一、遍历
深度优先遍历
深度优先遍历是对树的先序遍历
广度优先遍历
广度优先遍历是对树的层次遍历(很多地方说后序遍历,然后后续遍历和层次遍历是不一样的)
二、最小生成树
Kruskal算法描述
-
新建一个图
-
将带权值的边放入集合中,并对集合按权值大小排序(可以用队列存,在入队列的时候加限制,保证队列是有序的)
-
(在while循环中,集合不为空的条件下)取权值最小的边并移出集合,并找到权的
tail和head(可以遍历现有的图的顶点集合找到它们) -
(在新图中)先插入
tail顶点和tail顶点(如果存在就不插入,不能抛出异常),再插入这条边 -
判断插入后是否够成环(可以用深度优先或者拓扑序列验证是否成环)
- 如果成环就撤销插入操作(不撤销移出集合),下一个循环
- 如果不成环,下一个循环。
三、拓扑排序
意义
如果图的所有顶点都在这个图的拓扑序列中,则这个图不存在环
算法描述
-
随机找一个入度为0的顶点添加到
resultList -
移除这个顶点和与这个顶点相关的边
-
(顶点不为空的情况下)循环
四、最长路径/关键路径/至少需要的时间的路径
AOE网(Activity On Edge)的意义
可以求解完成一个复杂的工程时至少需要的时间和哪些活动是影响工程进度的关键活动
实现
五、最短路径
AOV网(Acticity On Vertex)的意义
可以实现地图中NPC自动寻路功能(通过最短路径来找到玩家,然后…)
Floyd算法
Floyd算法是一个经典的动态规划算法
用通俗的语言来描述的话,首先我们的目标是寻找从点i到点j的最短路径
从动态规划的角度看问题,我们需要为这个目标重新做一个诠释(这个诠释正是动态规划最富创造力的精华所在)
1、算法思想
从任意节点i到任意节点j的最短路径不外乎2种可能
- 直接从
i到j - 从
i经过若干个节点k到j
所以,我们假设Dis(i,j)为节点u到节点v的最短路径的距离。对于每一个节点k,我们检查Dis(i,k) + Dis(k,j) < Dis(i,j)是否成立。如果成立,证明从i到k再到j的路径比i直接到j的路径短,我们便设置Dis(i,j) = Dis(i,k) + Dis(k,j)。这样一来,当我们遍历完所有节点k,Dis(i,j)中记录的便是i到j的最短路径的距离
2、算法描述
- 从任意一条单边路径开始。所有两点之间的距离是边的权,如果两点之间没有边相连,则权为无穷大
- 对于每一对顶点
u和v,看看是否存在一个顶点w使得从u到w再到v比己知的路径更短。如果是则更新它。
3、代码实现
接口
import java.util.List;
/**
* TODO
* @author IceFery
* @see GraphImpl
* @date 2019/6/24
*/
public interface Graph<E, W> {
/**
* 默认最大顶点容量
*/
int DEFAULT_MAX_ELEMENT_NUM = 10;
/**
* 添加一个元素
* @param element
* @throws Exception
*/
void addElement(E element) throws Exception;
/**
* 添加一条边
* @param weight
* @param tailElement
* @param headElement
* @throws Exception
*/
void addEdge(W weight, E tailElement, E headElement) throws Exception;
/**
* 移除一个顶点
* @param element
* @throws Exception
*/
void removeElement(E element) throws Exception;
/**
* 移除一条边
* @param tailElement
* @param headElement
* @throws Exception
*/
void removeEdge(E tailElement, E headElement) throws Exception;
/**
* 取得某个顶点的入度和入度并放入数组中,第一个值为入度,第二个值为出度
* @param element
* @throws Exception
*/
int[] getDegree(E element) throws Exception;
/**
* 打印边表
* @throws RuntimeException
*/
void displayEdges() throws RuntimeException;
/**
* 对图进行深度优先遍历,并返回遍历的序列
* @param startElement
* @return traverseList
* @throws Exception
*/
List<E> DFSTraverse(E startElement) throws Exception;
/**
* 对图进行广度优先遍历,并返回遍历的序列
* @param startElement
* @return traverseList
* @throws Exception
*/
List<E> BFSTraverse(E startElement) throws Exception;
/**
* 获得图的拓扑序列
* @return
*/
List<E> getTopologicalList();
/**
* 获得两个顶点的关键路径序列
* @param startElement
* @param endElement
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
Object[] getCriticalPath(E startElement, E endElement) throws Exception;
/**
* 获得两个顶点的最短路径序列
* @param startElement
* @param endElement
* @return resultMap[0] = pathList
* @return resultMap[1] = pathLength
* @throws Exception
*/
Object[] getShortestPath(E startElement, E endElement) throws Exception;
}
实现类
import java.util.*;
/**
* TODO
* @author IceFery
* @date 2019/6/24
* @see Graph
*/
public class GraphImpl<E, W> implements Graph<E, W> {
private boolean isDirected = true;
private int elementNum = 0;
private int edgeNum = 0;
private List<E> elementArray = null;
private List<List<W>> edgeArray = null;
public GraphImpl(boolean isDirected) {
this.isDirected = isDirected;
this.elementArray = new ArrayList<>(DEFAULT_MAX_ELEMENT_NUM);
this.edgeArray = new ArrayList<>(DEFAULT_MAX_ELEMENT_NUM);
for (int i = 0; i < DEFAULT_MAX_ELEMENT_NUM; i++) {
ArrayList<W> headElementArray = new ArrayList<>(DEFAULT_MAX_ELEMENT_NUM);
for (int j = 0; j < DEFAULT_MAX_ELEMENT_NUM; j++) {
headElementArray.add(null);
}
edgeArray.add(headElementArray);
}
}
@Override
public void addElement(E element) throws Exception {
this.elementArray.add(element);
this.elementNum++;
}
@Override
public void addEdge(W weight, E tailElement, E headElement) throws Exception {
int tailElementIndex = this.elementArray.indexOf(tailElement);
int headElementIndex = this.elementArray.indexOf(headElement);
if (-1 == tailElementIndex || -1 == headElementIndex) {
throw new Exception(tailElement + "或者" + headElement + "顶点未找到异常");
}
this.edgeArray.get(tailElementIndex).set(headElementIndex, weight);
if (!this.isDirected) {
this.edgeArray.get(headElementIndex).set(tailElementIndex, weight);
}
this.edgeNum++;
}
@Override
public void removeElement(E element) throws Exception {
int index = this.elementArray.indexOf(element);
if (-1 == index) {
throw new Exception(element + "顶点未找到异常");
}
this.elementArray.remove(index);
this.elementNum--;
for (int elementIndex = 0; elementIndex < this.elementNum; elementIndex++) {
this.edgeArray.get(elementIndex).remove(index);
}
this.edgeArray.remove(index);
int newEdgeNum = 0;
for (int tailElementIndex = 0; tailElementIndex < this.elementNum; tailElementIndex++) {
for (int headElementIndex = 0; headElementIndex < this.elementNum; headElementIndex++) {
if (null != this.edgeArray.get(tailElementIndex).get(headElementIndex)) {
newEdgeNum++;
}
}
}
this.edgeNum = newEdgeNum;
}
@Override
public void removeEdge(E tailElement, E headElement) throws Exception {
int tailElementIndex = this.elementArray.indexOf(tailElement);
int headElementIndex = this.elementArray.indexOf(headElement);
if (-1 == tailElementIndex || -1 == headElementIndex) {
throw new Exception(tailElement + "或" + headElement + "顶点未找到异常");
}
this.edgeArray.get(tailElementIndex).set(headElementIndex, null);
this.edgeNum--;
}
@Override
public int[] getDegree(E element) throws Exception {
int elementIndex = this.elementArray.indexOf(element);
if (-1 == elementIndex) {
throw new Exception(element + "顶点未找到异常");
}
int[] degrees = new int[2];
Arrays.fill(degrees, 0);
for (int index = 0; index < this.elementNum; index++) {
if (null != this.edgeArray.get(elementIndex).get(index)) {
degrees[0]++;
}
if (null != this.edgeArray.get(index).get(elementIndex)) {
degrees[1]++;
}
}
return degrees;
}
@Override
public void displayEdges() throws RuntimeException {
for (int tailElementIndex = 0; tailElementIndex < this.elementNum; tailElementIndex++) {
System.out.print("以" + this.elementArray.get(tailElementIndex) + "为起点的边有:");
for (int headElementIndex = 0; headElementIndex < this.elementNum; headElementIndex++) {
if (null != this.edgeArray.get(tailElementIndex).get(headElementIndex)) {
System.out.print("<" + this.elementArray.get(tailElementIndex) + ", " + this.edgeArray.get(tailElementIndex).get(headElementIndex) + ", " + this.elementArray.get(headElementIndex) + ">");
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
@Override
public List<E> DFSTraverse(E startElement) throws Exception {
List<E> resultList = new ArrayList<>(this.elementNum);
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.elementNum];
Arrays.fill(visited, false);
int startElementIndex = this.elementArray.indexOf(startElement);
if (-1 == startElementIndex) {
throw new Exception(startElement + "顶点未找到异常");
}
stack.push(startElementIndex);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int tailElementIndex = stack.pop();
if (!visited[tailElementIndex]) {
resultList.add(this.elementArray.get(tailElementIndex));
visited[tailElementIndex] = true;
}
for (int headElementIndex = 0; headElementIndex < this.elementNum; headElementIndex++) {
if (null != this.edgeArray.get(tailElementIndex).get(headElementIndex) && !visited[headElementIndex]) {
stack.push(headElementIndex);
}
}
}
return resultList;
}
@Override
public List<E> BFSTraverse(E startElement) throws Exception {
List<E> resultList = new ArrayList<>(this.elementNum);
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.elementNum];
Arrays.fill(visited, false);
int startElementIndex = this.elementArray.indexOf(startElement);
if (-1 == startElementIndex) {
throw new Exception(startElement + "顶点未找到异常");
}
queue.offer(startElementIndex);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int tailElementIndex = queue.poll();
if (!visited[tailElementIndex]) {
resultList.add(this.elementArray.get(tailElementIndex));
visited[tailElementIndex] = true;
}
for (int headElementIndex = 0; headElementIndex < this.elementNum; headElementIndex++) {
if (null != this.edgeArray.get(tailElementIndex).get(headElementIndex) && !visited[headElementIndex]) {
queue.offer(headElementIndex);
}
}
}
return resultList;
}
@Override
public List<E> getTopologicalList() {
//TODO
return null;
}
@Override
public Object[] getCriticalPath(E startElement, E endElement) throws Exception {
//TODO
return null;
}
@Override
public Object[] getShortestPath(E startElement, E endElement) throws Exception {
int startElementIndex = this.elementArray.indexOf(startElement);
int endElementIndex = this.elementArray.indexOf(endElement);
if (-1 == startElementIndex || -1 == endElementIndex) {
throw new Exception(startElement + "或" + endElement + "顶点未找到异常");
}
/*
* 用一个2个位置的数组充当一个map
* 第一个维度存路径的element的集合 pathList
* 第二个维度存整个路径的长度 distance[startElementIndex][endElementIndex]
*/
Object[] results = new Object[2];
Arrays.fill(results, null);
List<E> pathList = new ArrayList<>(this.elementNum);
/*
* 用原来的Integer的MAX_VALUE 或者 从MAX_VALUE / 10 * 6开始,也就是只要大于这个值的一半,就会在参与运算后无法正常显示,目前没搞懂原因。
* 所以用 MAX_VALUE / 10 * 5来表示这个最大值,然后在后面就它换成null
*/
final int MY_MAX_VALUE = Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2;
/*
* 下面是比较大众的最短路径算法
* 需要一个path[][]数组,k = path[i][j]的意义是这条路径是:(i --> ... --> k -- >j)遍历的时候需要像对树一样中序遍历,然后就可以得到结果
* 还需要一个distance[][]数组,distance[i][j]表示i -- > j 的最短路径, 所以最开始就可以初始化为 i -- > j 的的权值
*/
Integer[][] path = new Integer[this.elementNum][this.elementNum];
Integer[][] distance = new Integer[this.elementNum][this.elementNum];
for (int tailElementIndex = 0; tailElementIndex < this.elementNum; tailElementIndex++) {
for (int headElementIndex = 0; headElementIndex < this.elementNum; headElementIndex++) {
distance[tailElementIndex][headElementIndex] = (null == this.edgeArray.get(tailElementIndex).get(headElementIndex)) ? MY_MAX_VALUE : (Integer) this.edgeArray.get(tailElementIndex).get(headElementIndex);
path[tailElementIndex][headElementIndex] = null;
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < this.elementNum; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.elementNum; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < this.elementNum; j++) {
Integer newDistance = distance[i][k] + distance[k][j];
if (newDistance < distance[i][j]) {
distance[i][j] = newDistance;
path[i][j] = k;
}
}
}
}
/*
* 将MY_MAX_VALUE还原为null,因为null比较好判断
*/
for (int i = 0; i < this.elementNum; i++) {
for (int headElementIndex = 0; headElementIndex < this.elementNum; headElementIndex++) {
distance[i][headElementIndex] = (MY_MAX_VALUE == distance[i][headElementIndex]) ? null : distance[i][headElementIndex];
}
}
/*
* 将路径添加到集合中
* 因为 k 只表示 i --> j 中j的前驱,所以只是startElementIndex -- > endElementIndex中间的路径,所以需要再集合的队头和队尾添加上起点和终点
* 下面是我把那个递归的中序遍历写成的非递归形式
* 也是用栈保存一个map,暂时不会用map,那就用数组吧
*/
pathList.add(this.elementArray.get(startElementIndex));
int m = startElementIndex;
int n = endElementIndex;
Integer k = path[m][n];
Stack<Integer[]> stack = new Stack<>();
while (null != k || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (null != k) {
stack.push(new Integer[]{m, n});
n = k;
k = path[m][n];
} else {
Integer[] map = stack.pop();
m = map[0];
n = map[1];
k = path[m][n];
pathList.add(this.elementArray.get(k));
k = path[k][n];
}
}
pathList.add(this.elementArray.get(endElementIndex));
/*
* 将路径集合和路径长度添加进待返回的 resultMap中
*/
results[0] = pathList;
results[1] = distance[startElementIndex][endElementIndex];
return results;
}
}
Main.java
import java.util.List;
/**
* TODO
* @author IceFery
* @date 2019/6/25
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Graph<String, Integer> g = new GraphImpl<>(true);
g.addElement("V1");
g.addElement("V2");
g.addElement("V3");
g.addElement("V4");
g.addElement("V5");
g.addElement("V6");
g.addElement("V7");
g.addElement("V8");
g.addElement("V9");
g.addEdge(6, "V1", "V2");
g.addEdge(4, "V1", "V3");
g.addEdge(5, "V1", "V4");
g.addEdge(1, "V2", "V5");
g.addEdge(1, "V3", "V5");
g.addEdge(2, "V4", "V6");
g.addEdge(9, "V5", "V7");
g.addEdge(7, "V5", "V8");
g.addEdge(4, "V6", "V8");
g.addEdge(2, "V7", "V9");
g.addEdge(4, "V8", "V9");
g.displayEdges();
System.out.println("入度和出度:" + g.getDegree("V1")[0] + "," + g.getDegree("V1")[1]);
// System.out.println("移除V1到V2的边:");
// g.removeEdge("V1", "V2");
// g.displayEdges();
// System.out.println("移除V1顶点:");
// g.removeElement("V1");
// g.displayEdges();
System.out.println("深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历的结果为:");
List<String> list = g.DFSTraverse("V1");
for (String str : list) {
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
System.out.println();
list = g.BFSTraverse("V1");
for (String str : list) {
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.print("最短路径为:");
Object[] shortest = g.getShortestPath("V1", "V9");
List<String> shortestPath = (List<String>) shortest[0];
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
for (String s : shortestPath) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
System.out.println(shortest[1]);
}
}
运行截图
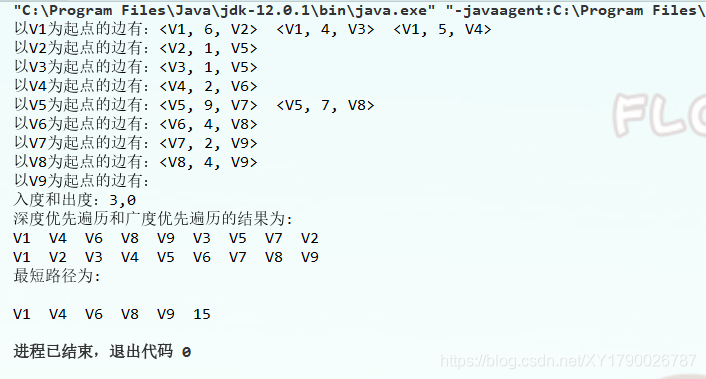
Floyd算法输出路径的递归算法这个博客里面
//递归算法
private void dfs(Integer[][] path, List<E> pathList, int i, int j) {
Integer k = path[i][j];
if (null == k) {
return;
} else {
this.dfs(path, pathList, i, k);
pathList.add(this.elementArray.get(k));
this.dfs(path, pathList, k, j);
}
}
将递归转换为非递归(以V1 --> V9的最短路径)
path矩阵如下
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | null | null | null | null | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | null | null | null | null | null | null | 4 | 4 |
| 2 | null | null | null | null | null | null | 4 | 4 |
| 3 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 5 |
| 4 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null |
| 5 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null |
| 6 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null |
| 7 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null |
| 8 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null |
二叉树的中序遍历非递归算法如下
void InOrderTraversal(BinTree BT){
BinTree T = BT;
Stack S = CreatStack(MaxSize); //创建并初始化堆栈S
while(T || !IsEmpty(S)){
while(T) { //一直向左并将沿途节点压入堆栈
Push(S,T);
T = T->Left;
}
if(!IsEmpty(S)){
T = Pop(S); //节点弹出堆栈
printf("%d\n", T->Data); //(访问) 打印结点
T = T->Right; //转向右子树
}
}
}
图示
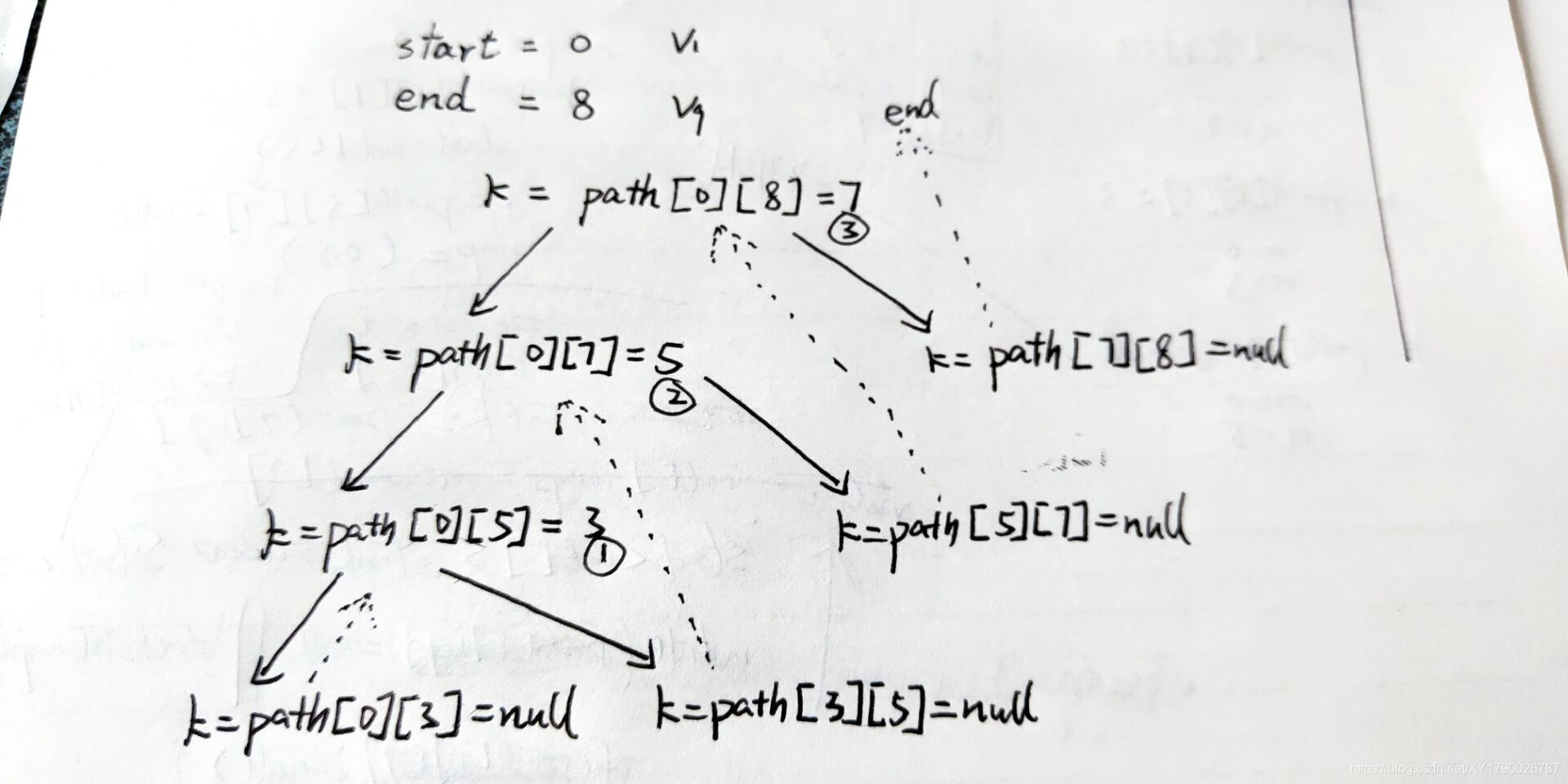
改成非递归算法
int m = startElementIndex;
int n = endElementIndex;
Integer k = path[m][n];
Stack<Integer[]> stack = new Stack<>();
while (null != k || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (null != k) {
stack.push(new Integer[]{m, n});
n = k;
k = path[m][n];
} else {
Integer[] map = stack.pop();
m = map[0];
n = map[1];
k = path[m][n];
pathList.add(this.elementArray.get(k));
k = path[k][n];
}
}
