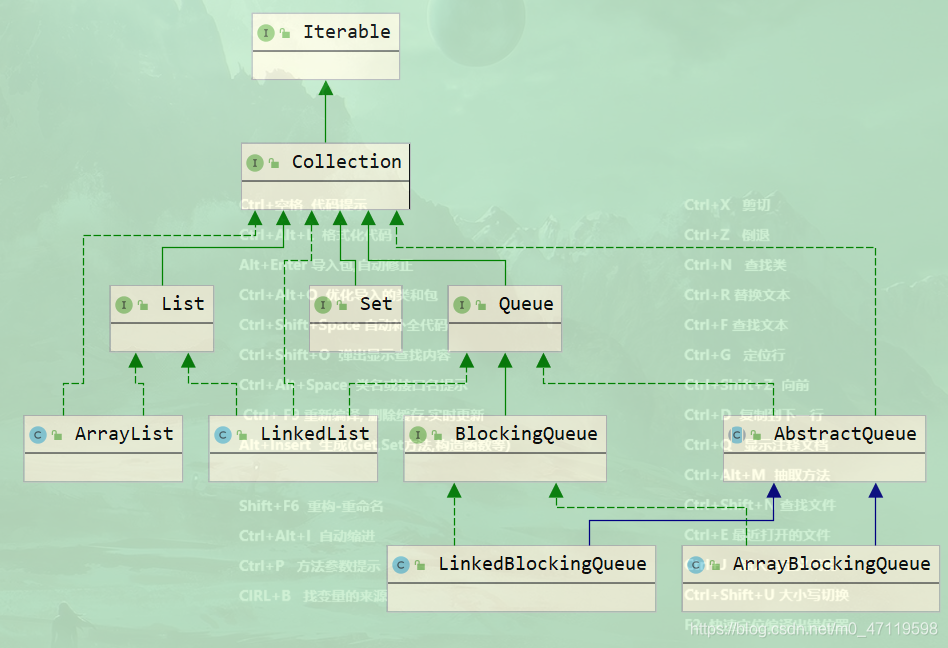
阻塞队列
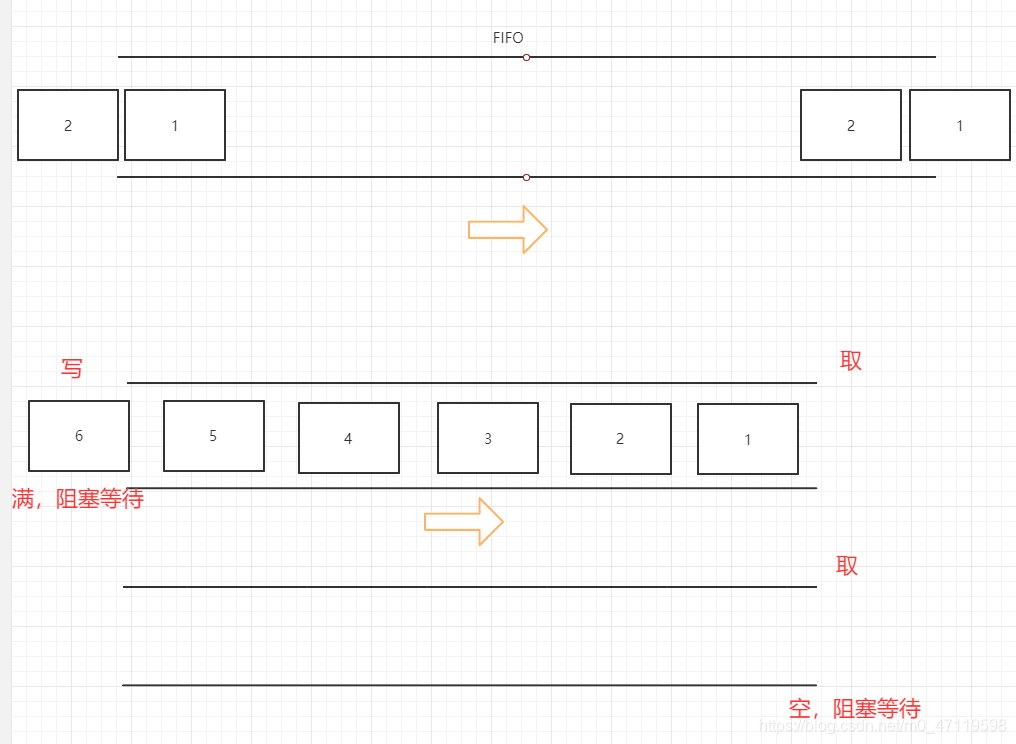
使用场景:多线程并发处理和线程池
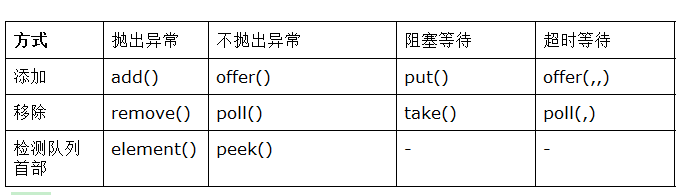
 四组API
四组API
- 抛出异常
- 不会抛出异常
- 阻塞 等待
- 超时等待
/**
* @Author Weton Li
* @Date 2021/2/10 20:49
*/
public class BlockingQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// test1();
// test2();
// test3();
test4();
}
/**
* 抛出异常
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void test1() throws InterruptedException {
// 队列容量为3
ArrayBlockingQueue arrayBlockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3); // 队列容量
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.add("a"));
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.add("b"));
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.add("c"));
// System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.add("d")); 报IllegalStateException异常,之前是报oncurrentModificationException
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.remove()); // a
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.remove()); // b
System.out.println("队首为:" + arrayBlockingQueue.element()); // 检测队首元素,当无队首时,报异常
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.remove()); // c
// System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.remove()); // 报NoSuchElementException异常
}
/**
* 有返回值,不抛异常
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void test2() throws InterruptedException {
// 队列容量为3
ArrayBlockingQueue arrayBlockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.offer("a"));
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.offer("b"));
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.offer("c"));
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.offer("d")); // false,不报异常
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll()); // null,不报异常
System.out.println("队首为:" + arrayBlockingQueue.peek()); // 队首为null,永不报异常
}
/**
* 等待,阻塞(一直阻塞)
*/
public static void test3() throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue arrayBlockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
arrayBlockingQueue.put("a");
arrayBlockingQueue.put("b");
arrayBlockingQueue.put("c");
// arrayBlockingQueue.put("d"); // 不报错抛异常,会永远阻塞
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.take());
// System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.take()); // 不报错抛异常,会永远阻塞
}
/**
* 等待,阻塞(等待超时)
*/
public static void test4() throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue arrayBlockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
arrayBlockingQueue.offer("a");
arrayBlockingQueue.offer("b");
arrayBlockingQueue.offer("c");
arrayBlockingQueue.offer("d", 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 因为队列容量为3,故等两秒
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll());
arrayBlockingQueue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 因队列容量为3,故等两秒自动退出
}
}
SynchronousQueue同步队列(容量唯一)特殊的阻塞队列
/**
* 放一个取一个
* 只有一个停车位,停一个开走后第二辆车才能停进来。
* 茵上厕所锁门,彤在外等待。安全。
* @Author Weton Li
* @Date 2021/2/10 22:52
*/
public class SynchronousQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynchronousQueue<String> synchronousQueue = new SynchronousQueue(); // 默认且只能为1
new Thread(()->{
try {
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put a");
synchronousQueue.put("a");
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put b");
synchronousQueue.put("b");
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put c");
synchronousQueue.put("c");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"T1").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+synchronousQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+synchronousQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+synchronousQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"T2").start();
}
}