“ Algorithms + Data Structures = Programs. ”
‣ dynamic connectivity
‣ quick find
‣ quick union
‣ improvements
‣ applications
1.dynamic connectivity(动态连接)
Given a set of N objects.
・Union command: connect two objects.(Union-连通两个分量)・Find/connected query: is there a path connecting the two objects?
We assume "is connected to" is an equivalence relation:(连通分量特性)
・Reflexive: p is connected to p.
・Symmetric: if p is connected to q, then q is connected to p.
・Transitive: if p is connected to q and q is connected to r, then p is connected to r
Goal:Design efficient data structure for union-find.
・Number of objects N can be huge.
・Number of operations M can be huge.
・Find queries and union commands may be intermixed
Problem:
How many connected components result after performing the following sequence of unionoperations on a set of 10
10 items?
1–2,3–4,5–6,7–8,7–9,2–8,0–5,1–9
The connected components are {0,5,6}, {3,4}, and {1,2,7,8,9}.
2.quick find(快速查找)
| element | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| group number | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
For the first point(0,1), update the group number of element 0 and 1 to 0 or 1.(Union并操作)
| element | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| group number | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
public class QuickFindUF {
private int[] id; // id[i] = component identifier of i
/**
* Initializes an empty union–find data structure with {@code n} sites
* {@code 0} through {@code n-1}. Each site is initially in its own
* component.
* @param n the number of sites
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code n < 0}
*/
public QuickFindUF(int n) {
id = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
id[i] = i;
}
/**
* Returns true if the the two sites are in the same component.
*
* @param p the integer representing one site
* @param q the integer representing the other site
* @return {@code true} if the two sites {@code p} and {@code q} are in the same component;
* {@code false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless
* both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n}
*/
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return id[p] == id[q];
}
/**
* Merges the component containing site {@code p} with the
* the component containing site {@code q}.
*
* @param p the integer representing one site
* @param q the integer representing the other site
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless
* both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n}
*/
public void union(int p, int q) {
int pID = id[p]; // needed for correctness
int qID = id[q]; // to reduce the number of array accesses
for(int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
// p and q are already in the same component
if (id[i] == pID) id[i] = qID ;
}
}Python:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# 作者: Adward Wang
# 邮箱: [email protected]
# 时间: 2018-06-11 16:13:22
# 描述: 佛性编程
id={}
def QuickFind(n):
for i in range(1,n+1):
id[i]=i
def connected(p,q):
return id[p] == id[q]
def unionid(p,q):
pID = id[p]
qID = id[q]
for i in range(0,n):
if(id[i] == pID):id[i] = qID
Constant time find.
| algorithm | initialize | union | find |
| quich-find | N | N | 1 |
Problem:
What is the maximum number of \verb#id[]#id[] array entries that can change (from one value to a different value) during one call to union when using the quick-find data structure on nn elements?
n-1
In the worst case, all of the entries except #id[q]#id[q] are changed from #id[p]#id[p] to #id[q]#id[q].
This doesn't work well on huge dataset.
3.quick union(快速合并)
Problem:
Suppose that in a quick-union data structure on 10 elements that the \verb#id[]#id[] array is
| i | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| id[i] | 0 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 5 |
The root of 3 is 6: 3→5→2→6.
The root of 7 is 6: 7→1→9→5→2→6.
Union the root of 2 numbers.
Java:
public class QuickFindUF {
private int[] id; // id[i] = component identifier of i
public QuickUnionUF(int N) {
id = new int[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N ; i++) id[i] = i;
}
private int root(int i) {
while(i != id[i]) i = id[i];
reruen i;
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return root[p] == root[q];
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int i = root[p];
int j = root[q];
id[i] = j;
}
}
algorithm |
initialize |
union |
find |
quich-find |
N |
N |
1 |
quich-union |
N |
N |
N |
What is the maximum number of array accesses during a find operation when using the quick-union data structure on n elements?
linear
4.quick union improvements(优化)
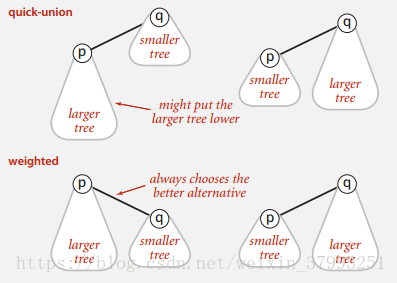
Avoid to put large trees below.
Improvements1: Weighted quick-union demo
Depth of any node x is at most lg N.
| algorithm | initialize | union | connected |
| quick-find | N | N | 1 |
| quick-union | N | N | N |
| weighted QU | N | lg N | lg N |
Java:
public class WeightedQuickUnionUF {
private int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i
private int[] size; // size[i] = number of sites in subtree rooted at i
private int count; // number of components
/**
* Initializes an empty union–find data structure with {@code n} sites
* {@code 0} through {@code n-1}. Each site is initially in its own
* component.
*
* @param n the number of sites
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code n < 0}
*/
public WeightedQuickUnionUF(int n) {
count = n;
parent = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
/**
* Returns the number of components.
*
* @return the number of components (between {@code 1} and {@code n})
*/
public int count() {
return count;
}
/**
* Returns the component identifier for the component containing site {@code p}.
*
* @param p the integer representing one object
* @return the component identifier for the component containing site {@code p}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= p < n}
*/
public int find(int p) {
validate(p);
while (p != parent[p])
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
// validate that p is a valid index
private void validate(int p) {
int n = parent.length;
if (p < 0 || p >= n) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (n-1));
}
}
/**
* Returns true if the the two sites are in the same component.
*
* @param p the integer representing one site
* @param q the integer representing the other site
* @return {@code true} if the two sites {@code p} and {@code q} are in the same component;
* {@code false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless
* both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n}
*/
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
/**
* Merges the component containing site {@code p} with the
* the component containing site {@code q}.
*
* @param p the integer representing one site
* @param q the integer representing the other site
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless
* both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n}
*/
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
// make smaller root point to larger one
if (size[rootP] < size[rootQ]) {
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
size[rootQ] += size[rootP];
}
else {
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
size[rootP] += size[rootQ];
}
count--;
}
/**
* Reads in a sequence of pairs of integers (between 0 and n-1) from standard input,
* where each integer represents some object;
* if the sites are in different components, merge the two components
* and print the pair to standard output.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = StdIn.readInt();
WeightedQuickUnionUF uf = new WeightedQuickUnionUF(n);
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int p = StdIn.readInt();
int q = StdIn.readInt();
if (uf.connected(p, q)) continue;
uf.union(p, q);
StdOut.println(p + " " + q);
}
StdOut.println(uf.count() + " components");
}
}python:
class WeightedQuickUnionUF(BaseComp):
""" UNION FIND: Weighted Quick-union [lazy approach] to avoid tall trees."""
def __init__(self, N): # $ = N
"""Initialize union-find data structure w/N objects (0 to N-1)."""
super(WeightedQuickUnionUF, self).__init__("WeightedQuickUnionUF")
self.ID = range(N) # Set if of each object to itself.
# Keep track of SIZE(# objects in tree) of each tree rooted at i
self.SZ = [1]*N # Needed to determine which tree is smaller/bigger
def _root(self, i):
"""Chase parent pointers until reach root."""
d = 0 # Used for informative prints for educational purposes
while i != self.ID[i]: # depth of i array accesses
i = self.ID[i]
d += 1
return BaseComp.NtRoot(rootnode=i, depth=d)
def connected(self, p, q): # $ = lg N
"""Return if p and q are in the same connected component (i.e. have the same root)."""
return self._root(p).rootnode == self._root(q).rootnode # Runs depth of p & q array accesses
def union(self, p, q): # $ = lg N
"""Add connection between p and q."""
# Runs Depth of p and q array accesses...
p_root = self._root(p).rootnode
q_root = self._root(q).rootnode
if p_root == q_root:
return
# IMPROVEMENT #1: Modification to Quick-Union to make it weighted: 4:03
# Balance trees by linking root of smaller tree to root of larger tree
# Modified quick-union:
# * Link root of smaller tree to root of larger tree.
# * Update the SZ[] array.
# Each union involves changing only one array entry
if self.SZ[p_root] < self.SZ[q_root]: # Make ID[p_root] a child of q_root
self.ID[p_root] = q_root # link root of smaller tree(p_root) to root of larger tree(q_root)
self.SZ[q_root] += self.SZ[p_root] # Larger tree size increases
else: # Make ID[q_root] a child of p_root
self.ID[q_root] = p_root # link root of smaller tree(q_root) to root of larger tree(p_root)
self.SZ[p_root] += self.SZ[q_root]
def __str__(self):
"""Print the size vector as well as the ID vector."""
return '\n'.join([
super(WeightedQuickUnionUF, self).__str__(),
"siz: " + ' '.join('{SZ:>2}'.format(SZ=e) for e in self.SZ)])
Improvements2: Path compression
private int root(int i)
{
while(i != id[i])
{
id[i] = id[id[i]];//compression
i = id[i];
}
return i;
}Proposition. [Hopcroft-Ulman, Tarjan] Starting from an
empty data structure, any sequence ofM union-find ops
onN objects makes ≤ c ( N + M lg* N ) array accesses.
・Analysis can be improved to N + M α(M, N).
・Simple algorithm with fascinating mathematics
Nearly to linear running time.
Problem:
Suppose that the id[] array during the weighted quick-union (by size) algorithm is given as below. Which id[] entry changes when we apply the union operation to 3 and 6?
id[8] = 0
5.applications
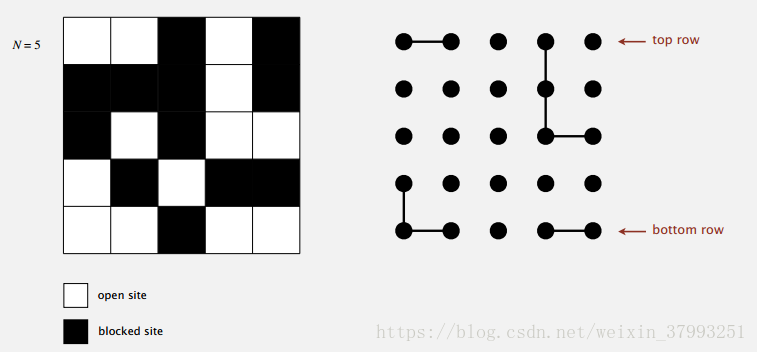
Percolation
A model for many physical systems:
・N-by-N grid of sites.
・Each site is open with probability p (or blocked with probability 1 – p).
・System percolates iff top and bottom are connected by open sites.
Monte Carlo simulation
・Initialize N-by-N whole grid to be blocked.
・Declare random sites open until top connected to bottom.
・Vacancy percentage estimates p*.
Dynamic connectivity solution to estimate percolation threshold
・Create an object for each site and name them 0 to N 2 – 1.
・Sites are in same component if connected by open sites.
・Percolates iff any site on bottom row is connected to site on top row.
嗯.....不太想翻译,能看懂就好。