胜利大逃亡
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 45713 Accepted Submission(s): 15848
Problem Description
Ignatius被魔王抓走了,有一天魔王出差去了,这可是Ignatius逃亡的好机会.
魔王住在一个城堡里,城堡是一个ABC的立方体,可以被表示成A个B*C的矩阵,刚开始Ignatius被关在(0,0,0)的位置,离开城堡的门在(A-1,B-1,C-1)的位置,现在知道魔王将在T分钟后回到城堡,Ignatius每分钟能从一个坐标走到相邻的六个坐标中的其中一个.现在给你城堡的地图,请你计算出Ignatius能否在魔王回来前离开城堡(只要走到出口就算离开城堡,如果走到出口的时候魔王刚好回来也算逃亡成功),如果可以请输出需要多少分钟才能离开,如果不能则输出-1.
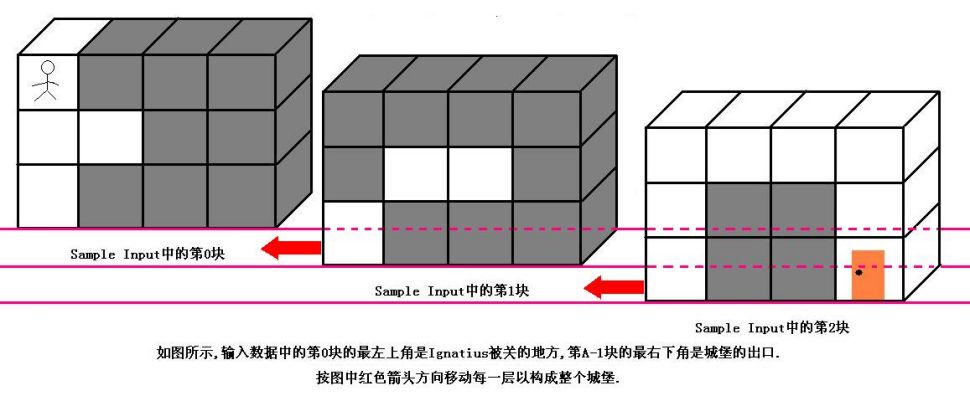
Input
输入数据的第一行是一个正整数K,表明测试数据的数量.每组测试数据的第一行是四个正整数A,B,C和T(1<=A,B,C<=50,1<=T<=1000),它们分别代表城堡的大小和魔王回来的时间.然后是A块输入数据(先是第0块,然后是第1块,第2块…),每块输入数据有B行,每行有C个正整数,代表迷宫的布局,其中0代表路,1代表墙.(如果对输入描述不清楚,可以参考Sample Input中的迷宫描述,它表示的就是上图中的迷宫)
特别注意:本题的测试数据非常大,请使用scanf输入,我不能保证使用cin能不超时.在本OJ上请使用Visual C++提交.
Output
对于每组测试数据,如果Ignatius能够在魔王回来前离开城堡,那么请输出他最少需要多少分钟,否则输出-1.
Sample Input
1
3 3 4 20
0 1 1 1
0 0 1 1
0 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 0 0 1
0 1 1 1
0 0 0 0
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0
Sample Output
11
经典的一道bfs广搜题,首先创建一个三维数组,选好自己的x-y-z轴,接下来的步骤就和其他基本的bfs题目一样啦。要注意的是若不能救出要输出的是-1,还有要用scanf读0 1,用cin就tle了。
下面附上ac代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;
int k;
int a,b,c,t;
int mp[60][60][60];
int sgn[60][60][60]; // z, i , j
int mv[8][5] = {{-1,0,0},{1,0,0},{0,0,-1},{0,0,1},{0,1,0},{0,-1,0}};
struct node {
int z,i,j,step;
};
bool check(int z,int i,int j) {
if(z < 0 || z >= a || i < 0 || i >= b || j < 0 || j >= c) {return false;}
if(sgn[z][i][j] == 1) {return false;}
if(mp[z][i][j] == 1) {return false;}
return true;
}
int bfs() {
memset(sgn,0,sizeof(sgn));
node cur,next;
cur.z = 0;
cur.i = 0;
cur.j = 0;
sgn[cur.z][cur.i][cur.j] = 1;
cur.step = 0;
queue<node>q;
q.push(cur);
while(!q.empty()) {
cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(cur.step > t) {return -1;}
if(cur.z == a-1 && cur.i == b-1 && cur.j == c-1 && cur.step <= t) {
return cur.step;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
next.z = cur.z + mv[i][0];
next.i = cur.i + mv[i][1];
next.j = cur.j + mv[i][2];
if(check(next.z,next.i,next.j)) {
sgn[next.z][next.i][next.j] = 1;
next.step = cur.step + 1;
q.push(next);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
cin >> k;
while(k--) {
cin >> a >> b >> c >> t;
for(int k = 0; k < a; k++) {
for(int i = 0; i < b; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
scanf("%d",&mp[k][i][j]);
}
}
}
cout << bfs() << endl;
}
return 0;
}