文章目录
1 运行结果
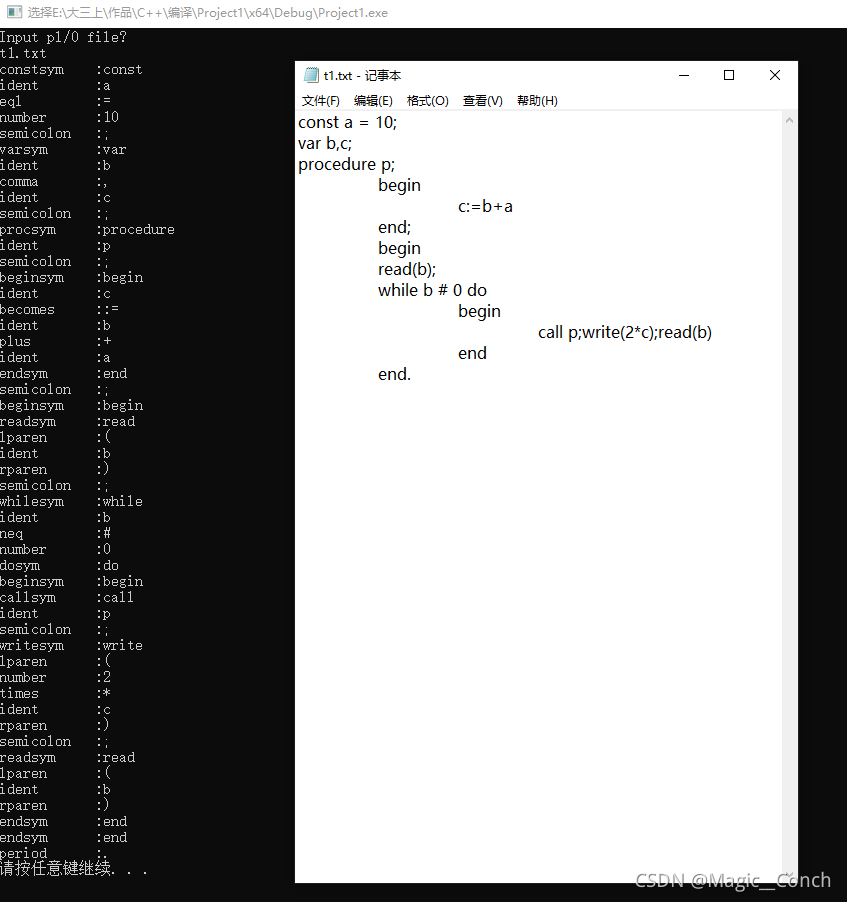
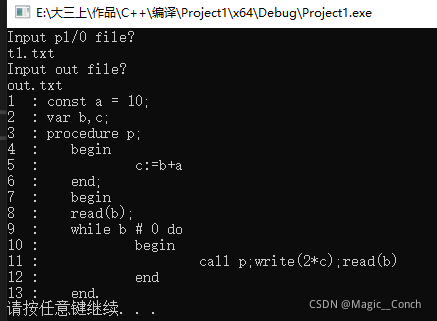
t1.txt:
const a = 10;
var b,c;
procedure p;
begin
c:=b+a
end;
begin
read(b);
while b # 0 do
begin
call p;write(2*c);read(b)
end
end.
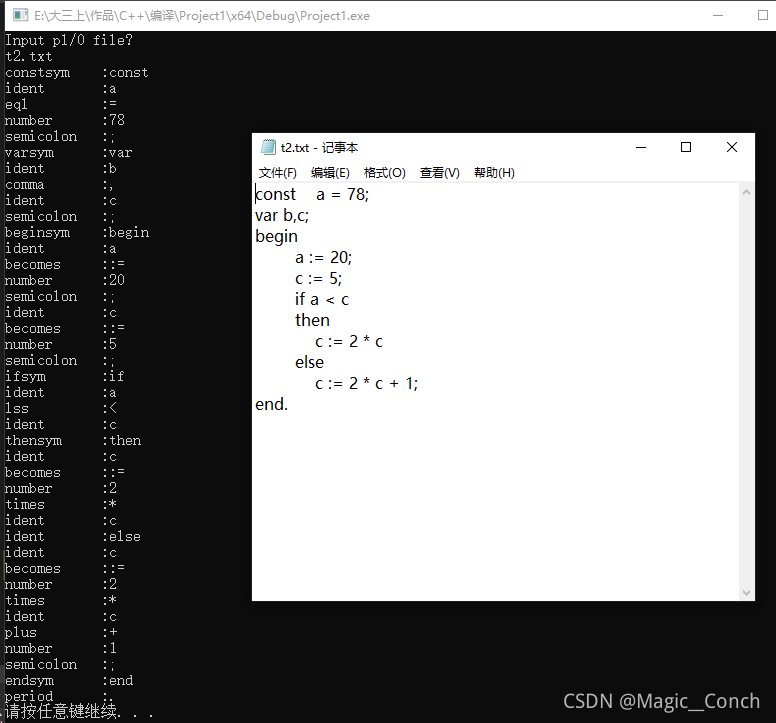
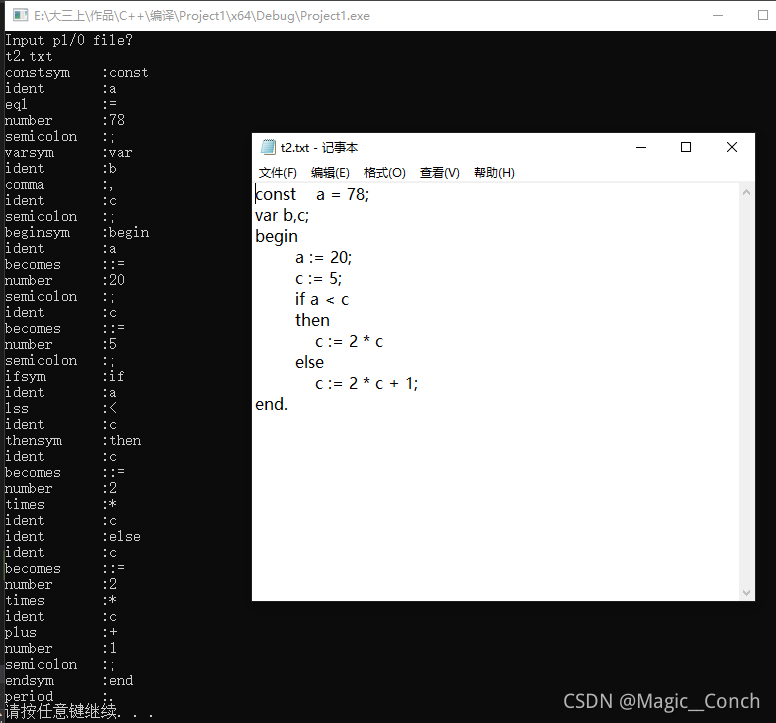
t2:
const a = 78;
var b,c;
begin
a := 20;
c := 5;
if a < c
then
c := 2 * c
else
c := 2 * c + 1;
end.
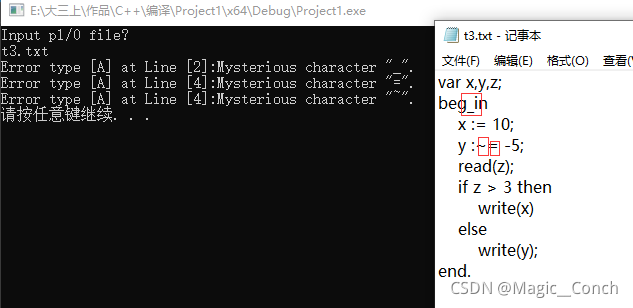
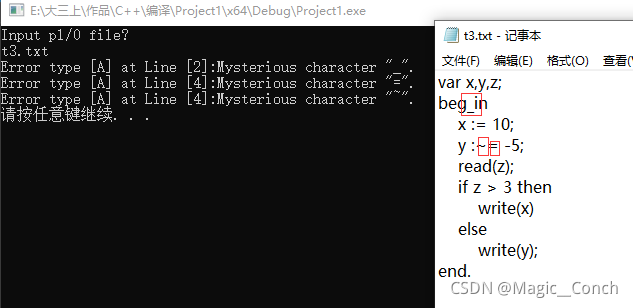
t3:
var x,y,z;
beg_in
x := 10;
y :~= -5;
read(z);
if z > 3 then
write(x)
else
write(y);
end.
2 项目代码
2.1 代码结构
2.2 具体代码
controll.h
#define printprogresstoscreen false
#define printprogresstofile false
#define printtypemap true
#define printerrortoscreen true
#define printerrortofile false
main.cpp
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
13464715 查看本文章


#include"pl0.h"
#include"controll.h"
#include<initializer_list>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
map<errorType, string> errorMap;
vector<pair< Symbol, string>> symbolmap;
void init() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 255; i++) {
ssym[i] = nul;
}
ssym['+'] = PLUS;
ssym['-'] = MINUS;
ssym['*'] = times;
ssym['/'] = slash;
ssym['('] = lparen;
ssym[')'] = rparen;
ssym['='] = eql;
ssym[','] = comma;
ssym['.'] = period;
ssym['#'] = neq;
ssym[';'] = semicolon;
strcpy(&(word[0][0]), "begin");
strcpy(&(word[1][0]), "call");
strcpy(&(word[2][0]), "const");
strcpy(&(word[3][0]), "do");
strcpy(&(word[4][0]), "end");
strcpy(&(word[5][0]), "if");
strcpy(&(word[6][0]), "odd");
strcpy(&(word[7][0]), "procedure");
strcpy(&(word[8][0]), "read");
strcpy(&(word[9][0]), "then");
strcpy(&(word[10][0]), "var");
strcpy(&(word[11][0]), "while");
strcpy(&(word[12][0]), "write");
//保留字符号;
wsym[0] = beginsym;
wsym[1] = callsym;
wsym[2] = constsym;
wsym[3] = dosym;
wsym[4] = endsym;
wsym[5] = ifsym;
wsym[6] = oddsym;
wsym[7] = procsym;
wsym[8] = readsym;
wsym[9] = thensym;
wsym[10] = varsym;
wsym[11] = whilesym;
wsym[12] = writesym;
//初始化错误类型与说明的关系
errorMap[A] = "Mysterious character \"?\".\n";
errorMap[D] = "The number is too loog.";
}
void error(errorType n, initializer_list<string> args) {
char space[81];
memset(space, 32, 81);
space[cc - 1] = 0;
string formatStr = errorMap[n];
for (auto p:args)
{
formatStr = formatStr.replace(formatStr.find_first_of('?', 0),1, p);//按格式替换字符串说明
}
if(printerrortoscreen)
printf("Error type [%c] at Line [%d]:", n+'A', cx);
if(printerrortofile)
fprintf(fal, "Error type [%c] at Line [%d]:", n+'A', cx);
if (printerrortoscreen)
printf(formatStr.c_str());
if (printerrortofile)
fprintf(fal, formatStr.c_str());
err++;
}
int getch() {
if (cc == ll) {
if (lastline) {
return -1;
}
if (feof(fin)) {
//文件为空则不为0
if (printprogresstoscreen)
printf("program incomplete");
if (printprogresstofile)
fprintf(fal,"program incomplete");
return -1;//文件为空;
}
ll = cc = 0;
++cx;
if (printprogresstoscreen)
printf("%-3d: ", cx);
if (printprogresstofile)
fprintf(fal, "%-3d", cx);
ch = ' ';
while (ch != 10)//ch==10 换行符;
{
if (fscanf(fin, "%c", &ch) == EOF)//读出终止字符;
{
lastline = true;
line[ll] = 0;//0就是'\0'??
break;
}
if (printprogresstoscreen)
printf("%c", ch);
if (printprogresstofile)
fprintf(fal, "%c", ch);
line[ll] = ch;
ll++;
}
}
ch = line[cc];
cc++;
return 0;
}
void recordpair() {
bool ina = false;
for (int i = 0; i < norw;i++) {
//关键字
ina = sym == wsym[i] ? true : ina;
}
if(sym == number)
symbolmap.push_back(pair<Symbol, string>(sym, to_string(num)));
else
symbolmap.push_back(pair<Symbol, string>(sym, a));
}
int getsym() {
int i, j, k;
while (ch == ' ' || ch == '\t' || ch == '\n') {
getchdo;
}
if ((ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A'&&ch <= 'Z')) {
//开头为字母,则为名字或保留字;
k = 0;
do {
if (k < al) {
a[k] = ch;
k++;
}
getchdo;
} while (((ch >= 'a'&&ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A'&&ch <= 'Z') || (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9')));
a[k] = 0;
strcpy(id, a);//将名字或保留字存入id;
i = 0;
j = norw - 1;
do {
k = (i + j) / 2;//二分法 搜索当前id是否为保留字;
if (strcmp(id, word[k]) <= 0) {
j = k - 1;//查找左边;
}
if (strcmp(id, word[k]) >= 0) {
i = k + 1;
}
} while (i <= j);
if (i - 1 > j) {
sym = wsym[k];//找到对应的保留字;
}
else {
sym = ident;//sym为标识符;
}
}
else {
if (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9') {
//数字
k = 0;
num = 0;
sym = number;
do
{
if (!(ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9')) {
//当不满足数字格式
sprintf(buf, "%c", ch);
error(A, {
buf });
}
num = 10 * num + ch - '0';
k++;
getchdo;
} while (ch>='0'&&ch<='9');
k--;
if (k > nmax) {
//当数字长度过长
error(G, {
});
}
}
else {
k = 0;
if (ch == ':') {
a[k++] = ch;
getchdo;
if (ch == '=') {
a[k++] = ch;
sym = becomes;
getchdo;
}
else {
sym = nul;//无法识别的符号 pl/0 :后非法算不算编译错误?
error(A, {
"=" });
}
}
else {
if (ch == '<') {
a[k++] = ch;
getchdo;
if (ch == '=') {
a[k++] = ch;
sym == leq;
getchdo;
}
else {
sym = lss;
}
}
else {
if (ch == '>') {
a[k++] = ch;
getchdo;
if (ch == '=') {
sym = geq;
a[k++] = ch;
getchdo;
}
else {
sym = gtr;
}
}
else {
a[k++] = ch;
a[k] = 0;
sym = ssym[ch];
if (sym == nul) {
//无法识别的符号
sprintf(buf, "%c", ch);
error(A, {
buf });
}
if (sym != period) {
getchdo;
}
else {
recordpair();
return -1;//读完
}
}
}
}
a[k] = 0;
}
}
recordpair();
return 0;
}
int main() {
bool nxtlev[symnum];
printf("Input pl/0 file?\n");
scanf("%s", fname);
fin = fopen(fname, "r");
if (printerrortofile || printprogresstofile) {
printf("Input out file?\n");
scanf("%s", fname);
fal = fopen(fname, "w");
}
if (&fin) {
//读入文件;
init();
err = 0;
cc = cx = ll = 0;
ch = ' ';
while (getsym() != -1) {
}
if(printprogresstoscreen)
printf("\n");
if (printprogresstofile)
fprintf(fal, "\n");
if (!err&&printtypemap) {
for (int i = 0; i < symbolmap.size(); i++) {
printf("%-12s:%s\n", typeMap[symbolmap[i].first], symbolmap[i].second.c_str());
}
}
}
if (printerrortofile || printprogresstofile) {
fclose(fal);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
pl0.h
#include <cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
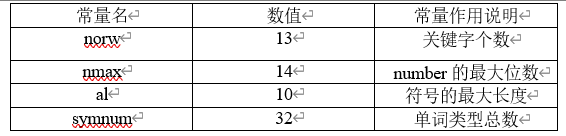
#define norw 13 //关键字个数
#define txmax 100 //名字表容量
#define nmax 14 //number的最大位数
#define al 10 //符号的最大长度
#define amax 2047 //地址上界
#define levmax 3 //最大允许过程嵌套声明
#define cxmax 200 //最多的虚拟机代码数
enum Symbol {
nul, ident, number,
PLUS, MINUS, times, slash, lparen, rparen, eql, neq, lss, leq, gtr, geq,
comma, semicolon, period,
becomes,
beginsym, endsym, ifsym, thensym, whilesym, writesym, readsym, dosym, callsym, constsym, varsym, oddsym, procsym
};
char typeMap[][10] = {
"nul","ident","number","plus","miuns","times","slash","lparen","rparen","eql","neq","lss","leq","gtr","geq",
"comma","semicolon","period","becomes","beginsym","endsym","ifsym", "thensym", "whilesym", "writesym",
"readsym", "dosym", "callsym", "constsym", "varsym", "oddsym", "procsym" };
#define symnum 32
enum object {
constant,varible,procedur
};
enum fct {
lit,opr,lod,sto,cal,inte,jmp,jpc,
};
struct instruction {
enum fct f;
int l, a;
};
enum Letter {
program,program_head,program_child,const_declare,const_define, var_define, var_declare,
procedure_declare,prodecure_head,statement_declare,statement_muti,statement,assign,read,write,
percedure_call,condition_statement,while_circulation,factor,item,operator_muti,expression,operator_add,
operator_relation,condition
};
struct NonTerminal
{
char explain[18];
};
bool listswitch;
bool tableswitch;
bool lastline;
//bool finalChar = false;
char ch;
enum Symbol sym;
char id[al + 1];
int num, cc, ll, cx;
char line[81];
char a[al + 1]; //临时符号
instruction code[cxmax];
char ord[norw][al]; //保留字
Symbol wsym[norw];
Symbol ssym[256];
//char mnemonic[fctnum][5]; //虚拟机代码指令名称
bool declbegsys[symnum];
bool statbegsys[symnum];
bool facbegsys[symnum];
FILE* fin, *fal;
FILE* fas, fa, fa2, fout;
struct tablestruct
{
char name[al];
object kind; //类型
int val;
int level; //所处层
int adr; //地址
int size; //分配的数据区空间
};
tablestruct table[txmax];
char fname[al];
int err;
char word[13][12];
#define getsymdo if( getsym() == -1) return -1;
#define getchdo if( getch()==-1) return -1;
enum errorType {
A,//词法错误
B,
C,
D,
E,
F,
G//长度过长
};
char buf[105];
3 实验内容
3.1 实验要求
程序要能够查出源代码中可能包含的词法错误:
词法错误(错误类型 A):即出现PL/0词法中未定义的字符以及任何不符合 PL/0词法单元定义的字符;
程序输入是一个包含 PL/0 源代码的文本文件,程 序需要能够接收一个输入文件名作为参数,以获得相应的输出结果。
3.2 算法描述
对整个程序绘制总算法流程图,如下图1.3.2-1,该图表示从读入、初始化数据、词法分析、出错管理等的总体的算法流程。

其中初始化数据包含建立符号类型映射、关键词映射、错误类型及描述映射、将初始值置零等操作。
出错处理包含根据错误类型和传入参数来生成出错提示语句和记录错误总数。
词法分析具体算法流程将在1.3.3给出。
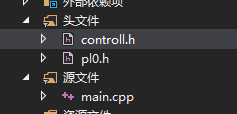
3.3 程序结构
本项目主要由2个头文件与一个cpp源文件组成,其中pl0.h存储了运行所需要的变量、常量和类型的定义,controll.h保存了一些可选信息包含是否可以将程序打印到屏幕/文件、是否将错误打印到屏幕/文件、是否将类型单词表打印到屏幕的定义,在运行开始前课通过设置这些来得到不同的观察效果。程序主要文件结构如下图1.3.3-1所示。

对main.cpp的程序结构描述的伪代码如下:
主函数:
输入文件名
if(文件名存在)
init()初始化数据
while(没读到文件尾也即getsym返回值不为-1)
getsym()
if(错误数==0)
输出单词类型表
else
根据错误列表输出错误信息
getsym()函数:
while(ch == ' ' || ch == '\t' || ch == '\n')
getch()
if(ch是字母)
调用getchar()读入整个单词
判断是保留字或标识符,保存类型于全局变量sym,单词于全局变量id
else
if(ch为数字)
getch()读入整个数字
if(数字过长)
触发错误G,调用error()
保存类型于sym,数值于全局变量num
else
if(ch==’:’)
getch()
if(ch==’=’)
设置sym为becomes,存入符号于a数组
else
sym=nul
else if(ch==’<’||ch==’>’)
if(下一个符号是否为等号)
设置sym为leq或geq
else
设置sym为lss或gtr
将词保存于a
else
getchar()
根据ssym获取类型
if(获取类型为空)
error()
else
设置sym与a
将类型与单词存入数组
getch()函数:
if(整个文件读完)
return -1
if(该改行读完)
根据行读入文件一行
获取ch的下一个字符存入ch中
error()函数:
formatStr=根据错误类型查找的错误语句模板
for(i=0;i<参数列表长度;i++)
将formatStr的占位符?替换为参数
err++;错误数加一
将错误存入错误列表
init()函数:
建立符号类型映射
建立关键词映射
建立错误类型及描述映射
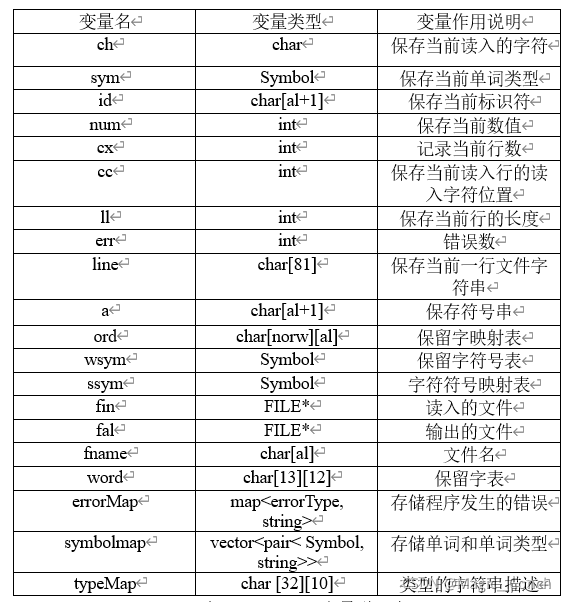
3.4 主要变量说明
3.5 主要常量及类型说明
3.6 扩展功能测试
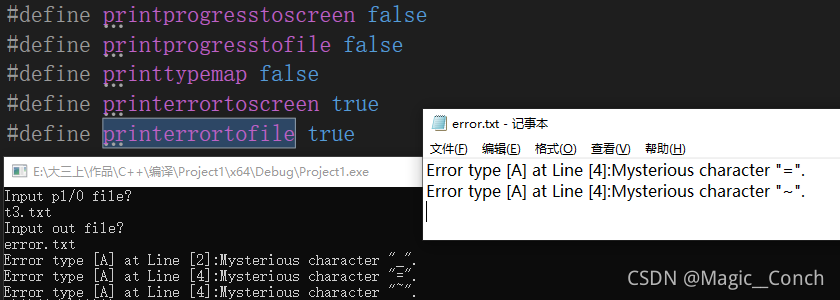
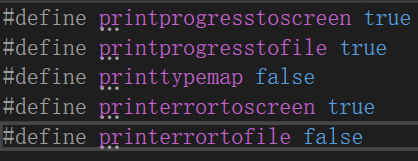
本程序增添了controll.h文件用于控制程序的输出情况,现进行如下测试。
首先将controll.h的前两个值改为true,将程序过程输入到控制台和文本文件,如下图1.3.8-1所示。
然后运行程序,控制台和记事本结果分别如图

同样可以让错误输出到文件,更改设置将printerrortofile设置为true,结果如下图