
1. Motivation
anchor-based method(RetinaNet)和 anchor-free method(FCOS)的主要差异体现在以下4点:
-
The number of anchors tiled per location.
-
The definition of positive and negative samples.
-
The regression starting status.
而目前FCOS的实验结果会比RetinaNet好,因此在这三个差异中,哪一点是造成这2个detectors的性能gap的主要因素值得研究。
In this paper, we first point out that the essential difference between anchor-based and anchor-free detection is actually how to define positive and negative training samples, which leads to the performance gap be- tween them.
在本文中,作者调查了anchor-based和anchor-free2种目标检测方法在精度上的的差异。通过排除2种方法在实现上不一致的地方,可以得出结论,2种方法在性能上的gap来源于正负样本的定义。
如何更好的制定正负样本值得进一步的研究,基于此动机,本文提出了自适应训练样本选择器(ATSS),基于物体的特征来自动的选择正负样本。
Then, we propose an Adaptive Training Sample Selection (ATSS) to automatically select positive and negative samples according to statistical characteristics of object.
2. Contribution
本文的主要贡献可以可以总结为以下4点:
- 实验表明,anchor-based和anchor-free detectors的差异性主要是源于正负样本的制定上。
- 提出了ATSS方法,根据物体的statistical characteristics,来自动选择正负样本。
- 展示了在图片的每个location上制定多个anchors是一个无用的操作。
- 在没有添加额外的开支的情况下,在MS COCO数据集上的实验达到了SOTA。
3. Difference Analysis of Anchor-based and Anchor-free Detection
在本章节中,作者关注于正负样本的制定以及回归的起始状态这2个差异,在RetinaNet上对于每一个location只制定一个anchor。
3.1 Experiment Setting
-
数据集采用MS COCO
-
Inference Detail
总结一下:首先,resize图片大小和和训练过程中保持一致,接着forward操作,输出带有预测类别的bbox。接着,使用0.05的scores来首选排除大量的背景的候选框(注意,通过FCOS中代码发现,这里的scores并不是每一个location上对于80个class预测中最大的socres,即不是每一个locations只比较max scores,而是每个locations所有的scores进行过滤,如果大于0.05就保留),并且在每一个FPN层中挑选得分最高的1000的候选框,最后在使用NMS,对于每一个class采用阈值为0.6进行最后的过滤,在每张图片上挑选最好的100个候选框。
3.2 Inconsistency Removal
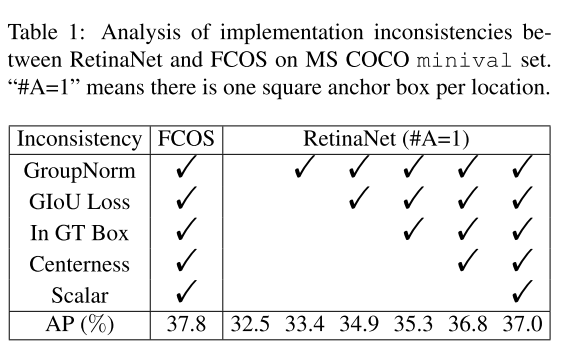
如表1所示,如果在RetinaNet上只制定一个anchor,那么效果是非常差的,AP只有32.5,通过加入多个imporvements,可以将精度提升至37.0,但还是和FCOS有0.8的差距。
3.3 Essential Difference
在应用了所有的improvements,RetinaNet和FCOS只有2处不同,第一处不同是分类子任务,第二点是回归子任务。
- Classification
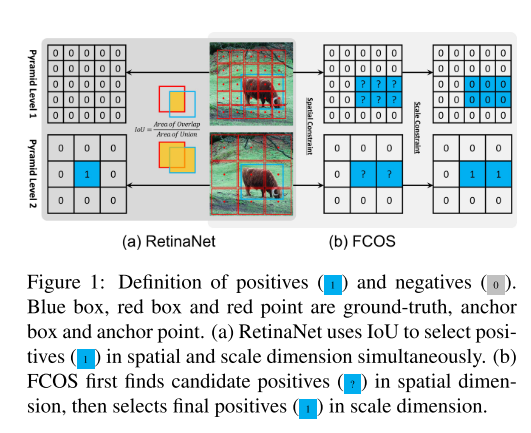
RetinaNet是根据IOU来进行判断正负样本,当anchor和gt的IOU大于阈值 θ p \theta_p θp时,将anchor当做为正样本;当anchor和gt的IOY小于阈值 θ n \theta_n θn,将此anchor当做为负样本。而FCOS则是使用了spatial(如果anchor point位于gt的center region)和scale(FPN上对于根据scale range将候选框制定在某一层上)的双重约束。
FCOS first uses the spatial constraint to find candidate positives in the spatial dimension, then uses the scale constraint to select final positives in the scale dimension.
In contrast, RetinaNet utilizes IoU to directly select the final positives in the spatial and scale di- mension simultaneously. These
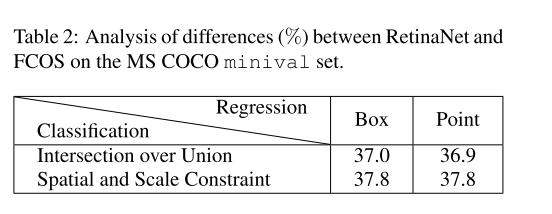
如表2所示,对于RetinaNet,如果将IOU策略替换为Spatial and Scale Constraint策略,这就使得其AP从37.0%提升37.8%。而对于FCOS,如果使用IOU的策略,会使得其AP从37.8%降到36.9%。
-
Regression
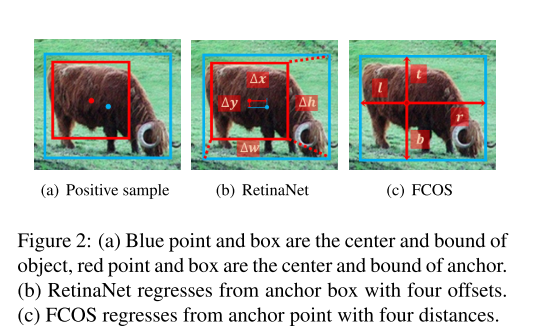
如图2所示,FCOS回归anchor point的4个距离(L,T,R,B),而RetinaNet则是回归anchor box的四个偏移量offsets。
4. Adaptive Training Sample Selection
