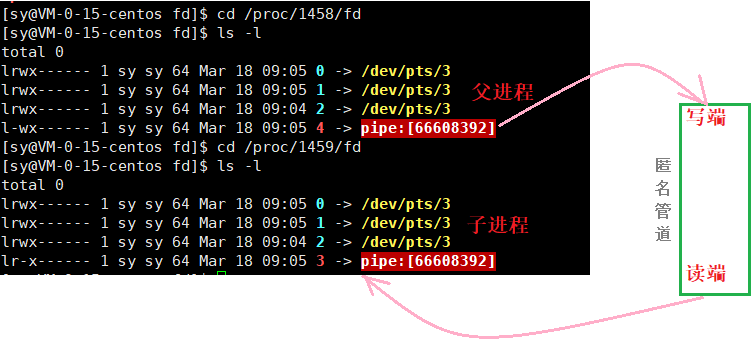
父子进程的匿名管道
-
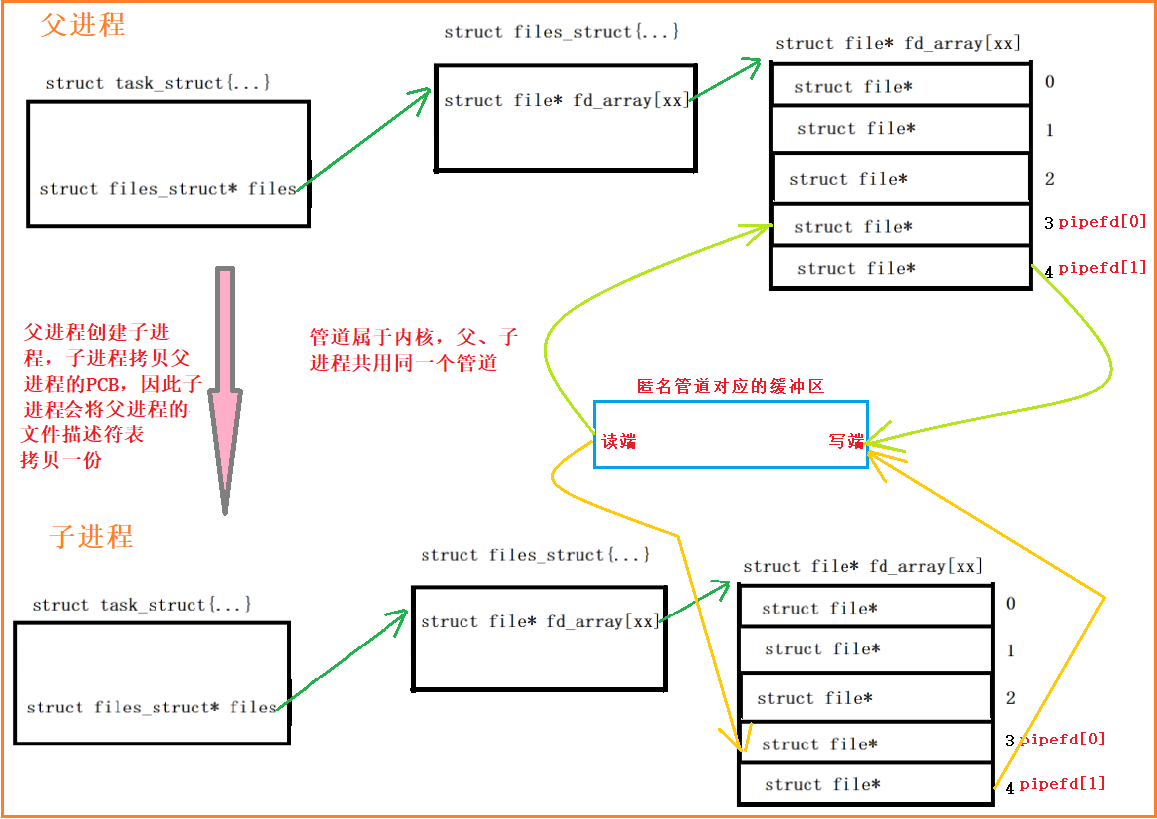
- 代码
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> int main(){ int fd[2]; int ret=pipe(fd); if(ret<0){ perror("pipe:"); } //管道创建成功 pid_t pid=fork(); if(pid < 0){ perror("fork:"); return 0; } else if(pid == 0){ //child printf("i an child process\n"); printf("fd[0]=%d fd[1]=%d\n",fd[0],fd[1]); } else{ //father printf("i am father process\n"); printf("fd[0]=%d fd[1]=%d\n",fd[0],fd[1]); } while(1){ sleep(1); } return 0; }
-
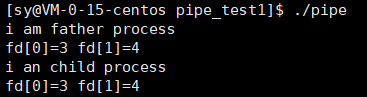
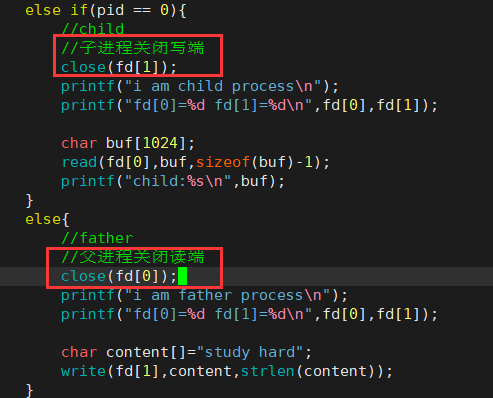
- 父进程写,子进程读
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> int main(){ int fd[2]; int ret=pipe(fd); if(ret<0){ perror("pipe:"); } //管道创建成功 pid_t pid=fork(); if(pid < 0){ perror("fork:"); return 0; } else if(pid == 0){ //child printf("i am child process\n"); printf("fd[0]=%d fd[1]=%d\n",fd[0],fd[1]); char buf[1024]; read(fd[0],buf,sizeof(buf)-1); printf("child:%s\n",buf); } else{ //father printf("i am father process\n"); printf("fd[0]=%d fd[1]=%d\n",fd[0],fd[1]); char content[]="study hard"; write(fd[1],content,strlen(content)); } return 0; } -
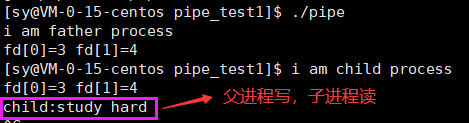
-
- 父子进程匿名管道的读写两端的引用计数为2,父进程的读端关闭后,管道读端的引用计数变为1,子进程的写端关闭后,管道写端的引用计数变为1,因此父进程写,子进程读是可以正常进行的。
-