Java 面试大全〖九〗生产者消费者模式
生产者消费者模式是通过一个容器来解决生产者和消费者的强耦合问题。生产者和消费者彼此之间不直接通讯,而通过阻塞队列来进行通讯,所以生产者生产完数据之后不用等待消费者处理,直接扔给阻塞队列,消费者不找生产者要数据,而是直接从阻塞队列里取,阻塞队列就相当于一个缓冲区,平衡了生产者和消费者的处理能力。这个阻塞队列就是用来给生产者和消费者解耦的。
一. synchronized实现
加粗样式
package JUC.ComuserAndProducer;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
class CandP1 {
private int num = 0;
public synchronized void increament() throws InterruptedException {
while (num != 0) {
this.wait();
}
num++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 线程生产了,还剩下: " + num);
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decreament() throws InterruptedException {
while (num == 0) {
this.wait();
}
num--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 线程消费了,还剩下: " + num);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
public class ComsumerAndProducerSync {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CandP1 candP1=new CandP1();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
candP1.increament();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
candP1.decreament();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"B").start();
}
}
二. Lock实现
package JUC.ComuserAndProducer;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
class CandP{
private int num=0;
Lock lock=new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition=lock.newCondition();
public void increament() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try{
while(num!=0){
condition.await();
}
num++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 线程生产了,还剩下: "+num);
condition.signalAll();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void decreament() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try{
while(num==0){
condition.await();
}
num--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 线程消费了,还剩下: "+num);
condition.signalAll();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class ComsumerAndProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CandP candP=new CandP();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
candP.increament();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
candP.decreament();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"B").start();
}
}
三. 阻塞队列实现
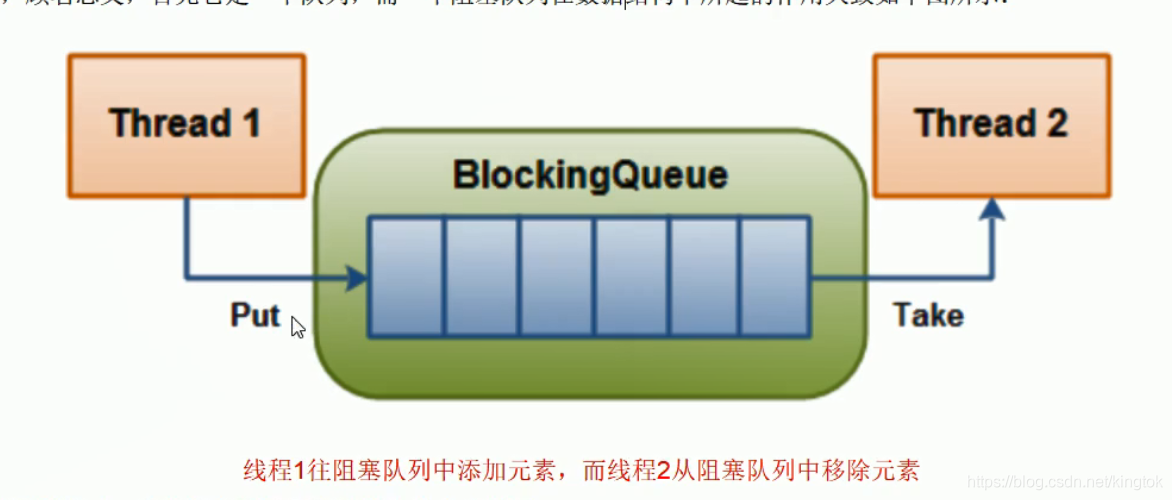
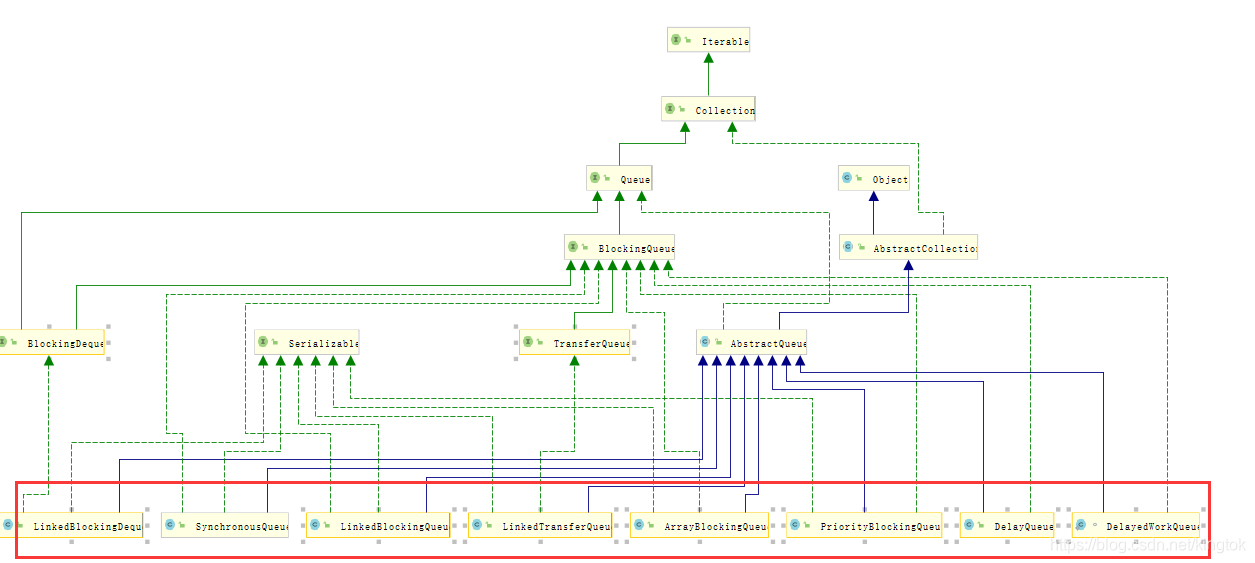

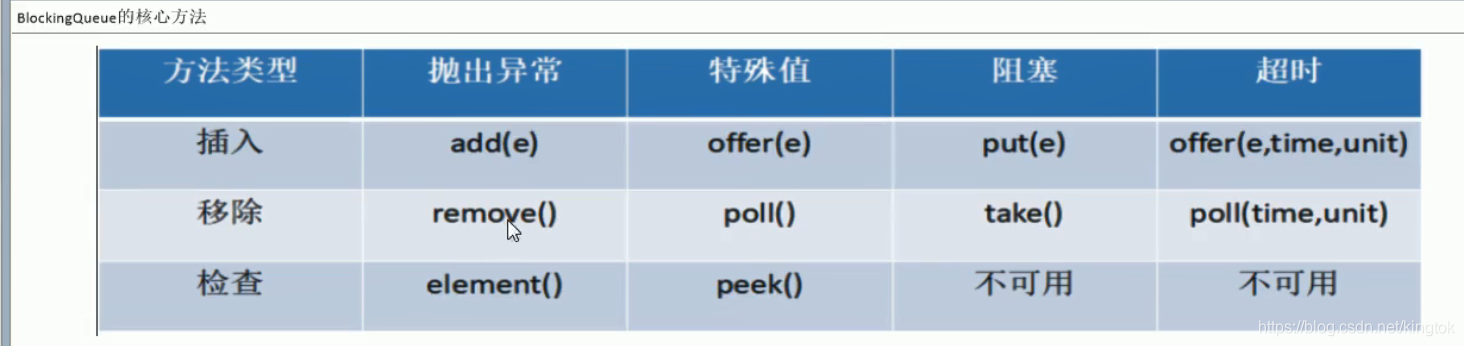
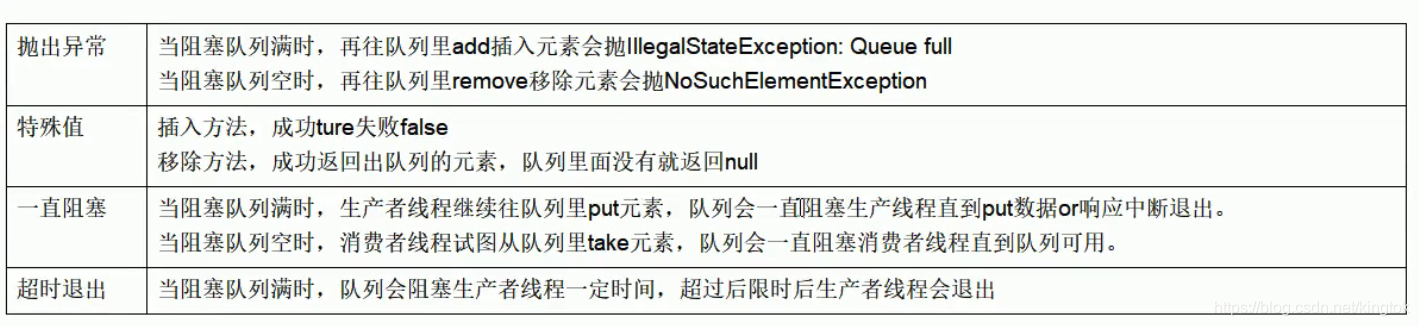


package JUC.ComuserAndProducer;
import java.sql.Time;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
class MyResource{
private volatile boolean Flag=true; //默认开启进行生产消费
private AtomicInteger atomicInteger=new AtomicInteger(); //原子整形
BlockingQueue blockingQueue=null;//我们传接口,不传具体实现类,具体实现类由我们自己决定,口子放的足够宽
public MyResource(BlockingQueue blockingQueue) {
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
System.out.println(blockingQueue.getClass().getName()); //检查进来的是什么对象
}
public void MyProducer1() throws InterruptedException {
String data=null;
while(Flag){
data = atomicInteger.getAndIncrement()+"";
boolean offer = blockingQueue.offer(data, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(offer){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+data+"插入成功");
}else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+data+"插入失败");
}
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"生产停止");
}
public void MyConsumer1() throws InterruptedException {
String data=null;
while(Flag){
data = (String) blockingQueue.poll(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(data==null||data.equalsIgnoreCase("")){
Flag=false;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+data+" 2s没取到消费失败");
System.out.println();
return;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+data+"消费成功");
}
}
public void StopAll(){
Flag=false;
}
}
public class ComsumerAndProducerBlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyResource myResource=new MyResource(new SynchronousQueue());
ExecutorService executorService=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
myResource.MyProducer1();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "生产者A1");
executorService.execute(thread);
new Thread(()->{
try {
myResource.MyConsumer1();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"消费者B1").start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(6);
myResource.StopAll();
executorService.shutdown();
}
}