spring boot day(2)
一、与前端交互存在的问题
1.1 关闭spring boot项目中的spring secyrity
- exclude = {SecurityAutoConfiguration.class
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {
SecurityAutoConfiguration.class})
//@SpringBootApplication(exclude= {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class HelloworldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloworldApplication.class, args);
}
}
1.2 在后端解决跨域
- controller类上加入@CrossOrigin(value = “http://localhost:8081”)
@CrossOrigin(value = "http://localhost:8081")
public class DogController {
......
}
1.3 读取文件
参考:读取文件方法大全
二、前后端交互
2.1 传递普通变量
- 后端代码
@RequestMapping("/getName")
public String getName(){
return "jack";
}
- 前端代码:
axios({
method:"get",
url:'http://localhost:8080/getName',
data:{
},
Headers:{
" Access-Control-Allow-Origin":"*"
}
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data)
})
2.2 传递多种类型数据
- 后端代码
@RequestMapping("/getName")
public ArrayList getName(){
Dog wo = new Dog("kk","12",3);
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add("jack");
list.add(12);
list.add(wo);
return list;
}
2.3 传递结构体类型数据
- 后端代码
@RequestMapping("/getDogEntity")
public Dog getDogEntity(){
Dog dog1 = new Dog("kkk","23",3);
return dog1;
}
- 前端代码
axios({
method:"get",
url:'http://localhost:8080/getDogEntity',
data:{
},
Headers:{
" Access-Control-Allow-Origin":"*"
}
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data)
})
2.4 返回file类型数据
@RequestMapping("/getFile")
public File getFile(HttpServletResponse response) {
//当前路径是项目下的路径
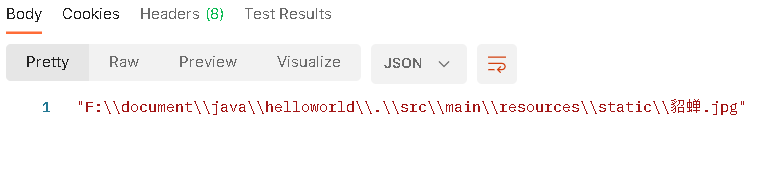
File file = new File("./src/main/resources/static/貂蝉.jpg");
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println(file.exists());
//response.setHeader("contentType", "image/jpeg");
return file;
}
- 前端得到的data
2.5 前端发送文件数据
upload() {
var formdate = new FormData();
for (var i = 0; i < this.images.length; i++) {
formdate.append("file", this.images[i]);
}
formdate.append("pid", "fileUpload");
var instance = axios.create({
baseURL: "http://localhost:8080",
timeout: 1000,
headers: {
"Content-Type": "multipart/form-data" },
});
instance.post("/receiveData", formdate).then((res) => {
console.log("发送成功");
console.log(res)
});
},
2.6 后端接收前端传来的文件
- 后端用的是:@RequestParam(“file”)
@RequestMapping("/receiveData")
public void getImage(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile[] file,@RequestParam("pid") String value,HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
for(int i=0;i < file.length;i++){
System.out.println(file[i].getOriginalFilename());
String path = "F:\\document\\java\\helloworld\\src\\main\\resources\\static\\";
File newFile = new File(path + file[i].getOriginalFilename());
System.out.println(newFile.getAbsolutePath());
file[i].transferTo(newFile);
}
System.out.println(value);
}
三、上传文件的细节
3.1 标签
- type是file,即文件类型
- multiple表示可以选择多个文件
<input type="file" @change="change($event)" multiple="multiple">
3.2 change函数,$event参数
- change函数表示选择文件时会产生相对应的事件
- 文件对象就会在event.target.files;
- @进行事件的绑定
change="change($event)
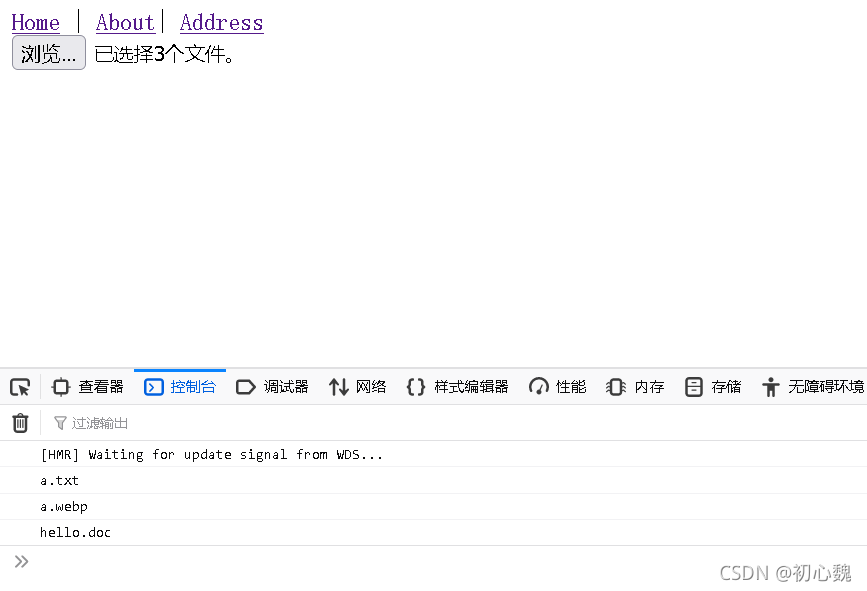
3.3 获取文件并打印在控制台
change(event){
this.images = event.target.files;
for(var i =0;i <this.images.length;i++){
console.log(this.images[i].name)
}
},
3.4 获取input中value
3.5 上传文件
- 将文件数据添加到FormData实例对象中
- “pid”,"fileUpload"以键值对的形式向后端发送数据,后端获取根据key获取。
- 设置请求头: ‘Content-Type’: ‘multipart/form-data’
var formdate = new FormData()
for(var i=0; i < this.images.length;i++){
formdate.append(this.images[i])
}
formdate.append("pid","fileUpload");
3.6 前端在Data:{}(body)中传入数据,后端通过RequestBody 进行接受
- 前端在data中添加数据
axios({
method:"post",
url:"http://127.0.0.1:8080/receiveData1",
data:{
file:"test",
},
}).then(res=>{
console.log("上传成功");
console.log(res)
})
- 后端通过RequestBody接受
@RequestMapping("/receiveData1")
public void getImage(@RequestBody Map<String, String> paras){
System.out.println(paras.get("file"));
}
四、前端常用功能
4.1前端页面的跳转加传参数
-页面跳转传参
turnToSecond() {
console.log("准备跳转到第二个页面");
this.$router.push({
path: "/second",
query: {
name: "jack",
age: 12,
},
});
},
4.2 页面跳转参数的查询
- 页面跳转接收参数
- 跳转页面添加的参数会展示在被跳转的页面上
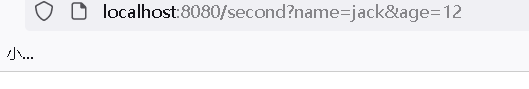
- 注意:接收是this. r o u t e . q u e r y . k e y 不 是 t h i s . route.query.key不是this. route.query.key不是this.router.query.key
getParams(){
console.log("输出")
console.log(this.$route.query.name);
console.log(this.$route.query.age);
}
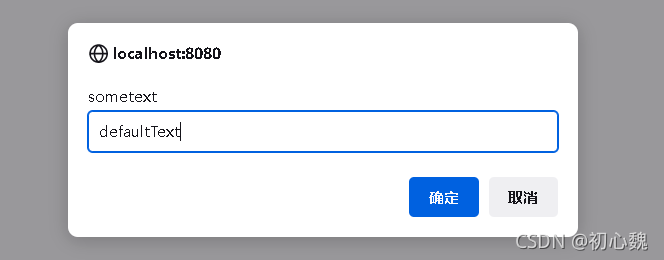
4.3 js的三种弹出框
alert("hahaha")
window.confirm("请按按钮");
window.prompt("sometext","defaultText");
4.4 返回上一页面
this.$router.go(-1)
4.5 vue中一个方法调用另一个方法
this.$options.methods.showTime();
五、vue的细节
5.1 proxy对象
- 比如这里得到的是代理对象,就把他看成后面代理的Array类型就行。

5.2 vue生命周期create(){}
- 在create执行方法,给变量赋初值
created(){
this.getTxtContent()
}
5.3 接受后端的数据,前端进行打印
<template>
<ul v-for="item in txtContent" :key="item.id">
<li>{
{
item.content}}</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
data(){
return{
txtContent:[],
name:"jack"
}
},
methods:{
getTxtContent(){
axios(({
method:"get",
url:"http://127.0.0.1:8080/getTxtContent",
})).then(res=>{
this.txtContent = res.data;
// console.log(this.txtContent);
})
}
},
created(){
this.getTxtContent()
}
}
</script>
5.4 v-html
- 前端代码
<template>
<p v-html="find"></p>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
data(){
return{
txtContent:[],
name:"jack",
find:"",
}
},
methods:{
getTxtContent(){
axios(({
method:"get",
url:"http://127.0.0.1:8080/find",
})).then(res=>{
this.find = res.data;
// console.log(this.txtContent);
})
}
},
created(){
this.getTxtContent()
}
}
</script>
- 后端代码
@RequestMapping("/find")
public String getFind(){
return "<span style=\"color:red;\">查找</span>";
}
六、vuex的简单使用
6.1 安装vuex
- es6-promise也是必须的
npm install vuex --save
npm install es6-promise --sav
6.2 什么是vuex
- 简单的说,可以把他看成所有vue组件之间的全局变量,全局方法调用点
- Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
6.3 vue3.0中有个store目录下的index.js
- index.js
import {
createStore } from "vuex";
export default createStore({
state(){
return{
Number:20
}
},
mutations: {
changeNumber(state){
state.Number ++;
}
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
},
});
6.4 其他vue组件对store中变量,方法的调用
useStore(){
this.$store.commit("changeNumber");
console.log(this.$store.state.Number);
}