0. 引言
本文是对以下博文中Pintos Project1源代码的思路分析,截取了重要的核心函数,以方便读者理解整个的实现思路。
参考源代码: https://blog.csdn.net/denghuang8508/article/details/101357600
1. 第一部分相关

图1 第一部分相关核心函数调用关系图
1.1 timer_ticks()
timer_ticks (void)
{
enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable ();
int64_t t = ticks;
intr_set_level (old_level);
return t;
}
这里的enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable ()和intr_set_level (old_level)两句语句比较重要。简单来说,这两句我们将经常会在代码中看到,这两句语句成对出现,代表这两句语句之间的语句将被保证不会被中断,以维持原子性操作。
背后的原理就是这两句语句实现了:禁用了中断->保存现场->恢复原来中断状态的变化。
除去这两句语句,(就剩了一行)其实timer_ticks也就是一个返回了ticks当前数值的函数。从pintos被启动开始, ticks变量就一直在计时, 代表着操作系统执行单位时间的前进计量。也就是一个用于计时的变量。
1.2 schedule()
static void
schedule (void)
{
struct thread *cur = running_thread ();
struct thread *next = next_thread_to_run ();
struct thread *prev = NULL;
ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_OFF);
ASSERT (cur->status != THREAD_RUNNING);
ASSERT (is_thread (next));
if (cur != next)
prev = switch_threads (cur, next);
thread_schedule_tail (prev);
}
schedule先把当前线程丢入就绪队列,切换就绪队列中下一个线程过来在CPU上运行。在切换之前,通过断言保证禁止中断、当前线程不处于运行态。若当前线程和下一个线程不同,则调用switch_thread切换线程,最后调用thread_schedule_tail恢复现场。
1.3 thread_yield()
void
thread_yield (void)
{
struct thread *cur = thread_current ();
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (cur != idle_thread)
list_push_back (&ready_list, &cur->elem);//如果当前线程不是空闲的线程,则把当前线程的元素扔到就绪队列里
cur->status = THREAD_READY;
schedule ();
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
暂时挂起一个线程,等待被唤醒。挂起线程的实现原理:把当前线程扔到就绪队列里, 然后切换下一个线程进入CPU.
1.4 thread_block()
void
thread_block (void)
{
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_OFF);
thread_current ()->status = THREAD_BLOCKED;
schedule ();
}
当前线程设置为阻塞状态,如果没有thread_unblock函数,将不会唤醒该线程。
1.5 timer_sleep()
void
timer_sleep (int64_t ticks)
{
if(ticks < 0){
return;
}
ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_ON);
enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable();
struct thread *current_thread = thread_current ();
current_thread->ticks_blocked = ticks;
thread_block();
intr_set_level(old_level);
}
用thread_block阻塞该线程。线程结构体成员ticks_blocked代表这个线程睡眠的时间,方便之后调用检测函数blocked_thread_check来判断该线程是否睡眠了足够时间。
1.6 thread_unblock()
void
thread_unblock (struct thread *t)
{
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (is_thread (t));
old_level = intr_disable ();
ASSERT (t->status == THREAD_BLOCKED);
list_push_back (&ready_list, &t->elem);
t->status = THREAD_READY;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
把阻塞的线程t放入就绪队列中。

1.7 blocked_thread_check()
void
blocked_thread_check (struct thread *t, void *aux UNUSED)
{
if (t->status == THREAD_BLOCKED && t->ticks_blocked > 0)
{
t->ticks_blocked--;
if (t->ticks_blocked == 0)
{
thread_unblock(t);
}
}
}
时间检测函数,每次调用该函数将线程的ticks_blocked减1, 如果减到0就调用thread_unblock唤醒这个线程。这样保证了线程有足够的睡眠时间。
1.8 thread_foreach()
void
thread_foreach (thread_action_func *func, void *aux)
{
struct list_elem *e;
ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_OFF);
for (e = list_begin (&all_list); e != list_end (&all_list);
e = list_next (e))
{
struct thread *t = list_entry (e, struct thread, allelem);
func (t, aux);
}
}
顾名思义,就是让每个线程都调用func函数,aux为可选参数。
1.9 timer_interrupt()
static void
timer_interrupt (struct intr_frame *args UNUSED)
{
ticks++;
thread_tick ();
thread_foreach(blocked_thread_check,NULL);
}
时间中断处理函数,通过调用thread_foreach对每个线程加入对它睡眠时间的检测函数blocked_thread_check。
2. 第二部分相关

图2 第二部分相关核心函数调用关系图
2.1 维护就绪队列为优先级队列
要解决优先级问题,首先我们要保证就绪队列为一个优先级队列。源代码中,就绪队列并不是优先级队列,自然无法实现任何有关优先级的操作。
2.1.1 thread_cmp_priority()
bool
thread_cmp_priority (const struct list_elem *a, const struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED)
{
return list_entry(a, struct thread, elem)->priority > list_entry(b, struct thread, elem)->priority;
比较函数,若线程a的优先级大于线程b的优先级则返回true。
2.1.2 list_insert_ordered()
void
list_insert_ordered (struct list *list, struct list_elem *elem,list_less_func *less, void *aux)
{
struct list_elem *e;
ASSERT (list != NULL);
ASSERT (elem != NULL);
ASSERT (less != NULL);
for (e = list_begin (list); e != list_end (list); e = list_next (e))
if (less (elem, e, aux))
break;
return list_insert (e, elem);
}
将elem通过循环查找有序地插入到队列list当中。其中,有序插入的实现依靠less函数,在项目的真正实现中, 这个less函数也就是上文提到的thread_cmp_priority函数。
2.1.3 如何解决?
什么时候我们会将一个线程加入就绪队列?有以下三种情况:
- 线程从阻塞态恢复(
thread_unblock) - 线程被初始化(
init_thread) - 线程挂起(
thread_yield)
这三个函数中,线程被加入就绪队列的方法都是调用list_push_back这个函数:
list_push_back (&ready_list, &t->elem);
显然,这个函数只能将元素单纯地加入队列,并不能有序地加入。所以就要把这个函数换成list_insert_ordered
2.1.4 thread_unblock()
void
thread_unblock (struct thread *t)
{
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (is_thread (t));
old_level = intr_disable ();
ASSERT (t->status == THREAD_BLOCKED);
list_insert_ordered (&ready_list, &t->elem, (list_less_func *) &thread_cmp_priority, NULL);
t->status = THREAD_READY;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
在将线程从阻塞态恢复到就绪队列的过程中,按线程优先级有序地加入就绪队列。
2.1.5 init_thread()
static void
init_thread (struct thread *t, const char *name, int priority)
{
ASSERT (t != NULL);
ASSERT (PRI_MIN <= priority && priority <= PRI_MAX);
ASSERT (name != NULL);
memset (t, 0, sizeof *t);
t->status = THREAD_BLOCKED;
strlcpy (t->name, name, sizeof t->name);
t->stack = (uint8_t *) t + PGSIZE;
t->priority = priority;
t->magic = THREAD_MAGIC;
list_insert_ordered (&all_list, &t->allelem, (list_less_func *) &thread_cmp_priority, NULL);
}
在创建线程时,按线程优先级有序地加入线程队列。
2.1.6 thread_yield()
void
thread_yield (void)
{
struct thread *cur = thread_current ();
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (cur != idle_thread)
list_insert_ordered (&ready_list, &cur->elem, (list_less_func *) &thread_cmp_priority, NULL);
cur->status = THREAD_READY;
schedule ();
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
在第一部分的基础上又改进了。在将线程挂起并加入到就绪队列中时按线程优先级有序加入。
2.1.7 thread_set_priority()
/* Sets the current thread's priority to NEW_PRIORITY. */
void
thread_set_priority (int new_priority)
{
thread_current ()->priority = new_priority;
thread_yield ();
}
设置线程优先级时,也要及时维护就绪队列的优先级顺序。当设置完线程优先级后,调用thread_yield函数将改变了优先级(新设置了优先级)的线程有序地加入就绪队列。
2.1.8 thread_create()
tid_t
thread_create (const char *name, int priority,
thread_func *function, void *aux)
{
struct thread *t;
struct kernel_thread_frame *kf;
struct switch_entry_frame *ef;
struct switch_threads_frame *sf;
tid_t tid;
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (function != NULL);
/* Allocate thread. */
t = palloc_get_page (PAL_ZERO);
t->ticks_blocked=0;
if (t == NULL)
return TID_ERROR;
/* Initialize thread. */
init_thread (t, name, priority);
tid = t->tid = allocate_tid ();
/* Prepare thread for first run by initializing its stack.
Do this atomically so intermediate values for the 'stack'
member cannot be observed. */
old_level = intr_disable ();
/* Stack frame for kernel_thread(). */
kf = alloc_frame (t, sizeof *kf);
kf->eip = NULL;
kf->function = function;
kf->aux = aux;
/* Stack frame for switch_entry(). */
ef = alloc_frame (t, sizeof *ef);
ef->eip = (void (*) (void)) kernel_thread;
/* Stack frame for switch_threads(). */
sf = alloc_frame (t, sizeof *sf);
sf->eip = switch_entry;
sf->ebp = 0;
intr_set_level (old_level);
/* Add to run queue. */
thread_unblock (t);
if(thread_current()->priority<priortiy){
thread_yield();
}
return tid;
}
创建线程时也会涉及到维护优先级队列问题。如果当前线程的优先级小于新创建线程优先级,那么将当前线程挂起加入就绪队列。
2.2 解决优先级反转
2.2.1 thread_update_priority()
void
thread_update_priority (struct thread *t)
{
enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable ();
int max_priority = t->base_priority;//锁的最大优先级属性初始化为原来持有该锁的线程的原始优先级
int lock_priority;
if (!list_empty (&t->locks))
{
list_sort (&t->locks, lock_cmp_priority, NULL);
lock_priority = list_entry (list_front (&t->locks), struct lock, elem)->max_priority;
if (lock_priority > max_priority)
max_priority = lock_priority;
}
t->priority = max_priority;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
进行优先级捐献或是释放锁时,我们需要更新持有锁线程的优先级。并且当这个线程还有持有其它锁时,要判断其它锁的最大优先级(也会被捐赠给这个线程)和这个线程的base_priority,如果其它锁的最大优先级大于base_priority,那么被捐赠的优先级lock_priority要更新成为那个最大优先级,而不是更新base_priority;反之,直接恢复base_priority。以此解决一个线程持有好几个锁的情况。
2.2.2 thread_donate_priority()
void
thread_donate_priority (struct thread *t)
{
enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable ();
thread_update_priority (t);
if (t->status == THREAD_READY)
{
list_remove (&t->elem);
list_insert_ordered (&ready_list, &t->elem, thread_cmp_priority, NULL);
}
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
通过调用thread_update_priority更新持有锁线程的优先级。然后在就绪队列中重新安排线程的先后顺序(按照新的优先级顺序),实现方法为将修改过的线程优先级先删除再有序地插入。
2.2.3 lock_cmp_priority()
bool
lock_cmp_priority (const struct list_elem *a, const struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED)
{
return list_entry (a, struct lock, elem)->max_priority > list_entry (b, struct lock, elem)->max_priority;
}
队列(等待获取该锁的线程队列)优先级比较函数,类似于2.1.1的thread_cmp_priority函数。
2.2.4 thread_hold_the_lock()
void
thread_hold_the_lock(struct lock *lock)
{
enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable ();
list_insert_ordered (&thread_current ()->locks, &lock->elem, lock_cmp_priority, NULL);//将获取该锁线程的优先级有序地插入到线程所持有的锁队列中
if (lock->max_priority > thread_current ()->priority)
{
thread_current ()->priority = lock->max_priority;
thread_yield ();
}//如果当前线程优先级小于等待获得锁的线程里的最大优先级,则提升当前线程优先级到那个最大的优先级,然后yield挂起放入就绪队列中参与竞争
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
一个线程获得锁后,重新对等待它的所有线程优先级排列,并根据其中的最大优先级实现捐赠。
2.2.5 lock_acquire()
void
lock_acquire (struct lock *lock)
{
struct thread *current_thread = thread_current ();
struct lock *l;
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (!lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
if (lock->holder != NULL && !thread_mlfqs)
{
current_thread->lock_waiting = lock;
l = lock;
while (l && current_thread->priority > l->max_priority)//当当前线程优先级大于获得这个锁的所有线程里的最高优先级时
{
l->max_priority = current_thread->priority;//把锁的最高优先级这个属性提升至这个线程的优先级
thread_donate_priority (l->holder);//优先级捐赠
l = l->holder->lock_waiting;//链式捐赠,遍历这个线程等待(想要获取)的所有锁,若他们被其它线程占据,则循环执行设置那个线程的优先级(进入循环)
}
}
sema_down (&lock->semaphore);//信号量减1,接下来获得锁
old_level = intr_disable ();
current_thread = thread_current ();//唤醒后获得锁
if (!thread_mlfqs)
{
current_thread->lock_waiting = NULL;//获得锁时,清空lock_waiting
lock->max_priority = current_thread->priority;//更新锁的最大优先级
thread_hold_the_lock (lock);
}
lock->holder = current_thread;//是当前线程持有锁
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
2.2.6 thread_remove_lock()
void
thread_remove_lock (struct lock *lock)
{
enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable ();
list_remove (&lock->elem);
thread_update_priority (thread_current ());
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
从锁队列里移除当前的优先级,从而释放一个锁。释放锁后,调用thread_update_priority更新当前线程的优先级。
2.2.7 lock_release()
void
lock_release (struct lock *lock)
{
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
if (!thread_mlfqs)
thread_remove_lock (lock);
lock->holder = NULL;
sema_up (&lock->semaphore);
}
当前线程调用thread_remove_lock释放锁。并更新锁的拥有者为空,信号量+1,表示锁已经释放。
2.2.8 thread_set_priority()
void
thread_set_priority (int new_priority)
{
if (thread_mlfqs)
return;
enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable ();
struct thread *current_thread = thread_current ();
int old_priority = current_thread->priority;
current_thread->base_priority = new_priority;
if (list_empty (¤t_thread->locks) || new_priority > old_priority)
{
current_thread->priority = new_priority;
thread_yield ();
}
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
实现了2.1功能的基础上,只有当当前线程仍有等待获取的锁或当前线程优先级被捐赠(即new_priority > old_priority)时,才设置当前线程优先级为新的指定优先级new_priority。
2.3 维护条件变量和信号量队列为优先级队列
2.3.1 cond_sema_cmp_priority()
bool
cond_sema_cmp_priority (const struct list_elem *a, const struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED)
{
struct semaphore_elem *sa = list_entry (a, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
struct semaphore_elem *sb = list_entry (b, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
return list_entry(list_front(&sa->semaphore.waiters), struct thread, elem)->priority > list_entry(list_front(&sb->semaphore.waiters), struct thread, elem)->priority;
}
比较等待条件变量的信号量大小的函数,类似于2.1.1的thread_cmp_priority函数。
2.3.2 修改条件变量队列 cond_signal()
void
cond_signal (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock UNUSED)
{
ASSERT (cond != NULL);
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
if (!list_empty (&cond->waiters))
{
list_sort (&cond->waiters, cond_sema_cmp_priority, NULL);
sema_up (&list_entry (list_pop_front (&cond->waiters), struct semaphore_elem, elem)->semaphore);
}
}
根据等待cond的线程的优先级大小修改cond队列顺序(list_sort),然后调用sema_up唤醒优先级最高的线程。
2.3.3 修改信号量队列 sema_up() sema_down()
void
sema_up (struct semaphore *sema)
{
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters))
{
list_sort (&sema->waiters, thread_cmp_priority, NULL);
thread_unblock (list_entry (list_pop_front (&sema->waiters), struct thread, elem));
}
sema->value++;
thread_yield ();
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
当信号量等待队列不为空时,根据信号量队列中线程的优先级大小修改sema队列顺序(list_sort),然后将优先级最高的线程解除阻塞状态。然后信号量+1,将当前线程加入就绪队列竞争。
void
sema_down (struct semaphore *sema)
{
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
while (sema->value == 0)
{
list_insert_ordered (&sema->waiters, &thread_current ()->elem, thread_cmp_priority, NULL);
thread_block ();
}
sema->value--;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
若信号量为0,表示不可继续获得锁。则把当前线程有序地插入到信号量等待线程队列当中去,然后阻塞该线程,信号量-1
3. 第三部分相关
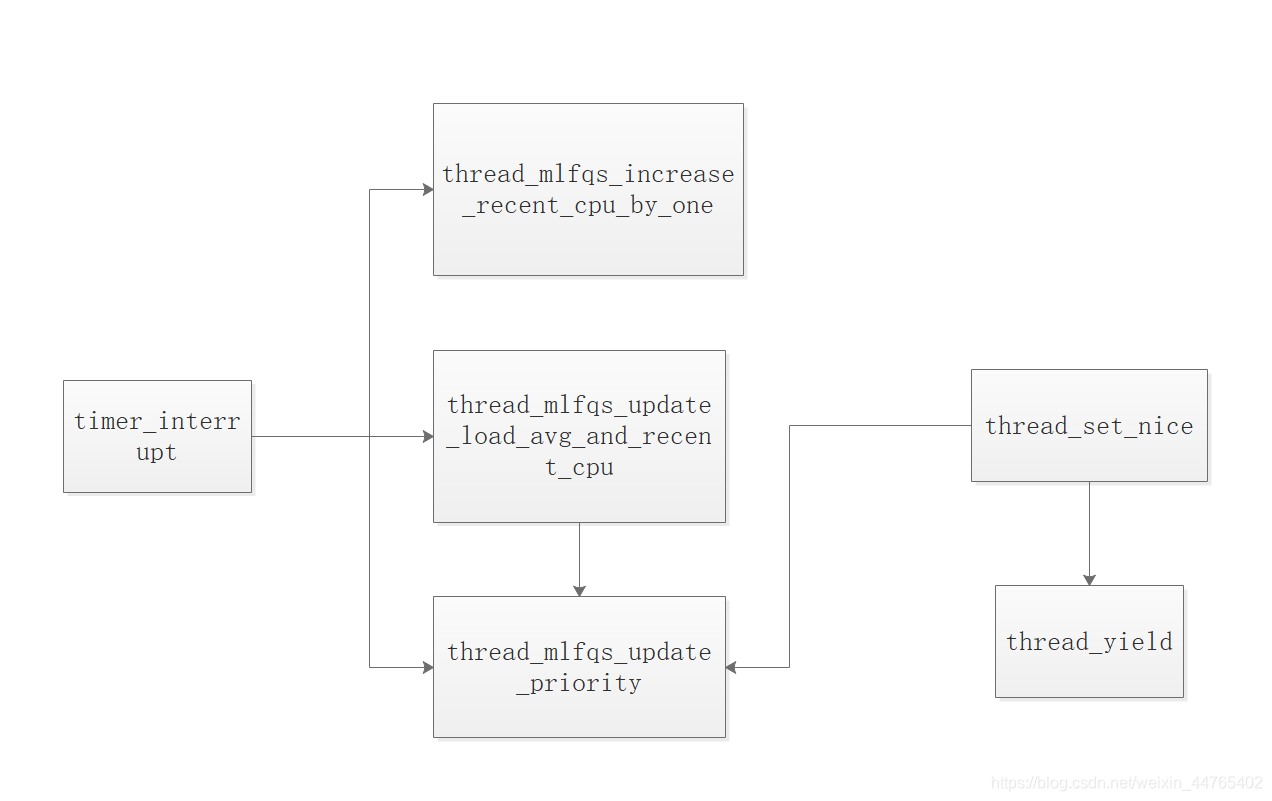
图3 第三部分相关核心函数调用关系图
3.1 thread_mlfqs_update_priority()
void
thread_mlfqs_update_priority (struct thread *t)
{
if (t == idle_thread)
return;
ASSERT (thread_mlfqs);
ASSERT (t != idle_thread);
t->priority = FP_INT_PART (FP_SUB_MIX (FP_SUB (FP_CONST (PRI_MAX), FP_DIV_MIX (t->recent_cpu, 4)), 2 * t->nice));//动态公式计算优先级
t->priority = t->priority < PRI_MIN ? PRI_MIN : t->priority;
t->priority = t->priority > PRI_MAX ? PRI_MAX : t->priority;
}
更新线程t的优先级,先根据公式计算t->priority,然后再修改它:t->priority先取它本身和PRI_MIN的最大值,再取它本身和PRI_MAX的最小值。
3.2 thread_mlfqs_increase_recent_cpu_by_one()
void
thread_mlfqs_increase_recent_cpu_by_one (void)
{
ASSERT (thread_mlfqs);
ASSERT (intr_context ());
struct thread *current_thread = thread_current ();
if (current_thread == idle_thread)
return;
current_thread->recent_cpu = FP_ADD_MIX (current_thread->recent_cpu, 1);
}
如果当前线程不是空闲的,那么就调用FP_ADD_MIX使得线程的recent_cpu+1(即timer_ticks中断次数+1次)
3.3 thread_mlfqs_update_load_avg_and_recent_cpu()
void
thread_mlfqs_update_load_avg_and_recent_cpu (void)
{
ASSERT (thread_mlfqs);
ASSERT (intr_context ());
size_t ready_threads = list_size (&ready_list);
if (thread_current () != idle_thread)
ready_threads++;//处于就绪状态的线程数+1
load_avg = FP_ADD (FP_DIV_MIX (FP_MULT_MIX (load_avg, 59), 60), FP_DIV_MIX (FP_CONST (ready_threads), 60));//计算load_avg(过去一分钟处于就绪状态的线程数)
struct thread *t;
struct list_elem *e = list_begin (&all_list);
for (; e != list_end (&all_list); e = list_next (e))
{
t = list_entry(e, struct thread, allelem);
if (t != idle_thread)
{
t->recent_cpu = FP_ADD_MIX (FP_MULT (FP_DIV (FP_MULT_MIX (load_avg, 2), FP_ADD_MIX (FP_MULT_MIX (load_avg, 2), 1)), t->recent_cpu), t->nice);//计算recent_cpu
thread_mlfqs_update_priority (t);
}
}
}
为所有线程更新load_avg和recent_cpu
3.4 timer_interrupt()
static void
timer_interrupt (struct intr_frame *args UNUSED)
{
ticks++;
thread_tick ();
thread_foreach(blocked_thread_check,NULL);
if (thread_mlfqs)
{
thread_mlfqs_increase_recent_cpu_by_one ();
if (ticks % TIMER_FREQ == 0)
thread_mlfqs_update_load_avg_and_recent_cpu ();
else if (ticks % 4 == 0)
thread_mlfqs_update_priority (thread_current ());
}
}
每个timer_tick 正在运行的线程的recent_cpu加一,每TIMER_FREQ时间计算一次load_avg和recent_cpu,然后每4次timer_ticks计算更新一次线程的优先级。
3.5 thread_set_nice()
void
thread_set_nice (int nice)
{
thread_current ()->nice = nice;
thread_mlfqs_update_priority (thread_current ());
thread_yield ();
}
其中,nice为线程属性,取值区间为[-20,+20],数值越大表示该线程出让更多的CPU时间。set_nice函数为线程设置nice的值。
3.6 thread_get_nice()
int
thread_get_nice (void)
{
return thread_current ()->nice;
}
获取当前线程的nice值。
3.7 thread_get_load_avg()
int
thread_get_load_avg (void)
{
return FP_ROUND (FP_MULT_MIX (load_avg, 100));
}
获取load_avg乘以100的值。
3.8 thread_get_recent_cpu()
int
thread_get_recent_cpu (void)
{
return FP_ROUND (FP_MULT_MIX (thread_current ()->recent_cpu, 100));
}
获取recent_cpu乘以100的值