题目描述
给定一棵有根多叉树,请求出指定两个点直接最近的公共祖先。
输入格式:
第一行包含三个正整数N、M、S,分别表示树的结点个数、询问的个数和树根结点的序号。
接下来N-1行每行包含两个正整数x、y,表示x结点和y结点之间有一条直接连接的边(数据保证可以构成树)。
接下来M行每行包含两个正整数a、b,表示询问a结点和b结点的最近公共祖先。
输出格式:
输出包含M行,每行包含一个正整数,依次为每一个询问的结果。
输入样例#1:
5 5 4
3 1
2 4
5 1
1 4
2 4
3 2
3 5
1 2
4 5
输出样例#1:
4
4
1
4
4
说明
时空限制:1000ms,128M
数据规模:
对于30%的数据:N<=10,M<=10
对于70%的数据:N<=10000,M<=10000
对于100%的数据:N<=500000,M<=500000
样例说明:
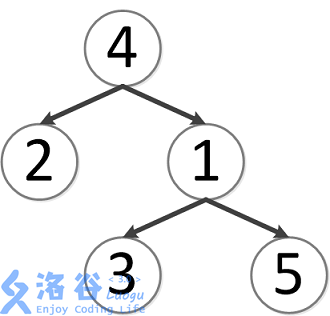
第一次询问:2、4的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第二次询问:3、2的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第三次询问:3、5的最近公共祖先,故为1。
第四次询问:1、2的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第五次询问:4、5的最近公共祖先,故为4。
故输出依次为4、4、1、4、4。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 500005;
int dep[maxn],f[maxn][21],head[maxn << 1],num_edge,n,m,s,a,b;
struct edge{
int to,next;
}e[maxn << 1];
inline void Swap(int &x,int &y){
int t = x;
x = y;
y = t;
}
inline int read(){
int res = 0,flag = 1;
char ch;
ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){
if(ch == '-') flag = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
res = res*10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return res*flag;
}
void pre(int u,int fa){
dep[u] = dep[fa] + 1;
f[u][0] = fa;
for(int i = 0;(1 << i) <= dep[u];i++){
f[u][i+1] = f[f[u][i]][i];
}
for(int i = head[u];i;i = e[i].next){
int t = e[i].to;
if(t == fa) continue;
pre(t,u);
}
}
inline int LCA(int x,int y){
if(dep[x] < dep[y]) Swap(x,y); // let x.depth >= y.depth
if(x == y) return x;
for(int i = 15;i >= 0;i--){
if(dep[f[x][i]] >= dep[y]) x = f[x][i];
if(x == y) return x;
}
for(int i = 15;i >= 0;i--){
if(f[x][i] != f[y][i]){
x = f[x][i];
y = f[y][i];
}
}
return f[x][0];
}
inline void add(int from,int to){
e[++num_edge].next = head[from];
e[num_edge].to = to;
head[from] = num_edge;
}
int main(){
n = read();
m = read();
s = read();
for(int i = 1;i < n;i++){
int u,v;
u = read();
v = read();
add(u,v);
add(v,u);
}
pre(s,0);
while(m--){
a = read();
b = read();
printf("%d\n",LCA(a,b));
}
return 0;
}