题目描述
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node’s key.
The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node’s key.
Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
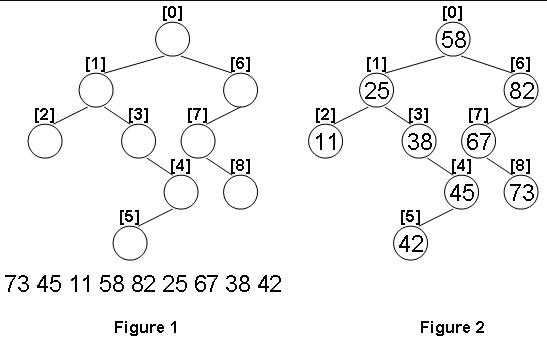
Given the structure of a binary tree and a sequence of distinct integer keys, there is only one way to fill these keys into the tree so that the resulting tree satisfies the definition of a BST. You are supposed to output the level order traversal sequence of that tree. The sample is illustrated by Figure 1 and 2.
输入格式
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤100) which is the total number of nodes in the tree. The next N lines each contains the left and the right children of a node in the format left_index right_index, provided that the nodes are numbered from 0 to N−1, and 0 is always the root. If one child is missing, then −1 will represent the NULL child pointer. Finally N distinct integer keys are given in the last line.
输出格式
For each test case, print in one line the level order traversal sequence of that tree. All the numbers must be separated by a space, with no extra space at the end of the line.
输入样例
9
1 6
2 3
-1 -1
-1 4
5 -1
-1 -1
7 -1
-1 8
-1 -1
73 45 11 58 82 25 67 38 42
输出样例
58 25 82 11 38 67 45 73 42
分析
数据结构可以使用一个struct建立节点数组root[],也可以直接用l[],r[]两个数组对左右节点信息进行存储。
二叉搜索树的中序遍历是其所有节点值从小到大进行排列。
输出层序遍历使用BFS()。
C++ 代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode{ //建立数据结构
int val;
int left;
int right;
}root[110];
int n,co;
int num[110];
vector<int> ans;
void dfs(int u) //中序遍历把值赋给root[].val
{
if(u==-1) return ;
dfs(root[u].left);
root[u].val=num[co++];
dfs(root[u].right);
}
void bfs() //层序遍历存储答案输出的值的顺序
{
queue<TreeNode> q;
q.push(root[0]);
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
ans.push_back(t.val);
if(t.left!=-1) q.push(root[t.left]);
if(t.right!=-1) q.push(root[t.right]);
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
int l,r;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>l>>r;
root[i].left=l;
root[i].right=r;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>num[i];
sort(num,num+n);
dfs(0);
bfs();
int f=0;
for(auto x:ans)
{
if(f) cout<<" ";
cout<<x;
f=1;
}
return 0;
}