文章目录
一、区别
-
语义分割:每个像素都打上标签(这个像素是人,树,背景等)语义分割只区分类别,不区分类别中的具体单元
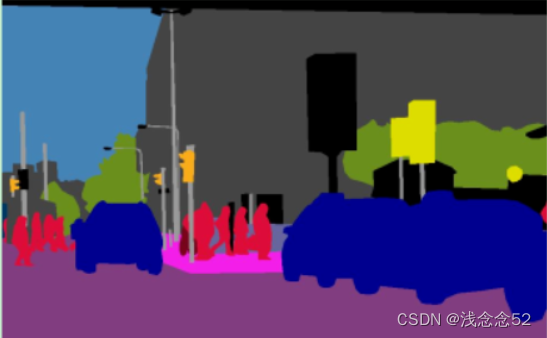
-
实例分割:不光要区分类别,还要区分类别中的每一个个体
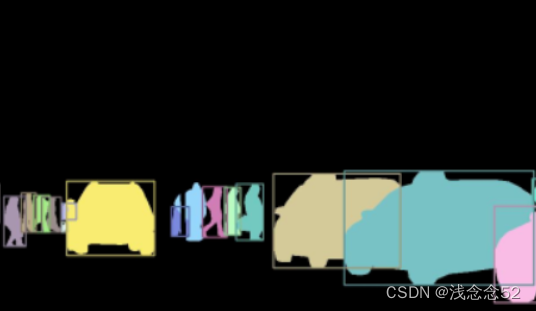
-
全景分割:相当于语义分割加上实例分割

二、代码演示原图像与mask融合
from PIL import Image
import imgviz
import numpy as np
image_file=r'D:\aaa\envs\labelme\Scripts\2_3_json\img.png'
mask_file=r'D:\aaa\envs\labelme\Scripts\2_3_json\label.png'
image=Image.open(image_file)
mask=Image.open(mask_file)
mask_img=Image.blend(image.convert("RGBA"),
mask.convert("RGBA"),0.5)
mask_img.save("vis2.png")
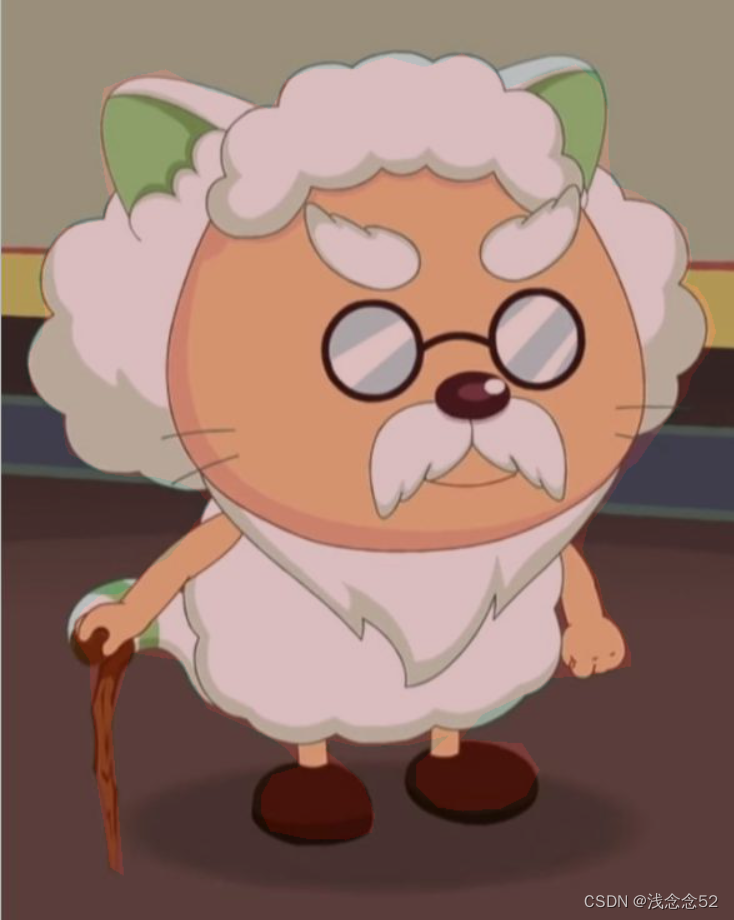

三、数据处理
将labelme标注好的json转换成mask图像
import json
import os
import imgviz
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import cv2
import glob
def save_colored_mask(mask,image_file):
lbl_image=Image.fromarray(mask.astype(np.uint8),mode='P')
colormap=imgviz.label_colormap()
lbl_image.putpalette(colormap.flatten())
lbl_image.save(image_file)
json_files=r'E:\桌面\资料\语义分割'
img_file=r'E:\桌面\资料\语义分割\图片'
json_l=glob.glob(os.path.join(json_files,'*.json'))
for json_ in json_l:
name=os.path.basename(json_)
img_name=name.replace('json','png')
fs=open(json_,encoding='utf-8')
dict_=json.load(fs)
# 获取图像 宽,高
height = dict_['imageHeight']
width = dict_['imageWidth']
shapes = dict_["shapes"]
# 生成一个全零图像
img = np.zeros((height, width), dtype=np.uint8)
label_color = {
"sheep": 1}
for shape in shapes:
# 解析多边形轮廓点的坐标
points = shape['points']
# 解析多边形的标签
label = shape['label']
points = np.array(points, dtype=np.int32)
# 绘制轮廓
cv2.polylines(img, [points], isClosed=True, color=(255), thickness=2)
# 填充多边形颜色
cv2.fillPoly(img, [points], color=label_color[label])
img_path=os.path.join(img_file,img_name)
print(img_path)
save_colored_mask(img, img_path)