1 简介
Spring Security 是 Spring 社区的一个顶级项目,也是 Spring Boot 官方推荐使用的安全框架。除了常规的认证(Authentication)和授权(Authorization)之外,Spring Security还提供了诸如ACLs,LDAP,JAAS,CAS等高级特性以满足复杂场景下的安全需求。另外,就目前而言,Spring Security和Shiro也是当前广大应用使用比较广泛的两个安全框架。
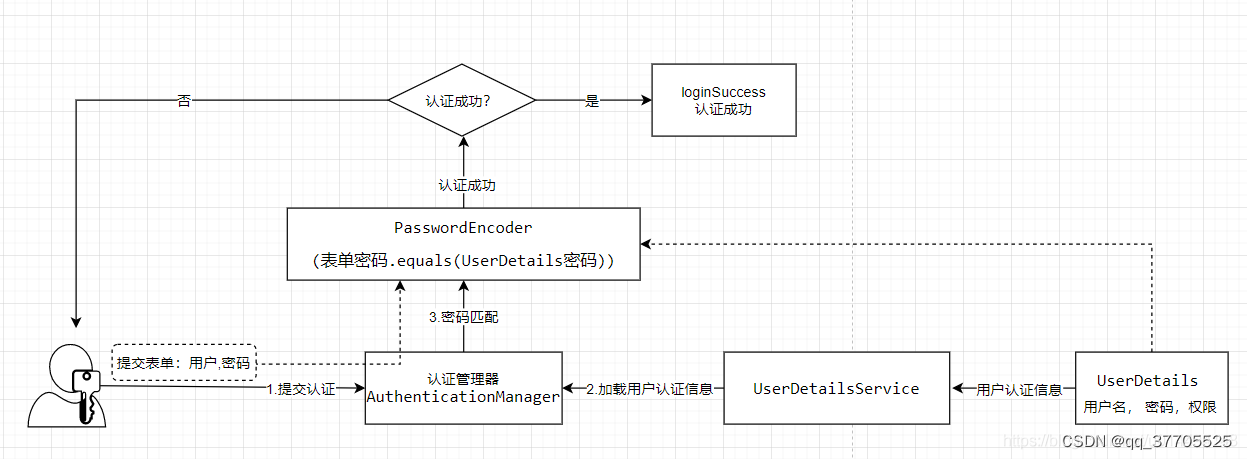
Spring Security 应用级别的安全主要包含两个主要部分,即登录认证(Authentication)和访问授权(Authorization),首先用户登录的时候传入登录信息,登录验证器完成登录认证并将登录认证好的信息存储到请求上下文,然后再进行其他操作,如在进行接口访问、方法调用时,权限认证器从上下文中获取登录认证信息,然后根据认证信息获取权限信息,通过权限信息和特定的授权策略决定是否授权。
本教程将首先给出一个完整的案例实现,然后再分别对登录认证和访问授权的执行流程进行剖析,希望大家可以通过实现案例和流程分析,充分理解Spring Security的登录认证和访问授权的执行原理,并且能够在理解原理的基础上熟练自主的使用Spring Security实现相关的需求。
认证流程
2 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
3 yml配置
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/security4?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: root
jpa:
database: mysql
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true
thymeleaf:
cache: false
check-template: true
check-template-location: true
servlet:
content-type: text/html
enabled: true
encoding: UTF-8
excluded-view-names:
mode: HTML
prefix: classpath:/templates/
suffix: .html
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /static/**
web:
resources:
static-locations: classpath:/static
logging:
level:
org:
springframework:
security: debug
4 SecurityConfig
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
UserDetailsService customUserService() {
return new CustomUserService();
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(customUserService())
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
/*@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder())
.withUser("1").password(passwordEncoder().encode("1")).roles("USER");
}*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(
HttpMethod.GET,
"/*.html",
"/**/*.html",
"/**/*.css",
"/**/*.js",
"/webSocket/**"
).permitAll()
.antMatchers("/swagger-ui.html").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/swagger-resources/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/webjars/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/*/api-docs").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/druid/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/auth/login", "/auth/logout").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/500").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/403").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/404").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/hello").hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/index/**").access("hasRole('USER')")
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasAnyRole("USER")
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin().loginPage("/login").loginProcessingUrl("/login").defaultSuccessUrl("/index").failureUrl("/login?error").permitAll().and()
.logout().permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}
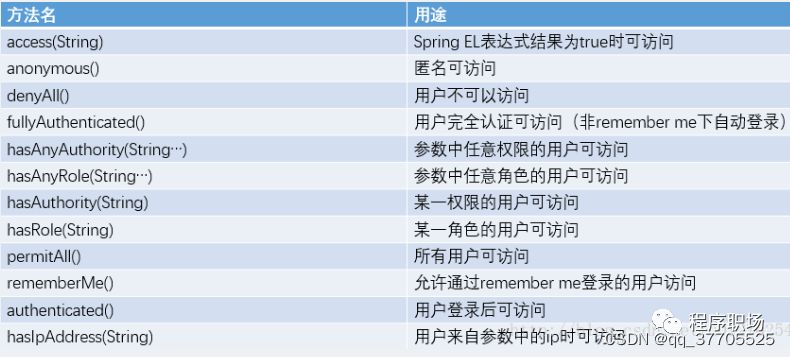
hasAuthority 如果当前的主体具有指定的权限,则可以访问
hasAnyAuthority 如果当前的主体有任何提供的角色的话,就可以访问 多个角色是一个以逗号进行分隔的字符串。如果当前用户拥有指定角色中的任意一个则返回true。
hasRole 如果用户具备给定角色就允许访问
hasAnyRole 用户具备任何一个角色都可以访问 多个角色是一个以逗号进行分隔的字符串。如果当前用户拥有指定角色中的任意一个则返回true。
hasRole 的处理逻辑和 hasAuthority 类似,不同的是,hasRole 这里会自动给传入的字符串加上 ROLE_ 前缀,所以在数据库中的权限字符串需要加上 ROLE_ 前缀。即数据库中存储的用户角色如果是 ROLE_admin,这里就是 admin。
对于权限可以直接设置,对于角色以ROLE_**的方式设置
loginProcessingUrl 登陆请求处理接口,我们无需编写该接口,security 会自动帮我们处理。

5 Model
@Entity
public class SysUser implements UserDetails {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
@ManyToMany(cascade = {CascadeType.REFRESH},fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
private List<SysRole> roles;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public List<SysRole> getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(List<SysRole> roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
Collection<GrantedAuthority> auths = new ArrayList<>();
List<SysRole> roles = this.getRoles();
for (SysRole role : roles) {
auths.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role.getName()));
}
return auths;
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return this.password;
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return this.username;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return true;
}
}
@Entity
@Data
public class SysRole {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
}
6 sql
insert into `sys_role`(`id`,`name`) values (1,'ROLE_ADMIN'),(2,'ROLE_USER');
insert into `sys_user`(`id`,`password`,`username`) values (1,'$2a$10$amIubr83OTF6vFyzsmg3pONp1/kmQYEKE8bQAEOpwPaEBMVsYGKSW','root'),(2,'$2a$10$44lTqwmGl1riyHABdk6uEuidhT4ChzGmnaYg82E9GU5ibMAqpoRAC','chen');
insert into `sys_user_roles`(`sys_user_id`,`roles_id`) values (1,1),(2,2);
public class CustomUserService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
SysUserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s)
throws UsernameNotFoundException {
SysUser user = userRepository.findByUsername(s);
if (user == null) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户名不存在");
}
// 返回UserDetails实现类
return new User(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), user.getAuthorities());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("chen"));
}
}
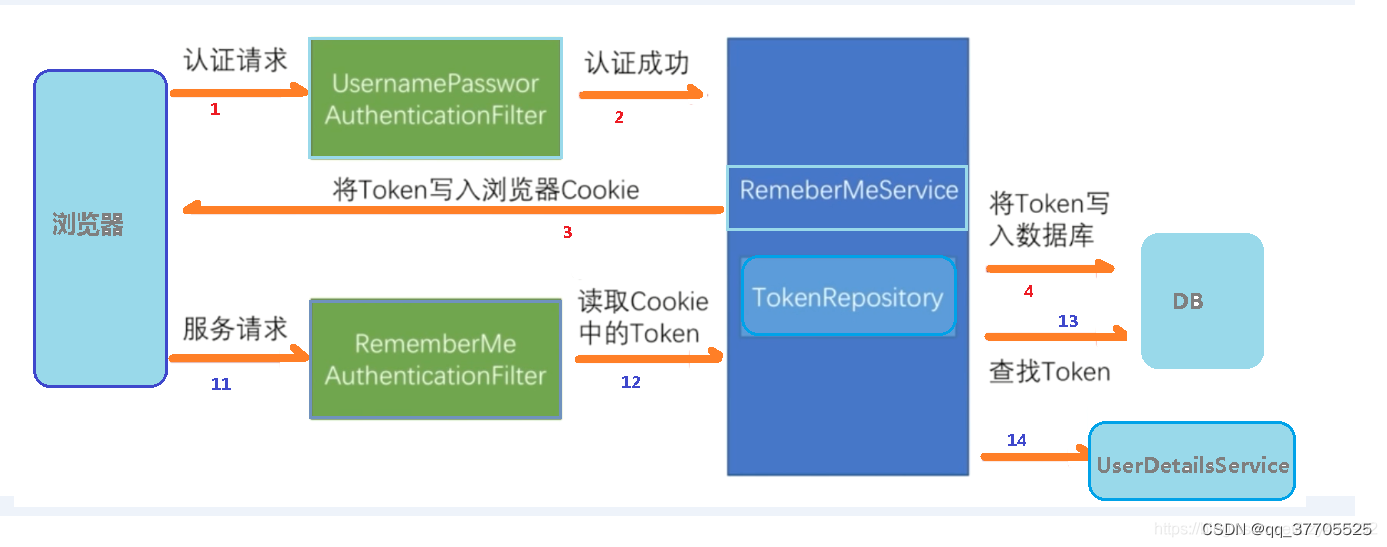
7 记住我
记住我功能和注销功能一样 只需要在配置中添加一个方法即可
http.rememberMe().rememberMeParameter(“remember”);
http.csrf().disable();
//没有权限 默认跳到登录页面
http.formLogin().loginPage("/tologin");
//注销 并跳到首页
http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/");
//记住我功能
http.rememberMe().rememberMeParameter("remember");
8 权限
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled=true,prePostEnabled = true)
@Secured:判断是否具有角色:
@Secured({“ROLE_normal”,“ROLE_admin”})
@PreAuthorize:进入方法前进行权限验证, @PreAuthorize 可以将登录用户的 roles/permissions 参数传到方法中
@PreAuthorize(“hasAnyAuthority(‘findAll’)”)
@PostAuthorize:方法执行后再进行权限验证,适合验证带有返回值的权限:
@PostAuthorize(“hasAnyAuthority(‘find’)”)
@PostFilter :权限验证之后对数据进行过滤,留下指定的数据,表达式中的 filterObject 引用的是方法返回值 List 中的某一个元素
@PostAuthorize(“hasAnyAuthority(‘findAll’)”)
@PostFilter(“filterObject.username == ‘admin1’”)
@PreFilter: 进入控制器之前对数据进行过滤
@PostAuthorize(“hasAnyAuthority(‘findAll’)”)
@PreFilter(value = “filterObject.id%2==0”)
9 问题
解决Request method ‘POST’ not supported问题
security的配置文件中使用.defaultSuccessUrl(“/index”)