vtkImageGaussianSmooth构造函数
默认计算Dimensionality为三维;每个方向上的标准标准偏差为2.0,每个方向上的半径因子1.5;
vtkImageGaussianSmooth::vtkImageGaussianSmooth() {
this->Dimensionality = 3;
this->StandardDeviations[0] = 2.0;
this->StandardDeviations[1] = 2.0;
this->StandardDeviations[2] = 2.0;
this->RadiusFactors[0] = 1.5;
this->RadiusFactors[1] = 1.5;
this->RadiusFactors[2] = 1.5;
}
ComputeKernel 计算核
计算出一维正态分布的参数;
void vtkImageGaussianSmooth::ComputeKernel(double *kernel, int min, int max, double std) {
int x;
double sum;
// handle special case
if (std == 0.0) {
kernel[0] = 1.0;
return;
}
// fill in kernel
sum = 0.0;
for (x = min; x <= max; ++x) {
sum += kernel[x - min] = exp(-(static_cast<double>(x*x)) / (std * std * 2.0));
}
// normalize
for (x = min; x <= max; ++x) {
kernel[x - min] /= sum;
}
}
一维正态分布的公式如下:
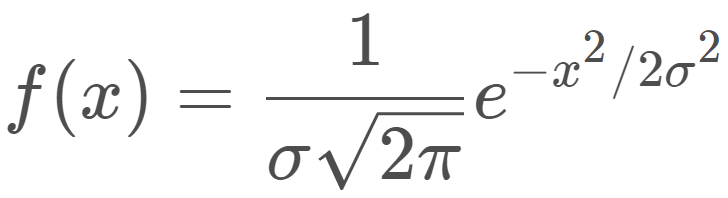
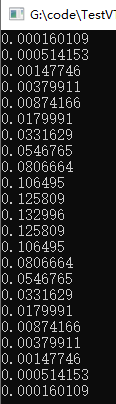
根据公式,计算[-11,11]范围内, σ \sigma σ=3.0时,ComputeKernel计算kernel的对应值23个结果;
double *kernel = new double[23]{
0 };
ComputeKernel(kernel, -11, 11, 3.0);
for (int i = 0 ; i < 23;i++){
cout << kernel[i] << endl;
}
打印的结果如下:
RequestUpdateExtent 更新Extent的六个值
经过vtkImageGaussianSmooth计算后的体数据会比原来的数据扩大一圈,所以三个维度上的尺寸都会改变;
InternalRequestUpdateExtent方法使用StandardDeviations和RadiusFactors计算一个扩展的像素个数;修改inExt[idx * 2]和inExt[idx * 2+1],并判断与wholeExtent[idx * 2]和wholeExtent[idx * 2+1]的有效值判断,防止数据下标的越界;如果wholeExtent和inExt相同时,不会改变三个维度上的尺寸;
int vtkImageGaussianSmooth::RequestUpdateExtent(
vtkInformation * vtkNotUsed(request),
vtkInformationVector **inputVector,
vtkInformationVector *outputVector) {
// get the info objects
vtkInformation *outInfo = outputVector->GetInformationObject(0);
vtkInformation *inInfo = inputVector[0]->GetInformationObject(0);
int wholeExtent[6], inExt[6];
outInfo->Get(vtkStreamingDemandDrivenPipeline::UPDATE_EXTENT(), inExt);
// Expand filtered axes
inInfo->Get(vtkStreamingDemandDrivenPipeline::WHOLE_EXTENT(), wholeExtent);
this->InternalRequestUpdateExtent(inExt, wholeExtent);
inInfo->Set(vtkStreamingDemandDrivenPipeline::UPDATE_EXTENT(), inExt, 6);
return 1;
}
void vtkImageGaussianSmooth::InternalRequestUpdateExtent(int *inExt, int *wholeExtent) {
int idx, radius;
// Expand filtered axes
for (idx = 0; idx < this->Dimensionality; ++idx) {
radius = static_cast<int>(this->StandardDeviations[idx] * this->RadiusFactors[idx]);
inExt[idx * 2] -= radius;
if (inExt[idx * 2] < wholeExtent[idx * 2]) {
inExt[idx * 2] = wholeExtent[idx * 2];
}
inExt[idx * 2 + 1] += radius;
if (inExt[idx * 2 + 1] > wholeExtent[idx * 2 + 1]) {
inExt[idx * 2 + 1] = wholeExtent[idx * 2 + 1];
}
}
}
高斯平滑代码
ExecuteAxis
ExecuteAxis方法对输入数据inData在一个指定轴向上对其进行卷积循环,针对数据的边界重新计算了核数据;

以上图为例,从y1到y2进行y方向上的高斯平滑;
1.如果开始位置在数据的边缘位置,就需要重新高斯平滑核数据;
2.遍历从y1到y2的数据;
2.1对同一个y值的坐标上的数据,调用函数vtkImageGaussianSmoothExecute进行y方向上的卷积处理,即向X、向Z方向上对Y值等于y的坐标的体素计算高斯平滑值;
// This method convolves over one axis. It loops over the convolved axis,
// and handles boundary conditions.
void vtkImageGaussianSmooth::ExecuteAxis(int axis,
vtkImageData *inData, int inExt[6],
vtkImageData *outData, int outExt[6],
int *pcycle, int target,
int *pcount, int total,
vtkInformation *inInfo){
int idxA, max;
int wholeExtent[6], wholeMax, wholeMin;
double *kernel;
// previousClip and currentClip rembers that the previous was not clipped
// keeps from recomputing kernels for center pixels.
int kernelSize = 0;
int kernelLeftClip, kernelRightClip;
int previousClipped, currentClipped;
int radius, size;
void *inPtr;
void *outPtr;
int coords[3];
vtkIdType outIncs[3], outIncA;
// Get the correct starting pointer of the output
outPtr = outData->GetScalarPointerForExtent(outExt);
outData->GetIncrements(outIncs);
outIncA = outIncs[axis];
// trick to account for the scalar type of the output(used to be only float)
switch (outData->GetScalarType()){
vtkTemplateMacro(
outIncA *= static_cast<vtkIdType>(vtkImageGaussianSmoothGetTypeSize(static_cast<VTK_TT*>(nullptr)))
);
default:
vtkErrorMacro("Unknown scalar type");
return;
}
// Determine default starting position of input
coords[0] = inExt[0];
coords[1] = inExt[2];
coords[2] = inExt[4];
// get whole extent for boundary checking ...
inInfo->Get(vtkStreamingDemandDrivenPipeline::WHOLE_EXTENT(), wholeExtent);
wholeMin = wholeExtent[axis * 2];
wholeMax = wholeExtent[axis * 2 + 1];
// allocate memory for the kernel
radius = static_cast<int>(this->StandardDeviations[axis] * this->RadiusFactors[axis]);
size = 2 * radius + 1;
kernel = new double[size];
// loop over the convolution axis
previousClipped = currentClipped = 1;
max = outExt[axis * 2 + 1];
for (idxA = outExt[axis * 2]; idxA <= max; ++idxA) {
// left boundary condition
coords[axis] = idxA - radius;
kernelLeftClip = wholeMin - coords[axis];
if (kernelLeftClip > 0) {
// front of kernel is cut off ("kernelStart" samples)
coords[axis] += kernelLeftClip;
}
else {
kernelLeftClip = 0;
}
// Right boundary condition
kernelRightClip = (idxA + radius) - wholeMax;
if (kernelRightClip < 0) {
kernelRightClip = 0;
}
// We can only use previous kernel if it is not clipped and new
// kernel is also not clipped.
currentClipped = kernelLeftClip + kernelRightClip;
if (currentClipped || previousClipped){
this->ComputeKernel(kernel, -radius + kernelLeftClip,
radius - kernelRightClip,
static_cast<double>(this->StandardDeviations[axis]));
kernelSize = size - kernelLeftClip - kernelRightClip;
}
previousClipped = currentClipped;
/* now do the convolution on the rest of the axes */
inPtr = inData->GetScalarPointer(coords);
switch (inData->GetScalarType()) {
vtkTemplateMacro(
vtkImageGaussianSmoothExecute(this, axis, kernel, kernelSize,
inData, static_cast<VTK_TT*>(inPtr),
outData, outExt,
static_cast<VTK_TT*>(outPtr),
pcycle, target, pcount, total)
);
default:
vtkErrorMacro("Unknown scalar type");
return;
}
outPtr = static_cast<void *>(static_cast<unsigned char *>(outPtr) + outIncA);
}
// get rid of temporary kernel
delete[] kernel;
}
vtkImageGaussianSmoothExecute
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// For a given position along the convolution axis, this method loops over
// all other axes, and performs the convolution. Boundary conditions handled
// previously.
template <class T>
void vtkImageGaussianSmoothExecute(vtkImageGaussianSmooth *self, int axis,
double *kernel, int kernelSize,
vtkImageData *inData, T *inPtrC,
vtkImageData *outData, int outExt[6],
T *outPtrC, int *pcycle, int target,
int *pcount, int total) {
int maxC, max0 = 0, max1 = 0;
int idxC, idx0, idx1, idxK;
vtkIdType inIncs[3], outIncs[3];
vtkIdType inInc0 = 0, inInc1 = 0, inIncK, outInc0 = 0, outInc1 = 0;
T *outPtr1, *outPtr0;
T *inPtr1, *inPtr0, *inPtrK;
double *ptrK, sum;
// I am counting on the fact that tight loops (component on outside)
// is more important than cache misses from shuffled access.
// Do the correct shuffling of the axes (increments, extents)
inData->GetIncrements(inIncs);
outData->GetIncrements(outIncs);
inIncK = inIncs[axis];
maxC = outData->GetNumberOfScalarComponents();
switch (axis){
case 0:
inInc0 = inIncs[1]; inInc1 = inIncs[2];
outInc0 = outIncs[1]; outInc1 = outIncs[2];
max0 = outExt[3] - outExt[2] + 1; max1 = outExt[5] - outExt[4] + 1;
break;
case 1:
inInc0 = inIncs[0]; inInc1 = inIncs[2];
outInc0 = outIncs[0]; outInc1 = outIncs[2];
max0 = outExt[1] - outExt[0] + 1; max1 = outExt[5] - outExt[4] + 1;
break;
case 2:
inInc0 = inIncs[0]; inInc1 = inIncs[1];
outInc0 = outIncs[0]; outInc1 = outIncs[1];
max0 = outExt[1] - outExt[0] + 1; max1 = outExt[3] - outExt[2] + 1;
break;
}
for (idxC = 0; idxC < maxC; ++idxC){
inPtr1 = inPtrC;
outPtr1 = outPtrC;
for (idx1 = 0; !self->AbortExecute && idx1 < max1; ++idx1){
inPtr0 = inPtr1;
outPtr0 = outPtr1;
for (idx0 = 0; idx0 < max0; ++idx0) {
inPtrK = inPtr0;
ptrK = kernel;
sum = 0.0;
// too bad this short loop has to be the inner most loop
for (idxK = 0; idxK < kernelSize; ++idxK){
sum += *ptrK * static_cast<double>(*inPtrK);
++ptrK;
inPtrK += inIncK;
}
*outPtr0 = static_cast<T>(sum);
inPtr0 += inInc0;
outPtr0 += outInc0;
}
inPtr1 += inInc1;
outPtr1 += outInc1;
// we finished a row ... do we update ???
if (total) {
// yes this is the main thread
*pcycle += max0;
if (*pcycle > target){
// yes
*pcycle -= target;
*pcount += target;
self->UpdateProgress(static_cast<double>(*pcount) / static_cast<double>(total));
}
}
}
++inPtrC;
++outPtrC;
}
}
ThreadedRequestData
ThreadedRequestData是继承并重写了vtkThreadedImageAlgorithm类的方法;
如果继承vtkThreadedImageAlgorithm类的子类没有定义Execute方法,那么任务将被分解,将产生多个线程,每个线程将调用此方法。ThreadedRequestData方法是公共的,因此线程函数可以调用此方法。
ThreadedRequestData方法的具体内容为:
1.确定像素个数total,计算target为total / 50,50表示开了50个progress;
2.判断输入数据类型和输出数据类型是否一致,不一致,显示错误并返回;
3.获取输入和输出信息vtkInformation,以及对应的三维尺寸;
4.根据不同维度,调用函数ExecuteAxis方法进行高斯平滑处理;
4.1 一维数据,只对X方向进行高斯平滑;
4.2 二维数据,先对X方向进行高斯平滑,在对Y方向进行高斯平滑;
4.3 三维数据,先对X方向进行高斯平滑,在对Y方向进行高斯平滑,最后对Z方向进行高斯平滑;
// This method decomposes the gaussian and smooths along each axis.
void vtkImageGaussianSmooth::ThreadedRequestData(
vtkInformation *vtkNotUsed(request),
vtkInformationVector **inputVector,
vtkInformationVector *outputVector,
vtkImageData ***inData,
vtkImageData **outData,
int outExt[6], int id)
{
int inExt[6];
int target, count, total, cycle;
// for feed back, determine line target to get 50 progress update
// update is called every target lines. Progress is computed from
// the number of pixels processed so far.
count = 0; target = 0; total = 0; cycle = 0;
if (id == 0)
{
// determine the number of pixels.
total = this->Dimensionality * (outExt[1] - outExt[0] + 1)
* (outExt[3] - outExt[2] + 1) * (outExt[5] - outExt[4] + 1)
* inData[0][0]->GetNumberOfScalarComponents();
// pixels per update (50 updates)
target = total / 50;
}
// this filter expects that input is the same type as output.
if (inData[0][0]->GetScalarType() != outData[0]->GetScalarType())
{
vtkErrorMacro("Execute: input ScalarType, "
<< inData[0][0]->GetScalarType()
<< ", must match out ScalarType "
<< outData[0]->GetScalarType());
return;
}
// Decompose
vtkInformation *inInfo = inputVector[0]->GetInformationObject(0);
vtkInformation *outInfo = outputVector->GetInformationObject(0);
int wholeExt[6];
inInfo->Get(vtkStreamingDemandDrivenPipeline::WHOLE_EXTENT(), wholeExt);
outInfo->Get(vtkStreamingDemandDrivenPipeline::UPDATE_EXTENT(), inExt);
this->InternalRequestUpdateExtent(inExt, wholeExt);
switch (this->Dimensionality)
{
case 1:
this->ExecuteAxis(0, inData[0][0], inExt, outData[0], outExt, &cycle, target, &count, total, inInfo);
break;
case 2:
int tempExt[6];
vtkImageData *tempData;
// compute intermediate extent
tempExt[0] = inExt[0]; tempExt[1] = inExt[1];
tempExt[2] = outExt[2]; tempExt[3] = outExt[3];
tempExt[4] = inExt[4]; tempExt[5] = inExt[5];
// create a temp data for intermediate results
tempData = vtkImageData::New();
tempData->SetExtent(tempExt);
tempData->AllocateScalars(inData[0][0]->GetScalarType(), inData[0][0]->GetNumberOfScalarComponents());
this->ExecuteAxis(1, inData[0][0], inExt, tempData, tempExt, &cycle, target, &count, total, inInfo);
this->ExecuteAxis(0, tempData, tempExt, outData[0], outExt, &cycle, target, &count, total, inInfo);
// release temporary data
tempData->Delete();
break;
case 3:
// we do z first because it is most likely smallest
int temp0Ext[6], temp1Ext[6];
vtkImageData *temp0Data, *temp1Data;
// compute intermediate extents
temp0Ext[0] = inExt[0]; temp0Ext[1] = inExt[1];
temp0Ext[2] = inExt[2]; temp0Ext[3] = inExt[3];
temp0Ext[4] = outExt[4]; temp0Ext[5] = outExt[5];
temp1Ext[0] = inExt[0]; temp1Ext[1] = inExt[1];
temp1Ext[2] = outExt[2]; temp1Ext[3] = outExt[3];
temp1Ext[4] = outExt[4]; temp1Ext[5] = outExt[5];
// create a temp data for intermediate results
temp0Data = vtkImageData::New();
temp0Data->SetExtent(temp0Ext);
temp0Data->AllocateScalars(inData[0][0]->GetScalarType(),
inData[0][0]->GetNumberOfScalarComponents());
temp1Data = vtkImageData::New();
temp1Data->SetExtent(temp1Ext);
temp1Data->AllocateScalars(inData[0][0]->GetScalarType(), inData[0][0]->GetNumberOfScalarComponents());
this->ExecuteAxis(2, inData[0][0], inExt, temp0Data, temp0Ext, &cycle, target, &count, total, inInfo);
this->ExecuteAxis(1, temp0Data, temp0Ext, temp1Data, temp1Ext, &cycle, target, &count, total, inInfo);
temp0Data->Delete();
this->ExecuteAxis(0, temp1Data, temp1Ext, outData[0], outExt, &cycle, target, &count, total, inInfo);
temp1Data->Delete();
break;
}
}