.out.println(sw.getElapsedTime());
}
}
class StopWatch {
private long startTime;
private long endTime;
public StopWatch(){
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public void start() {
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public void stop() {
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public long getElapsedTime() {
return endTime - startTime;
}
}


public class Demo108 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Fan f1 = new Fan();
System.out.println(f1);
f1.setOn(true);
f1.setSpeed(Fan.FAST);
f1.setColor("red");
f1.setRadius(10);
System.out.println(f1);
}
}
class Fan {
public static final int SLOW = 1;
public static final int MEDIUM = 2;
public static final int FAST = 3;
private int speed = SLOW;
private boolean on = false;
private double radius = 5;
private String color = "blue";
public Fan(){
}
public void setSpeed(int speed){
this.speed = speed;
}
public int getSpeed(){
return this.speed;
}
public void setOn(boolean on){
this.on = on;
}
public boolean isOn(){
return this.on;
}
public void setRadius(int radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius(){
return this.radius;
}
public void setColor(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor(){
return this.color;
}
public String toString(){
if(on){
return "The Fan speed is "+getSpeed()+" color is "+getColor()+" radius is "+getRadius();
}else{
return "Fan is off and the color is "+getColor()+" radius is "+getRadius();
}
}
}


public class Demo109 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RegularPolygon r1 = new RegularPolygon();
System.out.println(r1.getArea());
System.out.println(r1.getPerimeter());
RegularPolygon r2 = new RegularPolygon(5,6,5,6);
System.out.println(r2.getArea());
System.out.println(r2.getPerimeter());
}
}
class RegularPolygon {
private int n = 3;
private double side = 1;
private double x = 0;
private double y = 0;
public RegularPolygon(){
}
public RegularPolygon(int n,double side) {
this.n = n;
this.side = side;
}
public RegularPolygon(int n,double side,double x,double y) {
this.n = n;
this.side = side;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getPerimeter(){
return n * side;
}
public double getArea() {
return n * Math.pow(side,2) / (4 * Math.tan(Math.PI / n));
}
public void setN(int n){
this.n = n;
}
public int getN(){
return this.n;
}
public void setSide(double side){
this.side = side;
}
public double getSide(){
return this.side;
}
public void setX(double x){
this.x = x;
}
public double getX(){
return this.x;
}
public void setY(double y){
this.y = y;
}
public double getY(){
return this.y;
}
}


public class Demo110{
public static void main(String[] args) {
QuadraticEquation q = new QuadraticEquation(3,4,1);
System.out.println(q.getRoot1());
System.out.println(q.getRoot2());
}
}
class QuadraticEquation {
private double a;
private double b;
private double c;
public QuadraticEquation(double a,double b,double c){
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
public double getDiscriminant(){
double result = Math.pow(b,2) - 4 * a * c;
if(result < 0){
return 0;
}
return result;
}
public double getRoot1() {
return (-b + Math.sqrt(getDiscriminant())) / 2 * a;
}
public double getRoot2() {
return (-b - Math.sqrt(getDiscriminant())) / 2 * a;
}
public double getA(){
return this.a;
}
public void setA(double a){
this.a = a;
}
public double getB(){
return this.b;
}
public void setB(double b){
this.b = b;
}
public double getC(){
return this.c;
}
public void setC(double c){
this.c = c;
}
}

import java.util.*;
public class Demo111{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.print("Enter the number of rows and columns in the array: ");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int row = input.nextInt();
int column = input.nextInt();
double [][] array = new double[row][column];
System.out.println("Enter the array:");
for(int i =0; i<array.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<array[i].length;j++){
array[i][j] = input.nextDouble();
}
}
Location l = new Location();
Location a = l.locateLargest(array);
System.out.println("The location of the largest element is "+a.getMax()+" at ("+a.getRow()+", "+a.getColume()+")");
}
}
class Location{
private int row;
private int column;
private double maxValue;
public int getRow(){
return this.row;
}
public void setRow(int row){
this.row = row;
}
public double getMax(){
return this.maxValue;
}
public void setMax(double maxValue){
this.maxValue = maxValue;
}
public int getColume(){
return this.column;
}
public void setColume(int column){
this.column = column;
}
public static Location locateLargest(double[][] a){
int row = 0,column = 0;
double maxValue = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<a.length; i++){
for(int j = 0;j<a[i].length;j++){
maxValue = a[i][j] > maxValue ? a[i][j] : maxValue;
row = i;
column = j;
}
}
Location l = new Location();
l.row = row;
l.column =column;
l.maxValue = maxValue;
return l;
}
}

public class Demo112 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Time t1 = new Time();
System.out.println(t1.toString());
Time t2 = new Time(120233131L);
System.out.println(t2.toString());
Time t3 = new Time(12,30,56);
System.out.println(t3.toString());
t3.setTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(t3.toString());
}
}
class Time {
private long hour;
private long minute;
private long second;
public Time() {
this(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
public Time(long millis) {
hour = cacuHour(millis);
minute = cacuMinute(millis);
second = cacuSecond(millis);
}
public long getHour(){
return hour;
}
public long getMinute(){
return minute;
}
public long getSecond(){
return second;
}
public void setTime(long elapseTime) {
hour = cacuHour(elapseTime);
minute = cacuMinute(elapseTime);
second = cacuSecond(elapseTime);
}
public String toString(){
return hour+":"+minute+":"+second;
}
public Time(long hour,long minute,long second) {
this.hour = hour;
this.minute = minute;
this.second = second;
}
private long cacuHour(long millis) {
return millis / 1000 / 60 / 60 % 24 + 8;
}
private long cacuMinute(long millis) {
return millis / 1000 / 60 % 60;
}
private long cacuSecond(long millis) {
return millis / 1000 % 60;
}
}


public class Demo113 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyInteger m1 = new MyInteger(3);
System.out.println(m1.isEven());
System.out.println(m1.isOdd());
System.out.println(m1.isPrime());
MyInteger m2 = new MyInteger(4);
MyInteger m3 = new MyInteger(13);
System.out.println(MyInteger.isEven(m2));
System.out.println(MyInteger.isPrime(m3));
System.out.println(m2.equals(m3));
System.out.println(MyInteger.parseInt("1234") + 1);
}
}
class MyInteger {
private int value;
public MyInteger(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int get() {
return value;
}
public boolean isEven() {
return value % 2 == 0;
}
public boolean isOdd() {
return value % 2 == 1;
}
public boolean isPrime() {
for (int i = 2; i <= value / 2; i++) {
if (value % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static boolean isEven(MyInteger integer) {
return integer.get() % 2 == 0;
}
public static boolean isOdd(MyInteger integer) {
return integer.get() % 2 == 1;
}
public static boolean isPrime(MyInteger integer) {
for (int i = 2; i <= integer.get() / 2; i++) {
if (integer.get() % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean equals(int num) {
return value == num;
}
public boolean equals(MyInteger integer) {
return value == integer.get();
}
public static int parseInt(String str) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
int num = str.charAt(i) - '0';
result = num + result * 10;
}
return result;
}
}

public class Demo114 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyPoint p1 = new MyPoint();
MyPoint p2 = new MyPoint(10,30.5);
System.out.println(p1.distance(p2));
System.out.println(p2.distance(11,11));
}
}
class MyPoint {
private double x = 0;
private double y = 0;
public MyPoint(){
}
public MyPoint(double x, double y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double distance(MyPoint point){
return Math.hypot(point.getX() - x,point.getY() - y);
}
public double distance(double x, double y){
return Math.hypot(x - this.x,y - this.y);
}
public double getX(){
return x;
}
public double getY(){
return y;
}
}

public class Demo115 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue q1 = new Queue();
System.out.println(q1);
//遍历添加10个元素,队列进行扩容
for(int i=1; i <= 10;i++){
q1.enqueue(i);
}
System.out.println(q1);
//队列出6个元素,此时有效元素的个数小于队列的1/4大小,进行缩容
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++){
System.out.println(q1.dequeue());
System.out.println(q1);
}
System.out.println("当前队列的有效元素个数为:"+q1.getSize());
}
}
class Queue {
//队列容器用于存储元素,element.length == size 表示队列已满
private int[] element;
//队列中有效元素的个数
private int size;
//队列容器的默认值
private int capacity = 8;
//默认队列初始化为8
public Queue(){
element =new int[capacity];
size = 0;
}
//向队列添加一个元素
public void enqueue(int v) {
//先判断该队列是否已经满了,满了的话对其进行扩容1倍
if(size == element.length){
//扩容1倍
resize(element.length * 2);
}
//扩容还是没用扩容,都要将元素添加进队列,size要自增
element[size++] = v;
}
//删除并返回队列的第一个元素
public int dequeue() {
int result = element[0];
//当删除元素后队列的有效长度为当前队列的四分之一时,对队列进行缩容,并且默认缩容到最小为8
if(size <= element.length / 4 && element.length > capacity){
//对队列缩容二分之一,保证在入队时进行不必要的扩容,留有容量进行增加元素
resize(element.length / 2);
}
for(int i=1; i<size;i++){
element[i-1] = element[i];
}
//队列出队一个元素size要减1
size--;
return result;
}
//扩容和缩容函数
private void resize(int len) {
int[] newArray = new int[len];
//遍历原数组进行复制元素到新的数组
for(int i=0; i<size;i++) {
newArray[i] = element[i];
}
element = newArray;
}
//打印队列中的元素
public String toString(){
String str = "[";
//判断队列是否为空
if(isEmpty()){
return str += "]";
}else{
//遍历数组打印内容,并判断是否为最后一个元素,是的话就加],否则就加,
for(int i=0; i<size; i++){
if(i == size - 1){
str += element[i]+"]";
}else{
str += element[i]+",";
}
}
}
return str;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
//返回队列的大小
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
}


public class Demo117 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] ch = {
'a','b','c'};
MyString s1 = new MyString(ch);
MyString s2 = new MyString("abg");
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));
MyString s3 = new MyString("PPviuiNN");
s3.toLowerCase().show();
s1.toUpperCase().show();
System.out.println(s2.compareToIgnoreCase(s3));
s3.concat(s1).show();
System.out.println(s1.contains(s2));
MyString s4 = new MyString("xxx.mp4");
System.out.println(s4.endsWith(new MyString(".mp4")));
System.out.println(s4.equals(new MyString("xxx.mp")));
System.out.println(s4.equalsIgnoreCase(new MyString("xxx.MP4")));
System.out.println(s4.indexOf('m'));
System.out.println(s4.lastIndexOf('x'));
System.out.println(s3.indexOf(new MyString("iui")));
System.out.println(s3.lastIndexOf(new MyString("iui")));
s3.replace('P','a').show();
System.out.println(s3.startWith(new MyString("PP")));
s3.substring(2,5).show();
}
}
class MyString {
//定义一个字符数组来存放字符串
private char[] data;
public MyString(char[] chars) {
//将外部的字符数组,传递给内部的字符数组
data = new char[chars.length];
for(int i=0; i<chars.length; i++) {
data[i] = chars[i];
}
}
//将外部字符串传递给内部的data
public MyString(String s) {
data = new char[s.length()];
for(int i=0; i<s.length();i++){
data[i] = s.charAt(i);
}
}
//截取字符串
public MyString substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex){
char[] ch = new char[endIndex-beginIndex];
int index = 0;
for(int i=beginIndex;i<endIndex;i++){
ch[index++] = data[i];
}
return new MyString(ch);
}
//判断是否以字符开头
public boolean startWith(MyString s){
//定义两个指针,分别判断两个字符串的首字母是否相等,相等就继续判断
//判断到有一个字符串溢出为止,有溢出就返回true,否则就为false
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while(true){
if(charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)){
i++;
j++;
if(j >= s.length()){
return true;
}
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
//替换字符串中的字符
public MyString replace(char oldChar,char newChar){
char[] chars = new char[length()];
for(int i=0;i<length();i++){
if(charAt(i) == oldChar){
chars[i] = newChar;
}else{
chars[i] = data[i];
}
}
return new MyString(chars);
}
//返回第一个字符相等的角标
public int indexOf(char c){
for(int i=0;i<length();i++){
if(charAt(i) == c){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//返回最后一个字符相等的角标
public int lastIndexOf(char c){
for(int i=length()-1;i>=0;i--){
if(charAt(i) == c){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//返回字符串的第一个角标
public int indexOf(MyString s){
//将两个数组变为局部变量,方便比较
char[] ch1 = data;
char[] ch2 = s.data;
//循环数组,每次比较两个字符串的首字母是否相等,相等的就遍历第二个字符串
//并与接下去的第一个字符串的字符比较,只要有一个不相等就返回-1,否则就返回i对应的角标
for(int i=0;i<length() - ch2.length;i++){
if(ch1[i] == ch2[0]){
int j = i+1;
for(int l=1;l<ch2.length;l++,j++){
if(ch1[j] != ch2[l]){
return -1;
}
}
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//返回字符串相等的最后的一个角标
public int lastIndexOf(MyString s){
//将两个数组变为局部变量,方便比较
char[] ch1 = data;
char[] ch2 = s.data;
//循环数组,每次比较两个字符串的首字母是否相等,相等的就遍历第二个字符串
//并与接下去的第一个字符串的字符比较,只要有一个不相等就返回-1,否则就返回i对应的角标
for(int i = ch1.length-1;i>=ch2.length-1;i--){
if(ch1[i] == ch2[ch2.length-1]){
int j = i -1;
for(int l=ch2.length-2;l>=0;l--,j--){
if(ch1[j] != ch2[l]){
return -1;
}
}
return j+1;
}
}
return -1;
}
//判断两个字符串是否相等忽略大小写
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(MyString s){
return compareToIgnoreCase(s) == 0;
}
//判断两个字符串是否相等
public boolean equals(MyString s){
return compareTo(s) == 0;
}
//判断字符串是否以xx结尾
public boolean endsWith(MyString s) {
//都从字符串的最后一个字符开始遍历
//判断两个字符是否相等,不相等返回false,直到有一个字符遍历完了后就返回true
int i = length() - 1;
int l = s.length() - 1;
while(true){
if(charAt(i) == s.charAt(l)){
i--;
l--;
if(l<0){
return true;
}
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
//判断一个字符串是否包含另一个字符串
public boolean contains(MyString s){
//将两个数组变为局部变量,方便比较
char[] ch1 = data;
char[] ch2 = s.data;
//循环数组,每次比较两个字符串的首字母是否相等,相等的就遍历第二个字符串
//并与接下去的第一个字符串的字符比较,只要有一个不相等就返回false,否则就返回true
for(int i=0;i<length() - ch2.length;i++){
if(ch1[i] == ch2[0]){
int j = i+1;
for(int l=1;l<ch2.length;l++,j++){
if(ch1[j] != ch2[l]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//连接两个字符串
public MyString concat(MyString s) {
//创建一个行的数组,长度为两个字符串的总和
//分别遍历两个数组,将其内容复制到新的数组中返回即可
char[] chars = new char[length() + s.length()];
int index =0;
for(int i=0;i<length();i++){
chars[index++] = data[i];
}
for(int i=0; i<s.length();i++){
chars[index++] = s.charAt(i);
}
return new MyString(chars);
}
//比较两个字符串的大小,忽略大小写
public int compareToIgnoreCase(MyString s) {
//将两个字符串都转为小写的字符串,在比较大小
MyString s1 = toLowerCase();
MyString s2 = s.toLowerCase();
return s1.compareTo(s2);
}
//将字符串中大写的字母转换为小写的字母
public MyString toLowerCase() {
//创建一个新的字符数组来存放转变后的字符
char[] chars = new char[length()];
for(int i=0; i<length();i++){
char ch = data[i];
if(isUpperLetter(ch)){
//将大写的字母转换为小写的字母
chars[i] = (char) (ch + 32);
}else{
//不是字母就直接赋值
chars[i] = ch;
}
}
return new MyString(chars);
}
//转换为大写字母
public MyString toUpperCase() {
char[] chars = new char[length()];
for(int i=0; i<length();i++){
char ch = data[i];
if(isLowerLetter(ch)){
chars[i] = (char) (ch - 32);
}else{
chars[i] = ch;
}
}
return new MyString(chars);
}
//判断是否为小写的字母
public boolean isLowerLetter(char ch){
return ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z';
}
//判断是否为大写的字母
public boolean isUpperLetter(char ch){
return ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z';
}
//比较两个字符串的大小
public int compareTo(MyString s){
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
//定义左右指针,如果比较两个字符,如果相等就增加,有一个不等就返回两字符的差值,
//如果有一个字符已经遍历过了最大的角标就返回两个字符串长度的差值
while(true) {
if(charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)){
i++;
j++;
if(i == length() && j == s.length()){
return 0;
}
if(i < length() && j>=s.length() || i >= length() && j < s.length()){
return length() - s.length();
}
}else{
return charAt(i) - s.charAt(j);
}
}
}
//打印字符串
public void show() {
for(int i=0;i<length();i++){
System.out.print(data[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
//根据字符索引返回字符
public char charAt(int index) {
return data[index];
}
//将MyString的类型的字符串赋值到data中
public MyString(MyString str) {
data = new char[str.length()];
for(int i=0; i<str.length();i++){
data [i] = str.charAt(i);
}
}
//返回字符数组的长度
public int length() {
return data.length;
}
}