1、定义节点类
定义静态内部类 TreeNode 作为一个节点类,使用了泛型,data 为节点数据,lChild,rChild 为节点的左右子树,数据类型为 TreeNode
//静态内部节点类
public static class TreeNode<AnyType> {
//节点数据
public AnyType data;
//左子树
public TreeNode<AnyType> lChild, rChild;
public TreeNode() {
this(null);
}
public TreeNode(AnyType data) {
this(data, null, null);
}
public TreeNode(AnyType data, TreeNode<AnyType> lChild, TreeNode<AnyType> rChild) {
this.data = data;
this.lChild = lChild;
this.rChild = rChild;
}
}
2、定义根节点
定义该树的根节点及构造方法,根节点初始化为空
//根节点
TreeNode<AnyType> root = null;
public BiTree() {
this.root = null;
}
3、定义创建树的方式
定义变量 $ 来记录数组的位置,有先序遍历创建一颗二叉树,以 # 标志判断节点是否为空,可以定制自己需要的二叉树类型。
static int $ = 0;
//创建一棵树
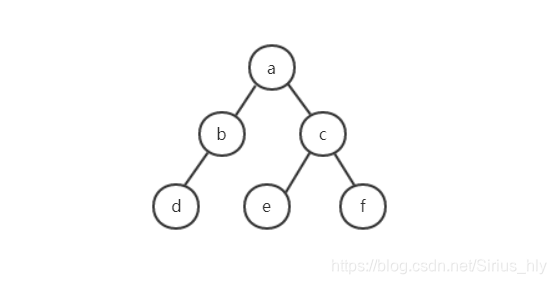
// "a","b","d","#","#","#","c","e","#","#","f","#","#"
public BiTree(AnyType[] preorder) {
AnyType data = preorder[$++];
if (data != "#") {
root = new TreeNode<AnyType>(data);
root.lChild = new BiTree<AnyType>(preorder).root;
root.rChild = new BiTree<AnyType>(preorder).root;
} else {
root = null;
}
}
4、二叉树的遍历
以下是二叉树的前,中,后序遍历
//前序遍历
public void preTraverse(TreeNode<AnyType> root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preTraverse(root.lChild);
preTraverse(root.rChild);
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixTraverse(TreeNode<AnyType> root) {
if (root != null) {
infixTraverse(root.lChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
infixTraverse(root.rChild);
}
}
//后续遍历
public void postTraverse(TreeNode<AnyType> root) {
if (root != null) {
postTraverse(root.lChild);
postTraverse(root.rChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
}
}
5、实现二叉树的翻转
这个问题是受到 Max Howell 的 原问题 启发的 :
谷歌:我们90%的工程师使用您编写的软件(Homebrew),但是您却无法在面试时在白板上写出翻转二叉树这道题,这太糟糕了。
//二叉树翻转递归
public void reverseRecursion(TreeNode<AnyType> root) {
if (root != null) {
TreeNode<AnyType> p = root.rChild;
root.lChild = root.rChild;
root.rChild = p;
reverseRecursion(root.lChild);
reverseRecursion(root.rChild);
}
}
//二叉树翻转迭代
public void reverseIteration(TreeNode<AnyType> root) {
Queue<TreeNode<AnyType>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode<AnyType> cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.lChild != null || cur.rChild != null) {
TreeNode<AnyType> t = cur.lChild;
cur.lChild = cur.rChild;
cur.rChild = t;
if (cur.lChild != null)
queue.offer(cur.lChild);
if (cur.rChild != null)
queue.offer(cur.rChild);
}
}
}
6、统计二叉树节点的个数
//统计二叉树节点个数
public int countNode(TreeNode<AnyType> root) {
int count = 0;
if (root != null) {
count++;
count += countNode(root.lChild);
count += countNode(root.rChild);
}
return count;
}
//统计二叉树节点个数
public int countNode2(TreeNode<AnyType> root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
return countNode2(root.lChild) + countNode2(root.rChild) + 1;
}
7、得到二叉树的深度
//得到树的深度
public int getDepth(TreeNode<AnyType> root) {
if (root != null) {
int lDepth = getDepth(root.lChild);
int rDepth = getDepth(root.rChild);
return 1 + (lDepth > rDepth ? lDepth : rDepth);
}
return 0;
}
8、得到叶子节点的个数
public int leaf(TreeNode<AnyType> root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
int c = leaf(root.lChild)+ leaf(root.rChild);
if (root.lChild == null && root.rChild == null) {
return c+1;
}else{
return c;
}
}
}
9、测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] a = {"a", "b", "d", "#", "#", "#", "c", "e", "#", "#", "f", "#", "#"};
BiTree<String> biTree = new BiTree<String>(a);// ABDEGCFH//DBGEAFHC
//BiTree<String> biTree = new BiTree<String>();// ABDEGCFH//DBGEAFHC
System.out.println();
//// abdcef
biTree.preTraverse(biTree.root);
System.out.println();
// dbaecf
biTree.infixTraverse(biTree.root);
System.out.println();
// dbefca
biTree.postTraverse(biTree.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("叶子" + biTree.leaf(biTree.root));
System.out.println("深度" + biTree.getDepth(biTree.root));
System.out.println("二叉树的节点个数 " + biTree.countNode(biTree.root));
}
我的 Github:Github
CSDN: CSDN
个人网站: sirius 的博客
E-mail: [email protected]
代码下载:二叉树的实现
