1、Springboot三大特性
1、帮助开发者快速整合第三方框架(原理maven依赖封装)
2、内嵌服务器(原理java语言创建服务器)
3、完全注解形式代替XML
传统的Spring项目:
-
基于xml
-
依赖第三方的模块,都是在xml文件中逐个依赖,还需要在xml文件中配置
配置的目的就是让spring区加载和管理这些Bean。
-
需要依赖外部的tomcat容器去部署项目才可以进行项目的发布和部署
-
日志管理,也需要额外的配置
-
配置组件或者应用的时候,非常的麻烦和繁复。
Springboot项目:
- 零配置,用注解的方式取代了传统意义上的xml文件
- starter机制,解决什么问题,如何解决的?
- 内置了tomcat容器和日志管理,开发起来只需要启动main函数即可,就可以让项目运行起来了。
- springboot管理的bean是如何注册到springioc容器中的,springboot是怎么和spring发生关系的?
2、如何去学习分析源码
- 心中要有目标和方向
3、Springboot项目整体结构
核心启动类:
package com.kuang.kuangstudybootsource;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class KuangstudyBootSourceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KuangstudyBootSourceApplication.class, args);
}
}
4、springboot的零配置是怎么解决的呢?
答案是用 : 注解
传统ssm的方法:
- xml – applicationContext.xml
<bean id="xxx" class="xxxx">
<bean id="xxx" class="xxxx">
<bean id="xxx" class="xxxx">
<bean id="xxx" class="xxxx">
- 扫包+注解
<component-scan basePackages="com.kuangstudy.service">
<component-scan basePackages="com.kuangstudy.mapper">
<component-scan basePackages="com.kuangstudy.controller">
注解:@Service 、@Controller 、@RestController 、 @Resposity 、 @Component等。
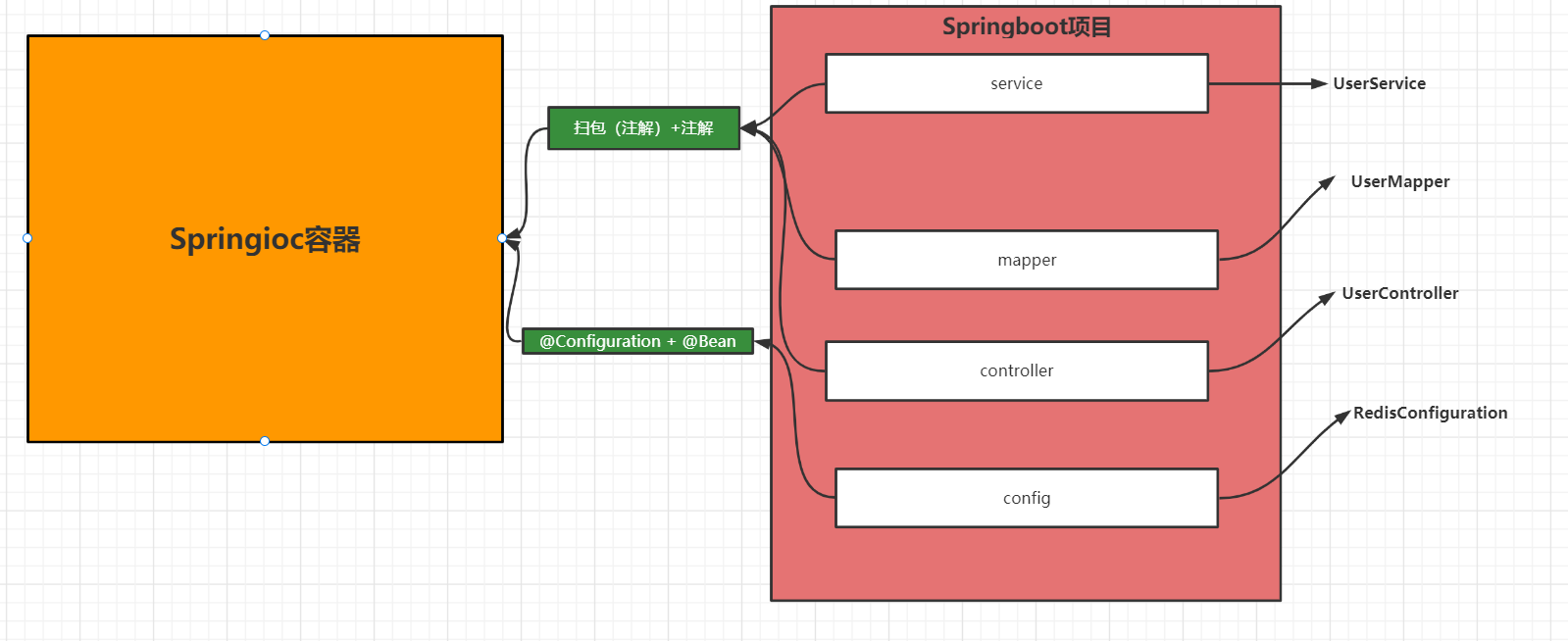
Springboot改进:
- 扫包 (注解)+ 注解
@ComponentScan + 注解 : @Service 、@Controller 、@RestController 、 @Resposity 、 @Component等。
- @Configuration (配置类)+ @Bean(初始化)
- Import机制
@Import(配置类&selector接口实现类,也可以写普通的bean)
@Import(RedisConfiguration.class)
@Import(UserService.class)
@Import(AxxxxxSelector.class)
- ImportResource
@ImportResource("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
5、springboot的零配置在解决一个什么问题?
- 抛弃传统的xml方式
- 也可以去整合传统的xml方式,通过@ImportResource 来解决,不建议混合使用
不管是传统的xml方式还是springboot提供的这四种机制,他们在解决什么问题?
他们都在解决一个问题:

通过不同的方式,把项目中的和第三方的依赖全部放在springioc容器中,springboot基础核心还是spring,只不过是对soring项目进行了一次升级和改造。
6、怎么认识项目中的bean
项目中的bean
第三方的依赖bean
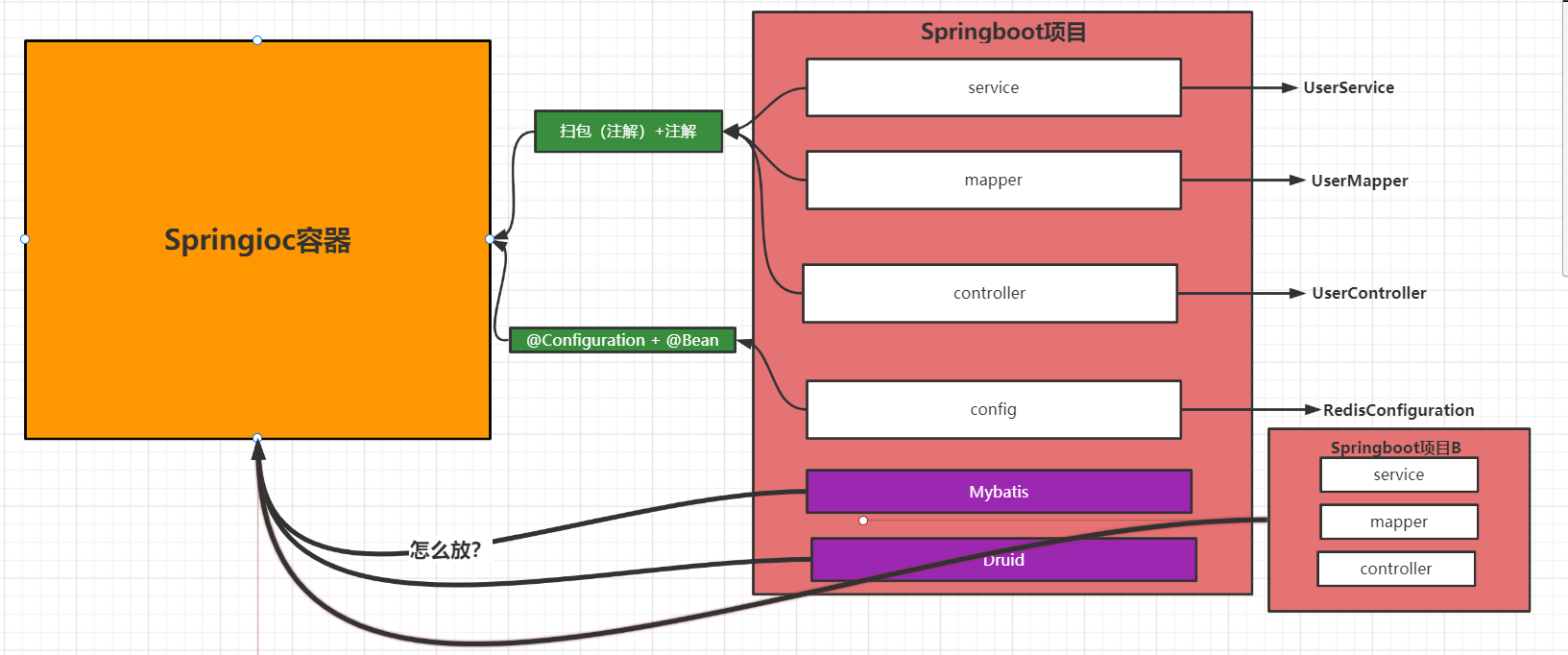
解决方案:
- 第一种解决方案: 必须这些第三方的包名必须要和当前项目的包名一致,不然加载不进去!!
- 扫包 + 注解
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {
"com.kuangstudy.kuangstudybootsource","org.mybatis","com.ablibb.druid","com.xxxxxx"})
上面的话,肯定是不可取的,因为这种方式去加载第三方的bean到项目中的ioc去,肯定非常麻烦,维护起来就是一 个灾难。
7、@Import机制,拯救第三方bean加载到ioc容器中
这个就是所谓的:starter机制
// 官方提供的
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
// 第三方提供的
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
官方提供的:spring-boot-starter-xxxx
两者的区别: 官方的不需要加版本号,因为通过parent指定的版本统一升级和管理。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
第三方提供的 :xxxx-boot-starter
它遵循springboot的starter机制开发出来的一种形式,它的导入就必须加version
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
8、这四种机制是如何bean加载到ioc容器中的
1、在启动springboot项目的时候
@SpringBootApplication
public class KuangstudyBootSourceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KuangstudyBootSourceApplication.class, args);
}
}
核心方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KuangstudyBootSourceApplication.class, args);
}
—1、调用方法如下:
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] {
primarySource }, args);
}
—2、调用方法如下:
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
—3、调用方法如下(核心):
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
// 方法的拆解
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(primarySources); // 初始化阶段
application.run(); // 运行阶段
08-01、初始化阶段
new SpringApplication(primarySources)
初始化阶段:把项目中所有的符合springboot机制的bean全部收集起来 ----> Map
----1、调用构造函数方法
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
----2、调用具体的初始化方法的过程(核心)
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
// 1、初始化数组、集合、开关标记等
this.sources = new LinkedHashSet();
this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE;
this.logStartupInfo = true;
this.addCommandLineProperties = true;
this.addConversionService = true;
this.headless = true;
this.registerShutdownHook = true;
this.additionalProfiles = Collections.emptySet();
this.isCustomEnvironment = false;
this.lazyInitialization = false;
this.applicationContextFactory = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT;
this.applicationStartup = ApplicationStartup.DEFAULT;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 核心代码1~
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = this.getBootstrapRegistryInitializersFromSpringFactories();
// 核心代码2~
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 核心代码3~
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
核心代码1、核心代码2、核心代码3 都在调用同一个方法:
核心代码1:
this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class)
核心代码2:
this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)
核心代码3:
this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)
这三个都传递了一个类:
1、为什么要传递类?
作用:触发类加载器
2、传递类作用是干什么?
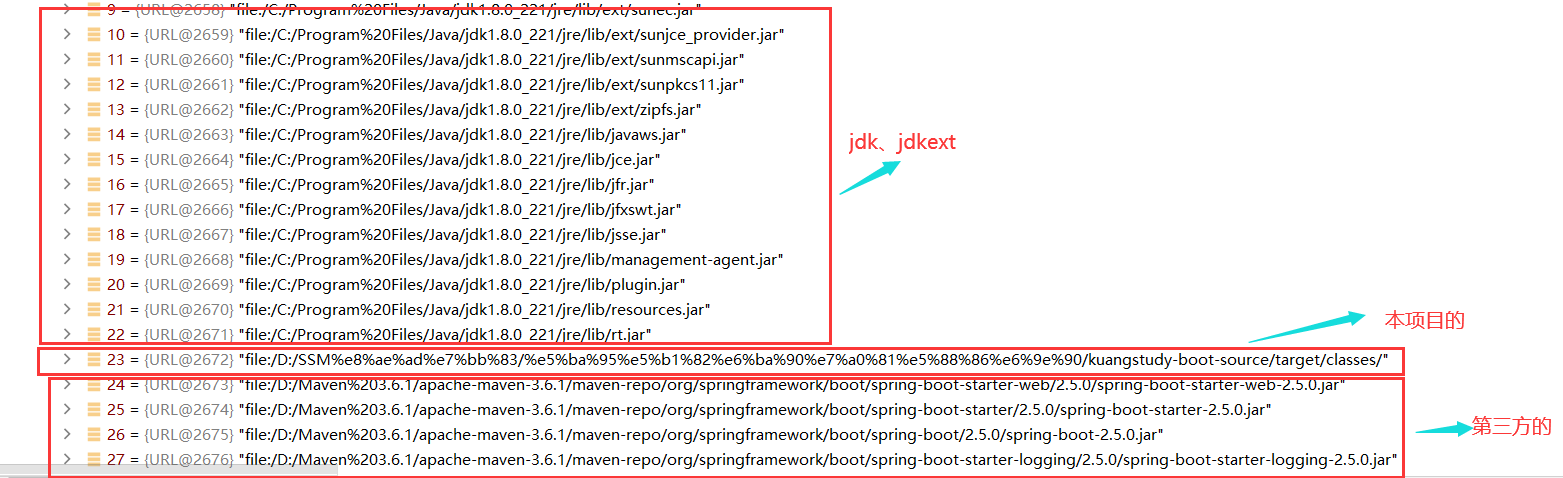
触发类加载器,通过双亲委派机制,把项目中所有的类,包括jdk、jdkext、target、classes、spring.jar、mybatis.jar等编译好的class文件全部找到,放入map中。
BootstrapRegistryInitializer(大哥)类的作用:
- 其实它这个类不具体干活,他提前把项目中的类全部找到放入缓存map中。
- 给后面的ApplicationContextInitializer、ApplicationListener的初始化提供一个缓存机制。
- 后面两者获取对应bean的时候就不用频繁的去触发类加载器,也不用频繁的扫描过滤了。
----3、调用具体的getSpringFactoriesInstances(核心)
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class[0]);
}
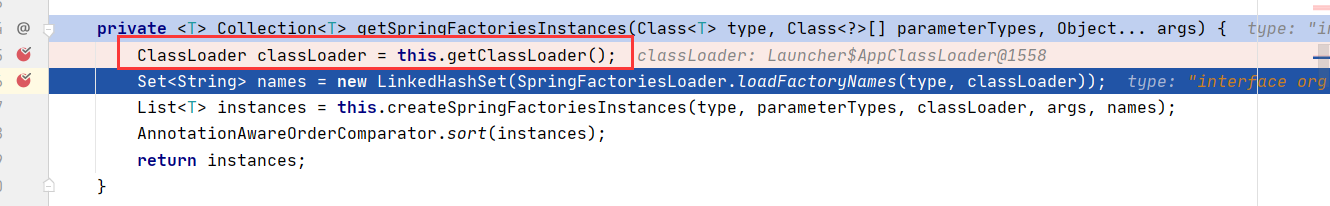
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = this.getClassLoader();
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = this.createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
下面就是一个类加载器:AppClassLoader — ExtClassLoader — BootstrapClassLoader(双亲委派模型)
ClassLoader classLoader = this.getClassLoader();
双亲委派模型:一句话,找到项目中所有的class字节文件,无论jdk、ext和项目写的target/classes、spring.jar等统统全部找到!
问:你项目中引入的jdk是怎么加载进去的,你项目引入spring.jar它里面的类你为什么可以用,你项目Spring,List为什么就可以使用了呢?
答案:就是因为在启动的时候,项目中会调用类加载器,通过双亲委派模型,把项目中所有的classes全部找到,然后放在JVM中去,只不过springboot把这些加载的classes进行匹配过滤把符合条件的bean放入到ioc容器中的过程
哪些是符合上面条件的bean呢?
- 扫包 + 注解(@Service、@Controller)
- 是不是符合import机制
- 是不是符合@Configuration + @Bean
----4、开始对类加载器加载的类进行过滤
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
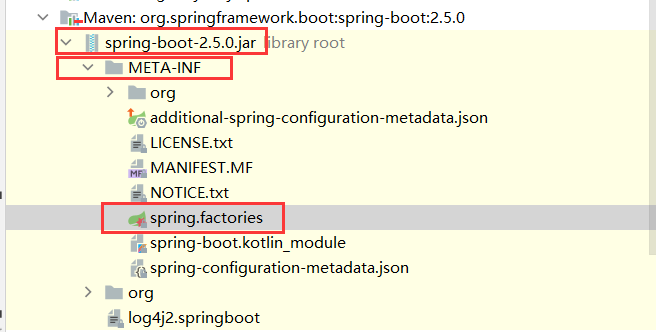
type: interface org.springframework.boot.Bootstrapper 开始进行匹配过滤,作用其实就是起到一个加载缓存的目的,作用就是,他会把类加载器中所有的jar文件中包含:META-INF/spring.factories文件中的内容全部找到,然后把这个文件中的bean全部放入到Map中,如下:
----5、把jar包中包含META-INF/spring.factories的内容找到(核心)
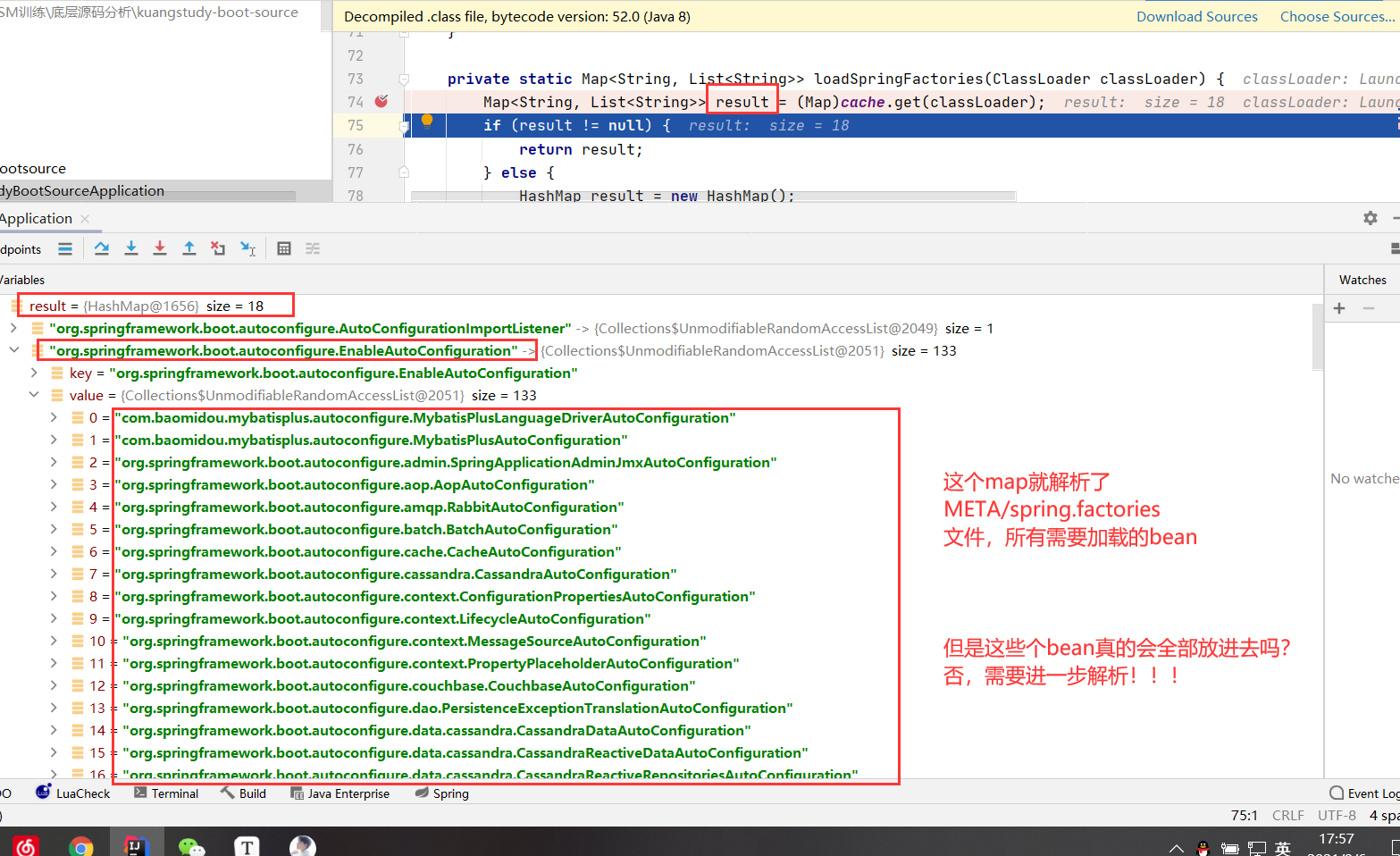
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = (Map)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
HashMap result = new HashMap();
try {
// 通过类加载器把jar包中包含META-INF/spring.factories,找到
// 这里的原理是一个双亲委派模型
Enumeration urls = classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
// 解析
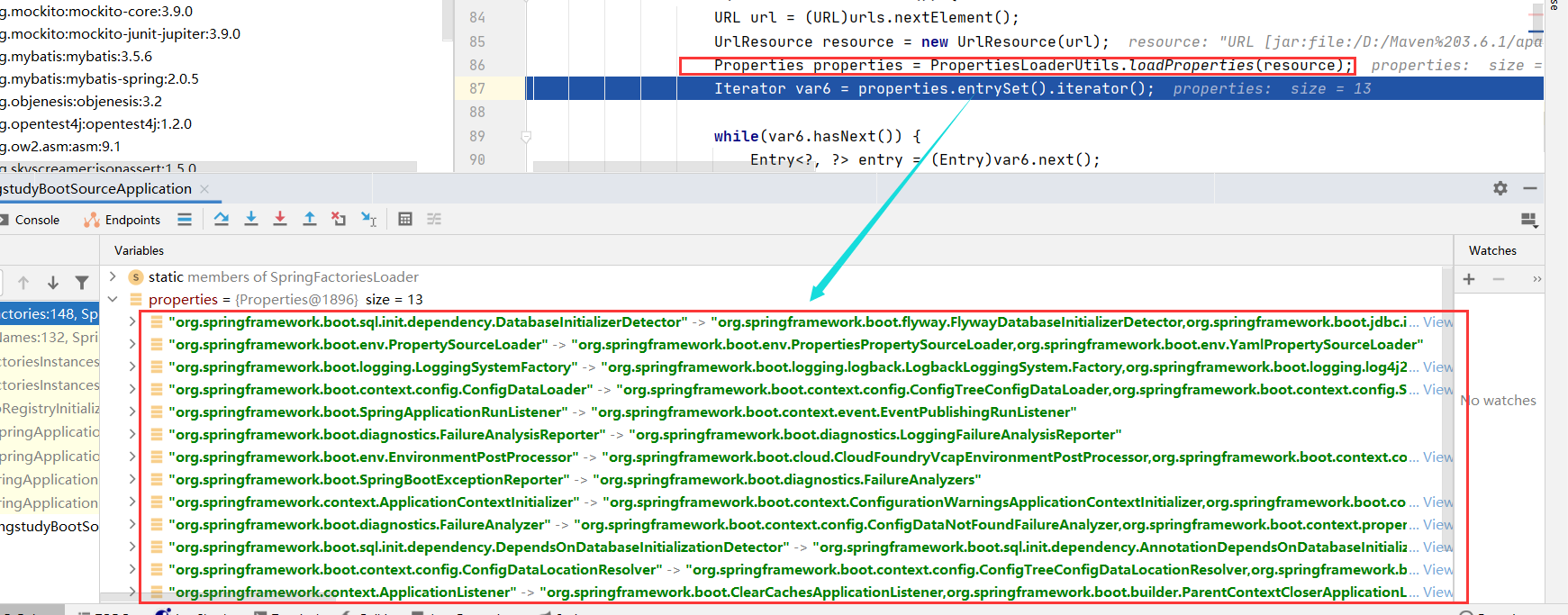
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
String[] var10 = factoryImplementationNames;
int var11 = factoryImplementationNames.length;
for(int var12 = 0; var12 < var11; ++var12) {
String factoryImplementationName = var10[var12];
((List)result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, (key) -> {
return new ArrayList();
})).add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> {
return (List)implementations.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList));
});
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var14) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var14);
}
}
}

08-02、springboot是如何把需要的bean加载出来的呢?
我们知道类载器,把项目中所有的classes统统都会加载到JVM中去,这么多的class,springboot是如何找到那些需要管理和初始化的bean呢?springboot借鉴了java9的新特性:spi机制,其实就是把需要被加载类放入到一个配置文件中,而springboot命名规则正好是:META-INF/spring.factories。
- 而这个文件中就定义了springboot需要加载的所有的bean。
- 现在要做的事情就是,找到这个文件
- 解析这个文件
- 解析之后放入到map中(仅此而已,千万记住,这时还没有和springioc产生任何关系)
找到的第一个需要解析的jar包:
file:/D:/Maven%203.6.1/apache-maven-3.6.1/maven-repo/org/springframework/boot/spring-boot/2.5.0/spring-boot-2.5.0.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories
内容如下:
# Logging Systems
org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingSystemFactory=\
org.springframework.boot.logging.logback.LogbackLoggingSystem.Factory,\
org.springframework.boot.logging.log4j2.Log4J2LoggingSystem.Factory,\
org.springframework.boot.logging.java.JavaLoggingSystem.Factory
# PropertySource Loaders
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\
org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader
# ConfigData Location Resolvers
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataLocationResolver=\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigTreeConfigDataLocationResolver,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.StandardConfigDataLocationResolver
# ConfigData Loaders
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataLoader=\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigTreeConfigDataLoader,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.StandardConfigDataLoader
# Run Listeners
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
# Error Reporters
org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzers
# Application Context Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener
# Environment Post Processors
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.RandomValuePropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.reactor.DebugAgentEnvironmentPostProcessor
# Failure Analyzers
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigDataNotFoundFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.IncompatibleConfigurationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.NotConstructorBoundInjectionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanCurrentlyInCreationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanDefinitionOverrideFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanNotOfRequiredTypeFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindValidationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.UnboundConfigurationPropertyFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ConnectorStartFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchMethodFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ValidationExceptionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyNameFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyValueFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PatternParseFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseChangelogMissingFailureAnalyzer
# Failure Analysis Reporters
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalysisReporter=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter
# Database Initializer Detectors
org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.DatabaseInitializerDetector=\
org.springframework.boot.flyway.FlywayDatabaseInitializerDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.jdbc.init.DataSourceScriptDatabaseInitializerDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseDatabaseInitializerDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.JpaDatabaseInitializerDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.r2dbc.init.R2dbcScriptDatabaseInitializerDetector
# Depends On Database Initialization Detectors
org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.DependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector=\
org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.AnnotationDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.jdbc.SpringJdbcDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.jooq.JooqDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.JpaDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector
找到第二个jar进行解析:
jar:file:/D:/Maven%203.6.1/apache-maven-3.6.1/maven-repo/org/springframework/spring-beans/5.3.7/spring-beans-5.3.7.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories
org.springframework.beans.BeanInfoFactory=org.springframework.beans.ExtendedBeanInfoFactory
找到第三个需要解析的文件:
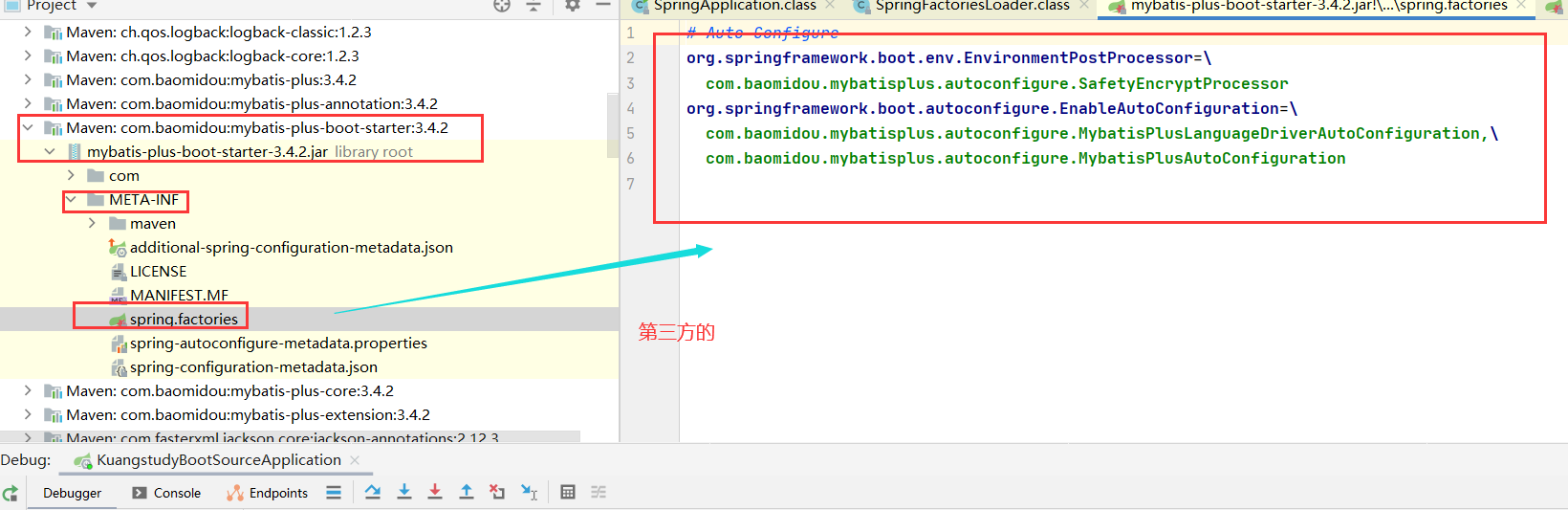
第四个需要解析的jar:(核心)
jar:file:/D:/Maven%203.6.1/apache-maven-3.6.1/maven-repo/org/springframework/boot/spring-boot-autoconfigure/2.5.0/spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.5.0.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories
# Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
# Environment Post Processors
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationPropertiesEnvironmentPostProcessor
# Auto Configuration Import Listeners
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener
# Auto Configuration Import Filters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition
# Auto Configure 核心,配置类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcDataAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.availability.ApplicationAvailabilityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.neo4j.Neo4jAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.netty.NettyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketRequesterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketStrategiesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.rsocket.RSocketSecurityAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.saml2.Saml2RelyingPartyAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sql.init.SqlInitializationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
# Failure analyzers
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisUrlSyntaxFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayMigrationScriptMissingFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBeanCreationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.HikariDriverConfigurationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.ConnectionFactoryBeanCreationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.NonUniqueSessionRepositoryFailureAnalyzer
# Template availability providers
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.template.TemplateAvailabilityProvider=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.JspTemplateAvailabilityProvider
# DataSource initializer detectors
org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.DatabaseInitializerDetector=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayMigrationInitializerDatabaseInitializerDetector
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration
就是这个注解@EnableAutoConfiguration对应的所有配置类
这些配置类如何加载到ioc容器中去呢?(运行阶段)
初始化阶段为什么还没有放入到ioc容器中去呢?
答案:因为初始化阶段仅仅只是一个解析和准备的工作,就把需要的bean全部找到,仅此而已
@Conditionxxxxxx
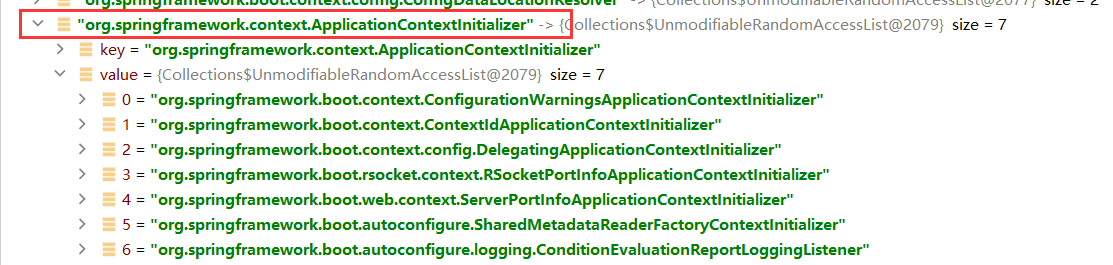
ApplicationContextInitializer
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,
org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,
org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer,
org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
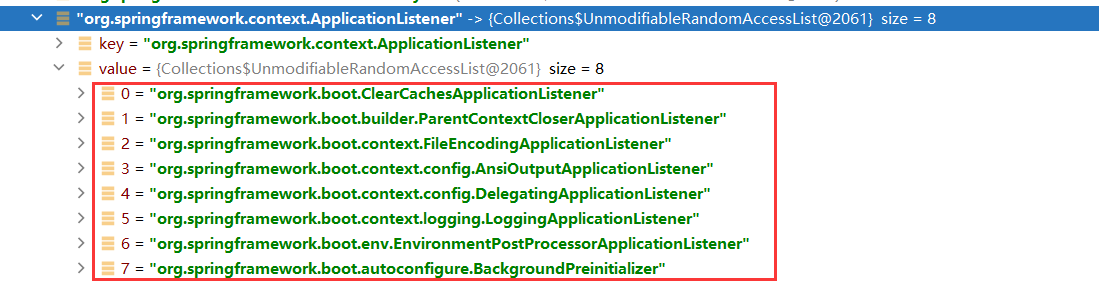
ApplicationListener
org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,
org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener
08-03、运行阶段
.run(args);
运行阶段:把初始化阶段的所有bean收集起来,全部放在ioc容器中,再去经历spring中bean的生命周期,运行结束,项目就被运行起来了!
08-03-01、证明:启动类在启动默认情况下,会把当前主类的包名作为包入口
也就是@ComponentScan的原理,其实它背后就是一个类在做事情,如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer
如何证明:注解的解析和放入ioc是在运行阶段去执行和解析的呢?
-
在初始化的构造函数结束行打个断点 – run方法开头打个断点 – 在解析类中打个断点
如果是按照这个执行的话,说明我的初始化阶段仅仅就解析了spring.factories这个文件和收集对应需要初始化的bean
-
并且证明注解的解析和bean的初始化都是在run执行的方法中
-
在初始化的构造函数结束行打个断点-- 在解析类中打个断点(错的)
@EnableAutoConfiguration在什么时候加载@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})的呢?
答案:触发bean的生命周期,里面会有一个ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类的processGroupImports方法中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors来加载。
run ------ 1234567 — selectImports
1:
2:
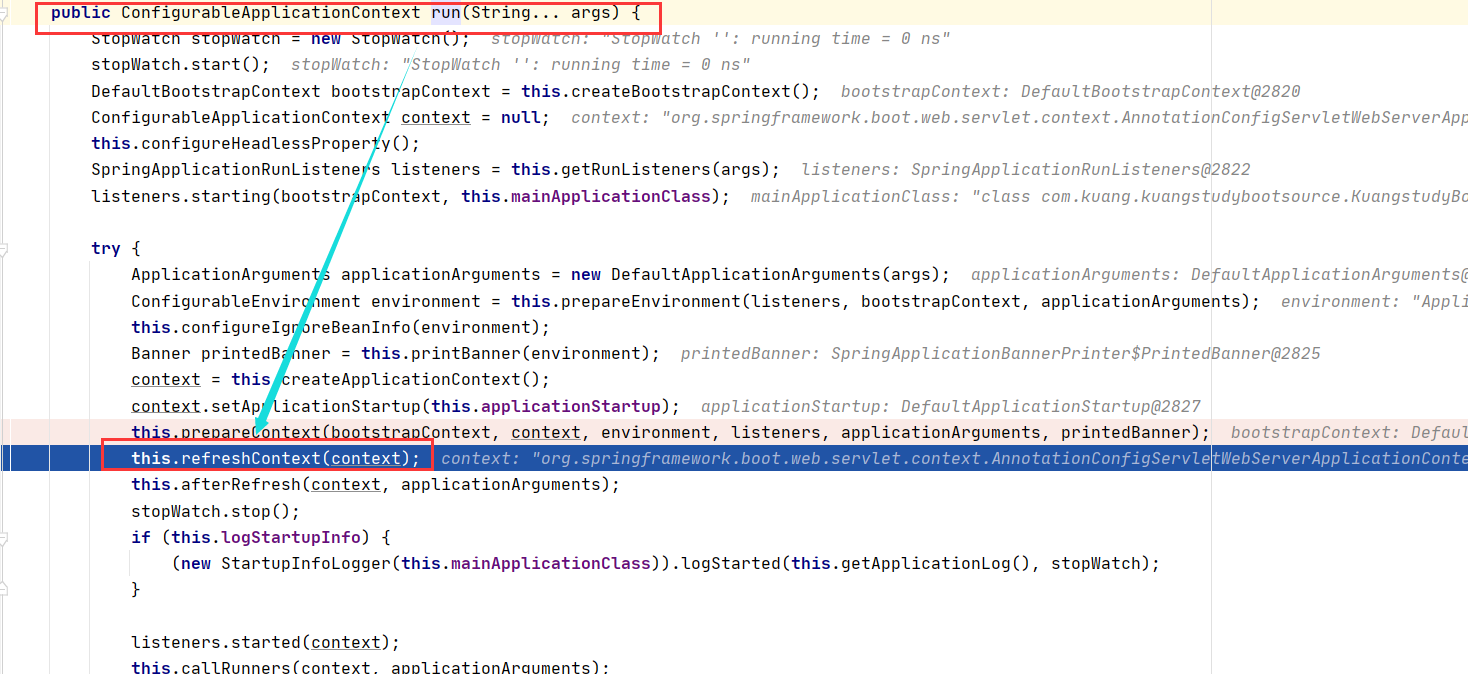
protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.refresh();
}
3:
protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.refresh();
}
4:
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, this.getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean("loadTimeWeaver")) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
5:
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
6:
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
7:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
parser.parse(candidates);
}
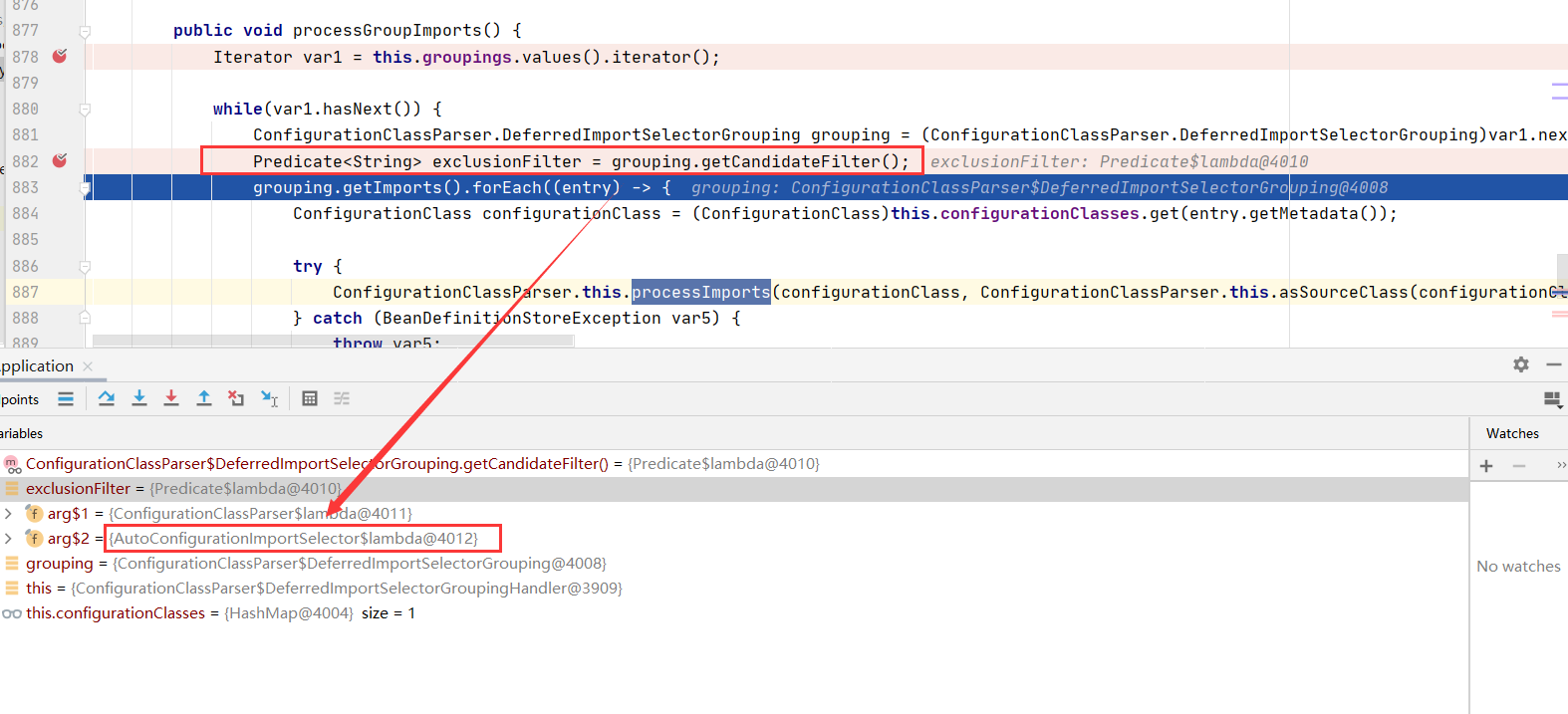
public void processGroupImports() {
Iterator var1 = this.groupings.values().iterator();
while(var1.hasNext()) {
ConfigurationClassParser.DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping = (ConfigurationClassParser.DeferredImportSelectorGrouping)var1.next();
Predicate<String> exclusionFilter = grouping.getCandidateFilter();
grouping.getImports().forEach((entry) -> {
ConfigurationClass configurationClass = (ConfigurationClass)this.configurationClasses.get(entry.getMetadata());
try {
ConfigurationClassParser.this.processImports(configurationClass, ConfigurationClassParser.this.asSourceClass(configurationClass, exclusionFilter), Collections.singleton(ConfigurationClassParser.this.asSourceClass(entry.getImportClassName(), exclusionFilter)), exclusionFilter, false);
} catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException var5) {
throw var5;
} catch (Throwable var6) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" + configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]", var6);
}
});
}
}
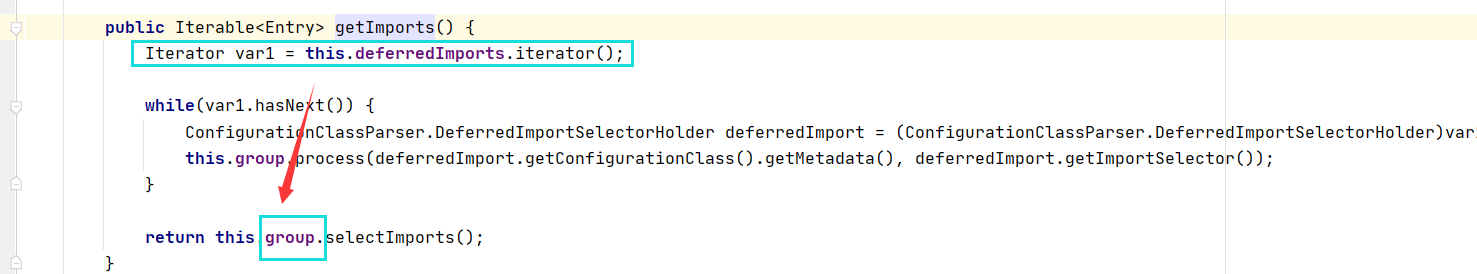
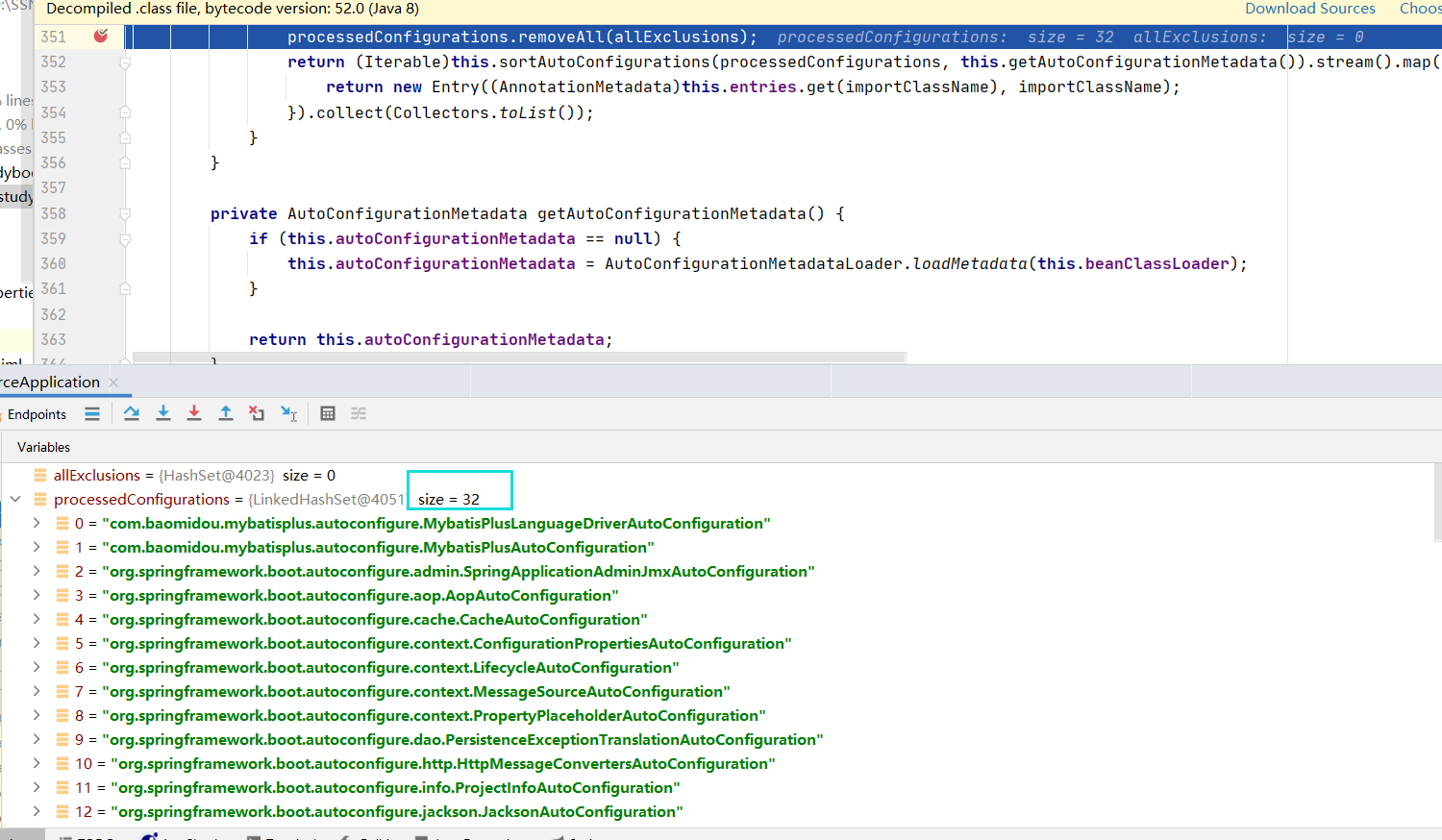
08-04、如何与springioc发生关系
run方法执行的时候,执行this.refreshContext(context);的时候产生的关系
08-05、Spring生命周期的阶段
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
this.prepareRefresh();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
this.initMessageSource();
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.onRefresh();
this.registerListeners();
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var10) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var10);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var10);
throw var10;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}