图的邻接矩阵
namespace Graph_Structure
{
//Vertex是代表顶点的数据类型,Weight是边的权值的数据类型,MAX_W是权值的上限值(表示不相两)
//Direction表示图是否为有向图
template<class Vertex, class Weight = int, Weight MAX_W = INT_MAX, bool Direction = false>
class Graph
{
typedef Graph<Vertex, Weight, MAX_W, Direction> Self;
public:
//使用编译器的默认构造函数
Graph() = default;
//给定一个存放顶点的数组用来初始化图
Graph(const Vertex* a, size_t n)
{
_vertexs.reserve(n);
_indexMap.rehash(n);
_matrix.resize(n, std::vector<Weight>(n, MAX_W));
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
_vertexs.push_back(a[i]);
//建立顶点和数组下标的映射(目的是为了邻接矩阵的边存储)
_indexMap[a[i]] = i;
}
}
//获取顶点在邻接矩阵中对应的下标
size_t GetVertexIndex(const Vertex& vertex)
{
if (_indexMap.find(vertex) == _indexMap.end())
{
throw "invalued_para";
return -1;
}
return _indexMap[vertex];
}
void _AddEdge(size_t srci, size_t dsti, const Weight& w)
{
//判断是有向图还是无向图
if (Direction == false)
{
_matrix[dsti][srci] = w;
}
_matrix[srci][dsti] = w;
}
//给定起点和终点,在邻接矩阵中添加一条边
void AddEdge(const Vertex& src, const Vertex& dst, const Weight& w)
{
if (_indexMap.find(src) == _indexMap.end() || _indexMap.find(dst) == _indexMap.end())
{
throw "invalued_para";
}
size_t srci_index = GetVertexIndex(src);
size_t dst_index = GetVertexIndex(dst);
_AddEdge(srci_index, dst_index, w);
}
//将图的邻接矩阵打印出来
void Print()
{
for (auto e : _vertexs)
{
std::cout << e << '[' << _indexMap[e] << ']' << std::endl;
}
std::cout << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); ++i)
{
std::cout << i << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
int i = 0;
for (auto arry : _matrix)
{
std::cout << i++ << ' ';
for (auto e : arry)
{
if (e == MAX_W)
{
printf("%4c ", '*');
}
else
{
printf("%4d ", e);
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
//图的广度优先遍历
void BFS(const Vertex& src)
{
size_t begin = GetVertexIndex(src);
std::queue<int> QNode;
std::vector<bool> Label(_vertexs.size(), false);
QNode.push(begin);
Label[begin] = true;
size_t Level = 0;
while (!QNode.empty())
{
size_t LevelSize = QNode.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < LevelSize; ++i)
{
size_t front = QNode.front();
QNode.pop();
std::cout << _vertexs[front] << '[' << front << ']' << std::endl;
for (int j = 0; j < _vertexs.size(); ++j)
{
if (Label[j] == false && _matrix[front][j] != MAX_W)
{
QNode.push(j);
Label[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
//图的深度优先遍历
void DFS(const Vertex& src)
{
std::vector<bool> visited(_vertexs.size(), false);
_DFS(GetVertexIndex(src), visited);
}
private:
void _DFS(size_t srci, std::vector<bool>& visited)
{
visited[srci] = true;
std::cout << _vertexs[srci] << '[' << srci << ']' << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); ++i)
{
if (_matrix[srci][i] != MAX_W && visited[i] == false)
{
_DFS(i, visited);
}
}
}
private:
std::vector<Vertex> _vertexs; // 顶点集合
std::unordered_map<Vertex, size_t> _indexMap; // 顶点映射下标
std::vector<std::vector<Weight>> _matrix; // 邻接矩阵
};
}
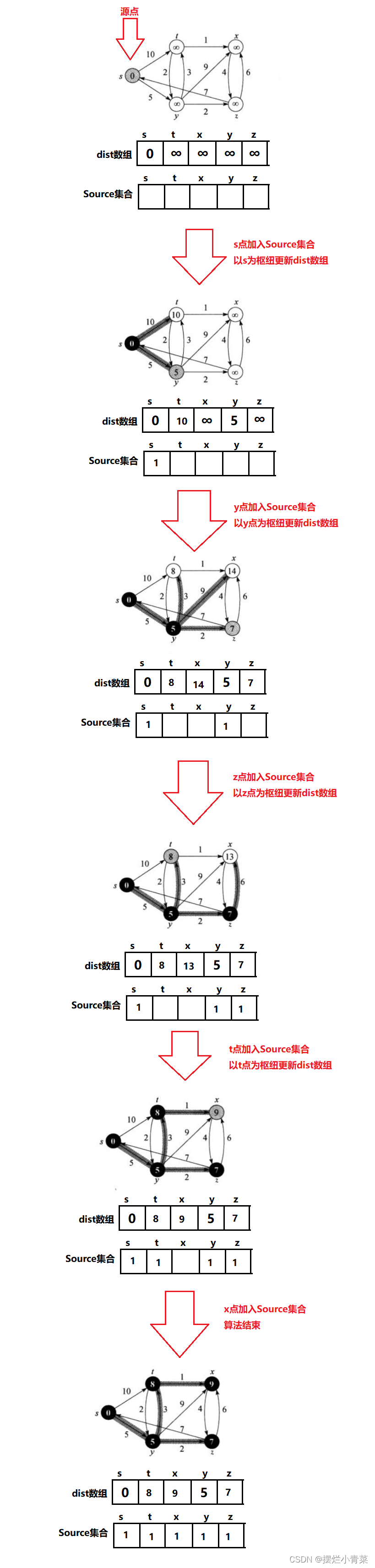
在有向带权图中给定一个起始顶点(源点),Dijkstra算法可以求出所有其他顶点到源点的最短路径,Dijkstra算法不能用于同时含有正负权值的边的图
一.Dijkstra算法分析
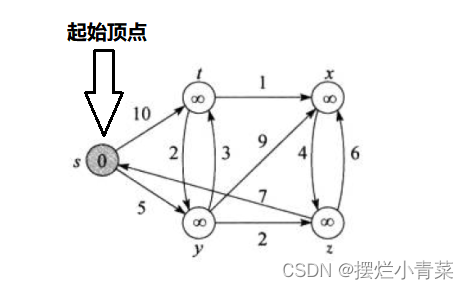
算法的核心逻辑要素
Source顶点集合:已经确定到源点的最短路径的顶点就会加入Source集合中,Source集合初始时只有源点dist数组:用于记录每个顶点到源点的距离,dist数组具有如下性质:- 对于存在于
Source集合中的顶点,该顶点在dist数组中对应的值为该顶点到源点最短路径的距离(一类顶点) - 对于不在
Source集合中但是与Source集合直接相连的顶点,该顶点在dist数组中对应的值为该顶点经过Source集合达到源点的最短路径的距离(二类顶点) - 对于不在
Source集合中且不与Source集合直接相连的顶点,该顶点在dist数组中对应的值为无穷大(三类顶点)
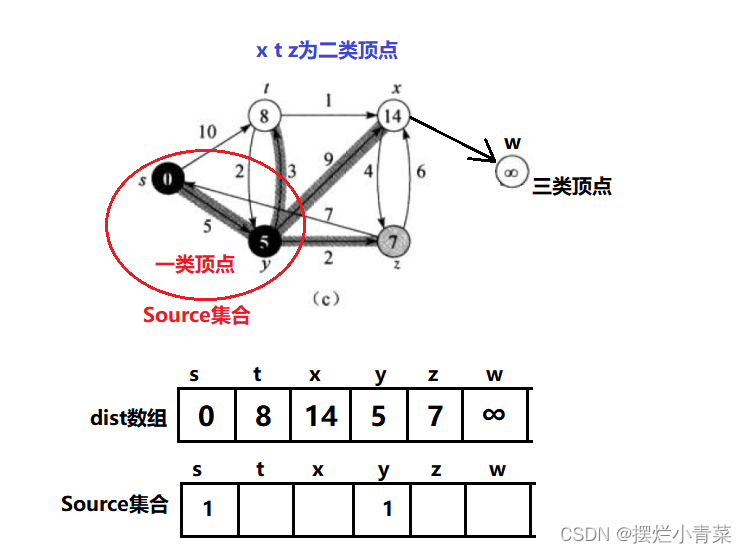
- 对于存在于
算法的执行逻辑
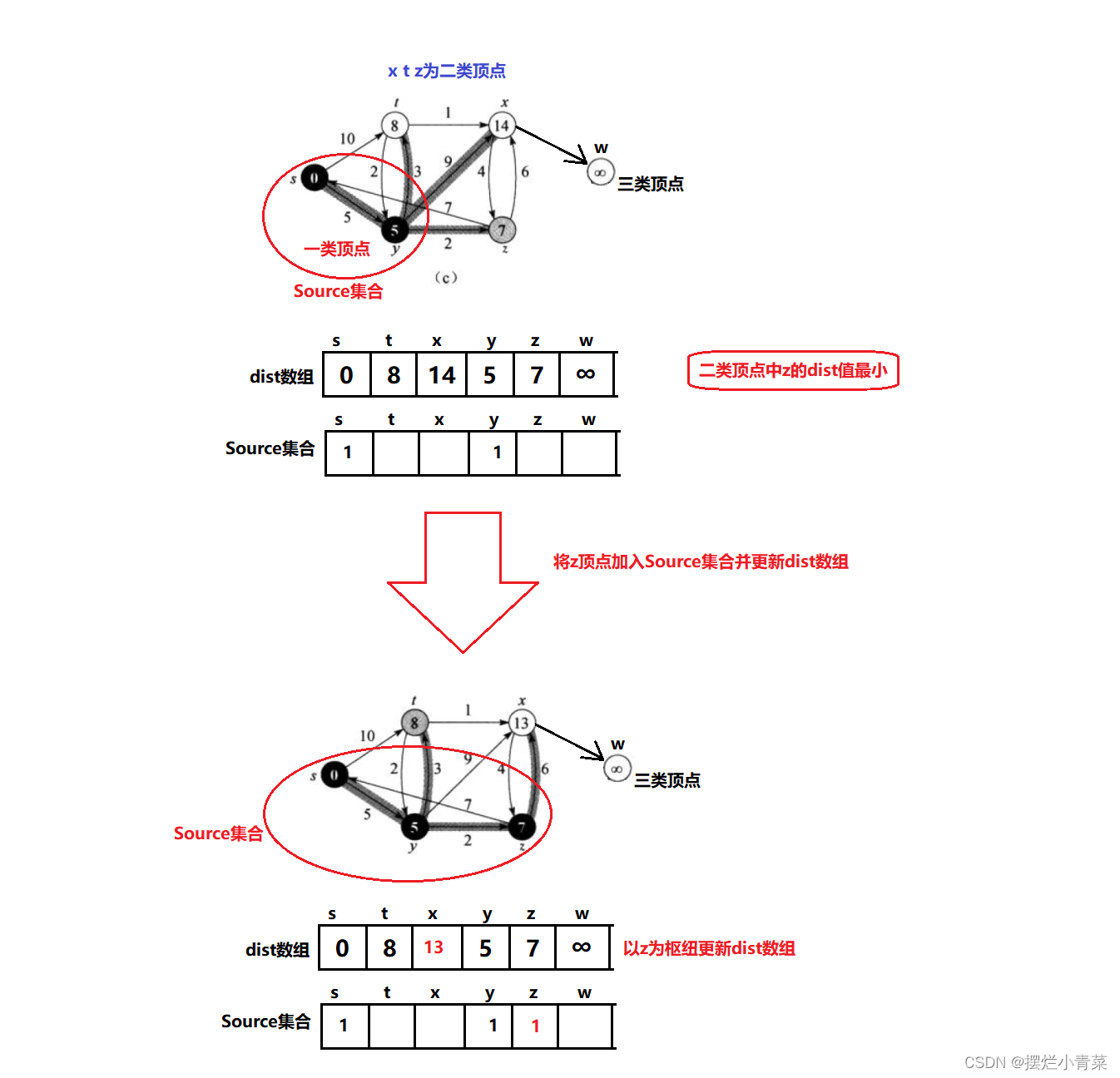
- 容易证明,
dist数组只要保持上述的性质,那么,在二类顶点中,dist值最小的顶点就可以加入Source集合而且这个最小值就是该顶点到源点的最短距离. - 每当有一个顶点加入了
Source集合,就以该顶点为枢纽对dist数组进行更新保持其原本的性质 - 如此往复直到图中所有顶点都加入了
Source集合,dist数组就记录了图中所有顶点到源点的最短距离.
二.Dijkstra算法接口实现
//单源最短路径算法,src为起始顶点(源点)
//dist用于记录各顶点到源点的距离
//parentPath用于记录最短路径中各顶点的前驱顶点
void Dijkstra(const Vertex& src, std::vector<Weight>& dist, std::vector<int>& parentPath)
{
dist.resize(_vertexs.size(), MAX_W);
parentPath.resize(_vertexs.size(), -1);
//用于标记Source集合中顶点的表,初始时只有源点在其中
std::vector<bool> Source(_vertexs.size(), false);
int srcindex = GetVertexIndex(src);
dist[srcindex] = 0; //源点自己到自己的距离为0
//图共有多少个顶点就执行多少次循环
for (int i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); ++i)
{
//从dist数组中选出距离源点最近的二类顶点加入到Source集合中
int MinWeight = MAX_W;
int Minindex = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < dist.size(); ++j)
{
if (Source[j] == false && dist[j] < MinWeight)
{
MinWeight = dist[j];
Minindex = j;
}
}
//将顶点加入Source集合中
Source[Minindex] = true;
//更新与Source集合直接相连且不在Source集合中的顶点距离源点的距离(dist数组的更新)
for (int j = 0; j < _matrix.size(); ++j)
{
if (_matrix[Minindex][j] != MAX_W &&
Source[j] == false && _matrix[Minindex][j] + dist[Minindex] < dist[j])
{
dist[j] = _matrix[Minindex][j] + dist[Minindex];
//记录顶点前驱
parentPath[j] = Minindex;
}
}
}
}
- 接口中的
parentPath数组用于记录最短路径中每个顶点的前驱顶点,算法结束后,借助parentPath数组中可以完整地得到每一条最短路径
邻接矩阵堆优化版本:
- 从
dist数组中选出距离源点最近的二类顶点这个过程可以借助堆来完成,邻接矩阵堆优化版本:
//堆优化版本
struct vertex_dist
{
int _dest;
Weight _v_source;
vertex_dist(int dest,Weight v_source)
:_dest(dest),
_v_source(v_source){
}
//小堆比较运算符
bool operator>(const vertex_dist& v_d) const
{
return _v_source > v_d._v_source;
}
};
void Dijkstra_heap(const Vertex& src, std::vector<Weight>& dist, std::vector<int>& parentPath)
{
dist.resize(_vertexs.size(), MAX_W);
parentPath.resize(_vertexs.size(), -1);
//用于标记Source集合中顶点的表,初始时只有源点在其中
std::vector<bool> Source(_vertexs.size(), false);
int srcindex = GetVertexIndex(src);
dist[srcindex] = 0; //源点自己到自己的距离为0
//创建小堆
std::priority_queue<vertex_dist, std::vector<vertex_dist>, std::greater<vertex_dist>> Heap;
Heap.push(vertex_dist(srcindex, 0));
while (!Heap.empty())
{
vertex_dist Smallest = Heap.top();
Heap.pop();
//若顶点已经在Source集合中则跳过
if (Source[Smallest._dest]) continue;
//将顶点加入Source集合中
Source[Smallest._dest] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); ++i)
{
if (_matrix[Smallest._dest][i] != MAX_W &&
Source[i] == false && _matrix[Smallest._dest][i] + dist[Smallest._dest] < dist[i])
{
dist[i] = _matrix[Smallest._dest][i] + dist[Smallest._dest];
Heap.push(vertex_dist(i, dist[i]));
//记录顶点前驱
parentPath[i] = Smallest._dest;
}
}
}
}
- 邻接矩阵堆优化版本并不能降低算法的时间复杂度(仍然为
O(N^2)),要想降低Dijkstra算法的时间复杂度就要使用邻接表存储结构或链式前向星存储结构(配合堆优化)可以将复杂度降为O(mlogn)(n表示点数,m表示边数)
